At its core, a box furnace's heating capability is defined by its heating elements, which are primarily categorized as either metallic alloys or advanced ceramic/non-metallic materials. The most common types include metallic resistance wires (like FeCrAl and NiCr) for lower temperatures, and silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) for high-temperature applications.
The selection of a heating element is not arbitrary; it is a critical engineering decision dictated almost entirely by the furnace's maximum required operating temperature and the chemical environment (atmosphere) inside the chamber.

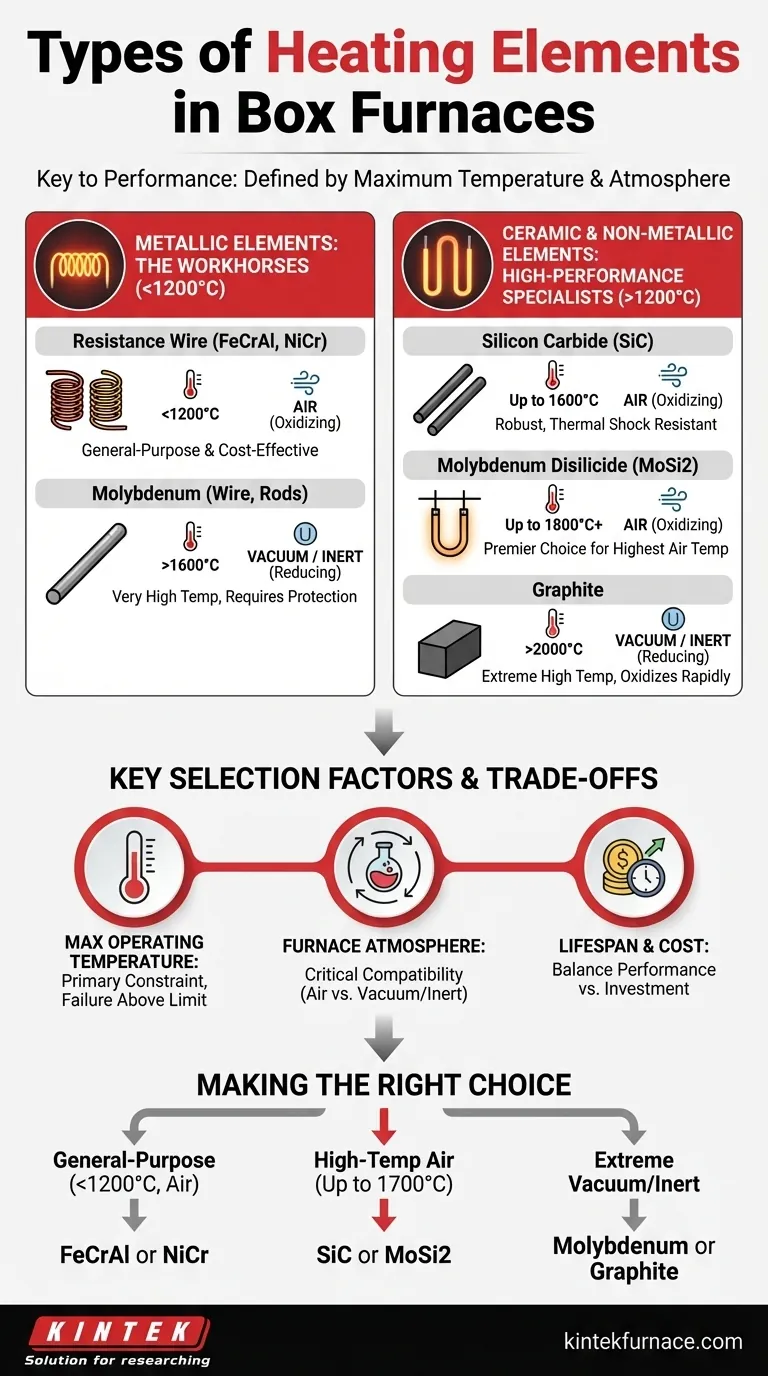
Metallic Heating Elements: The Workhorses
Metallic elements are common in general-purpose furnaces, particularly those operating at or below 1200°C. They function by resisting the flow of electricity, which generates heat.
Resistance Wire (FeCrAl, NiCr)
Iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) and nickel-chromium (NiCr) alloys are the most prevalent heating elements in laboratory and industrial furnaces operating up to 1200°C.
These wires are typically wound into coils and mounted in grooves within the furnace's insulation or are wound around ceramic tubes. This embedded design maximizes thermal uniformity and protects the elements.
Molybdenum (Wire, Rods)
Molybdenum is a refractory metal capable of reaching very high temperatures, well above what standard resistance wires can handle.
However, molybdenum readily oxidizes in the presence of air at high temperatures. Therefore, it can only be used in furnaces that operate with a vacuum or an inert/reducing atmosphere.
Ceramic & Non-Metallic Elements: High-Performance Specialists
When temperatures need to exceed 1200°C, engineers turn to advanced ceramic or non-metallic materials that offer superior stability and longevity in extreme heat.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon Carbide elements are robust, reliable, and capable of operating at temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F) in air. They are often formed into rods or U-shapes.
SiC elements are known for their high strength and resistance to thermal shock, making them a durable choice for many high-temperature processes.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2)
For the highest temperatures in air, molybdenum disilicide is the premier choice, capable of sustained operation at 1700°C and even reaching peaks of over 1800°C (3272°F).
These elements are almost always suspended from the furnace roof and hang freely in the chamber. This configuration allows for easy replacement and prevents interaction with the furnace insulation at extreme temperatures.
Graphite
Graphite elements can achieve the highest temperatures of all, exceeding 2000°C and even approaching 3000°C. They are essential for specialized applications like graphitizing or certain vacuum brazing processes.
Like molybdenum, graphite must be used in a vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent it from rapidly oxidizing and burning away.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Temperature, Atmosphere, and Cost
Choosing an element involves balancing performance requirements against material limitations and cost.
Maximum Operating Temperature
This is the single most important factor. An element operated above its recommended maximum will fail quickly.
- < 1200°C: FeCrAl / NiCr wire is standard and cost-effective.
- 1200°C - 1600°C: Silicon Carbide (SiC) is the typical choice.
- > 1600°C in Air: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) is necessary.
- > 1600°C in Vacuum/Inert: Molybdenum or Graphite are required.
Furnace Atmosphere
The chemical environment inside the furnace is the second critical constraint. Using the wrong element in an oxidizing atmosphere (air) is a common and costly mistake.
Elements like molybdenum and graphite will be destroyed by oxygen at high temperatures. In contrast, SiC and MoSi2 form a protective glassy layer (silicon dioxide) that allows them to function in air.
Lifespan and Cost
High-performance elements like MoSi2 come with a higher initial cost but offer unparalleled temperature capability. The lifespan of any element is affected by the intensity of use, the speed of heating/cooling cycles, and chemical contamination from the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be aligned with your specific processing goals.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating or lab work below 1200°C: A furnace with FeCrAl or NiCr resistance wire elements offers the best balance of cost and performance.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sintering or processing in air (up to 1700°C): You must use a furnace equipped with Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements.
- If your primary focus is very high-temperature vacuum or inert-atmosphere processing: Your application demands a furnace with Molybdenum or Graphite elements.
Matching the heating element's properties to your operational temperature and atmosphere is the key to a successful and reliable thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Max Temperature (°C) | Atmosphere Compatibility | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| FeCrAl / NiCr Wire | Up to 1200 | Air, Oxidizing | General-purpose heat treating, lab work |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1600 | Air, Oxidizing | High-temperature sintering, robust processes |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Up to 1800+ | Air, Oxidizing | Highest temp air processes, sustained high heat |
| Molybdenum | Above 1600 | Vacuum, Inert/Reducing | High-temp vacuum processing, specialized uses |
| Graphite | Above 2000 | Vacuum, Inert/Reducing | Graphitizing, extreme high-temp applications |
Upgrade your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and performance. Don't settle for less—contact us today to discuss how we can tailor the perfect heating solution for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How is a muffle furnace utilized for AlN crystal post-processing? Optimize Surface Purity via Staged Oxidation
- What is the function of laboratory high-temperature box furnaces in T6 aluminum treatment? Key to Material Strength
- Why is a box muffle furnace used for the 800°C annealing of titanium LMD samples? Optimize Your Material Performance
- Why is a laboratory high-temperature box furnace essential for KNN ceramic powders? Mastering Solid-State Synthesis
- How is a laboratory muffle furnace utilized during the debinding stage of HAp green bodies? Precision Thermal Control



















