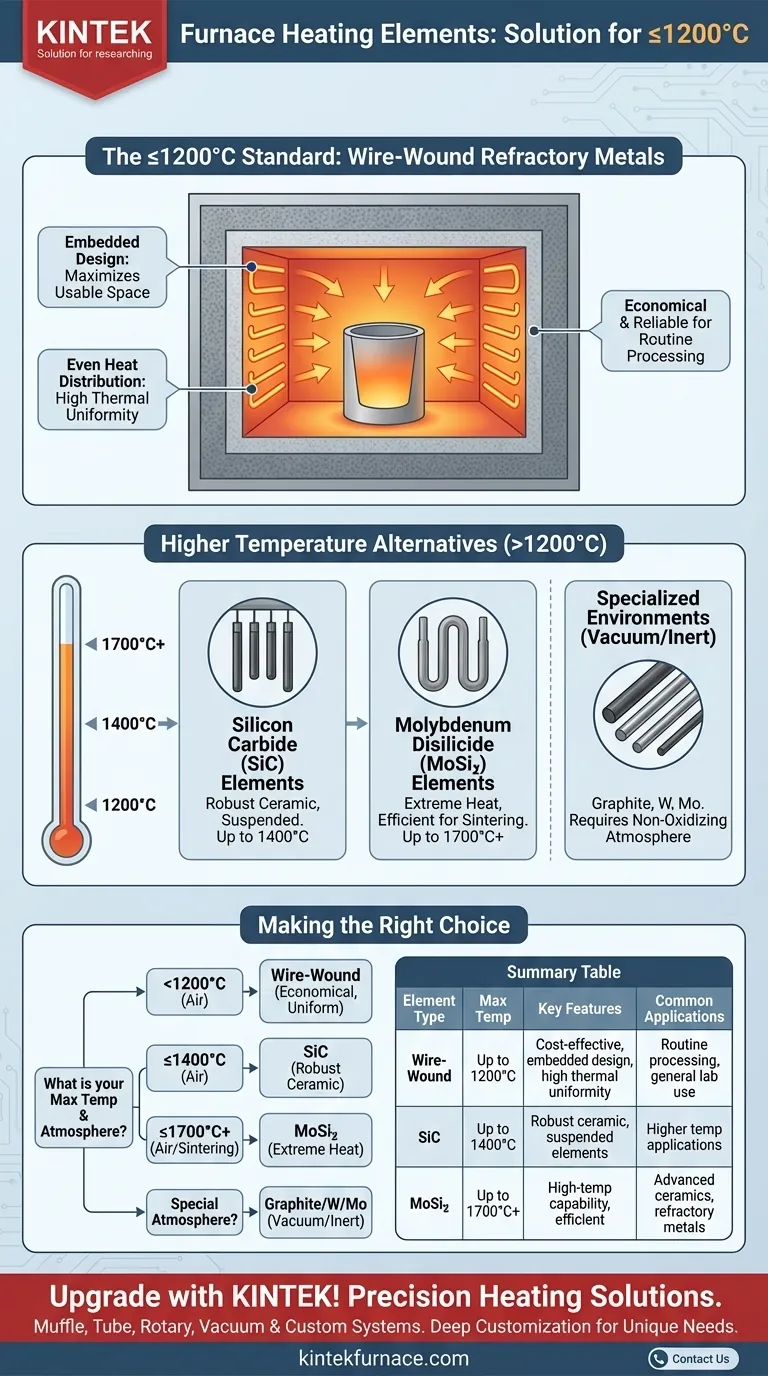
For furnaces operating at 1200°C or less, the standard heating element is a wire-wound refractory metal. These metallic heating wires are designed for high electrical resistance and are typically embedded directly into the furnace's insulated chamber walls, a design that maximizes usable space and promotes excellent thermal uniformity.
The choice of a furnace heating element is a direct function of its maximum required operating temperature. Below 1200°C, metallic wire elements offer an efficient and reliable solution, while higher temperatures demand more exotic ceramic or refractory metal elements like silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂).

The Standard for Temperatures Up to 1200°C
Furnaces designed for this moderate temperature range are built around a proven and cost-effective heating technology. The specific element type and its placement are key to the furnace's performance.
Wire-Wound Refractory Metals
The workhorse for this category is the wire-wound heating element. These are metallic alloy wires specifically engineered to generate heat when an electric current passes through them.
Why This Design Is Effective
Embedding these wire elements into the insulated walls of the furnace chamber provides two distinct advantages. First, it maximizes the internal chamber volume, leaving it unobstructed. Second, it allows for more even heat distribution, leading to high thermal uniformity across the entire workspace.
Understanding Higher Temperature Alternatives
To fully grasp why wire elements are used below 1200°C, it is crucial to understand what is required for higher temperatures. The material science of heating elements changes significantly as thermal demands increase.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements (Up to 1400°C)
When applications require temperatures above the limit of standard heating wires, silicon carbide (SiC) elements are the next step. These are robust ceramic elements that can operate reliably at higher temperatures.
Unlike embedded wires, SiC elements are typically suspended from the furnace roof in arrays along the chamber sides.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Elements (Up to 1700°C+)
For very high-temperature processes, such as sintering advanced ceramics, molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) elements are used. These are the two most common elements in modern high-temperature sintering furnaces, capable of reaching extreme temperatures efficiently.
Other Specialized Elements
In specific environments, such as vacuum or inert atmospheres, other materials are used. These include graphite, tungsten, and molybdenum elements, which can reach very high temperatures but are not suitable for operation in the presence of oxygen.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing performance, cost, and operational requirements. The heating element is at the center of these trade-offs.
Cost vs. Temperature Capability
There is a direct correlation between an element's maximum temperature and its cost. Wire-wound elements are highly economical for work up to 1200°C. Stepping up to SiC or MoSi₂ elements for higher temperature capability comes with a significant increase in initial furnace cost.
Element Placement and Durability
Embedded wire elements are protected by the furnace insulation. Suspended elements like SiC and MoSi₂ are more exposed within the chamber, making them more susceptible to mechanical shock, though they are designed for easy replacement.
Atmospheric Requirements
The choice of element dictates the atmosphere you can work in. Wire-wound, SiC, and MoSi₂ elements are designed to operate in air. In contrast, elements like graphite or tungsten will rapidly oxidize and fail if operated outside of a vacuum or inert gas environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a furnace begins with defining your maximum temperature and atmospheric needs.
- If your primary focus is routine processing below 1200°C: A furnace with wire-wound elements embedded in the insulation is the most economical and effective choice.
- If your primary focus is working with materials requiring up to 1400°C: You will need to invest in a furnace that utilizes silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements.
- If your primary focus is advanced ceramics or refractory metals above 1400°C: Furnaces equipped with molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) or other specialized elements are necessary for the task.
Understanding these material limits is the first step toward selecting a furnace that aligns perfectly with your technical and budgetary requirements.
Summary Table:
| Element Type | Max Temperature | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wire-Wound Refractory Metals | Up to 1200°C | Cost-effective, embedded design, high thermal uniformity | Routine processing, general lab use |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1400°C | Robust ceramic, suspended elements | Higher temp applications |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Up to 1700°C+ | High-temp capability, efficient for extreme heat | Advanced ceramics, refractory metals |
| Graphite/Tungsten/Molybdenum | Varies (high temp) | Requires vacuum/inert atmosphere | Specialized environments |
Upgrade your laboratory with precision heating solutions from KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with advanced high-temperature furnace options, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs—whether you require cost-effective wire-wound elements or specialized high-temp systems. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















