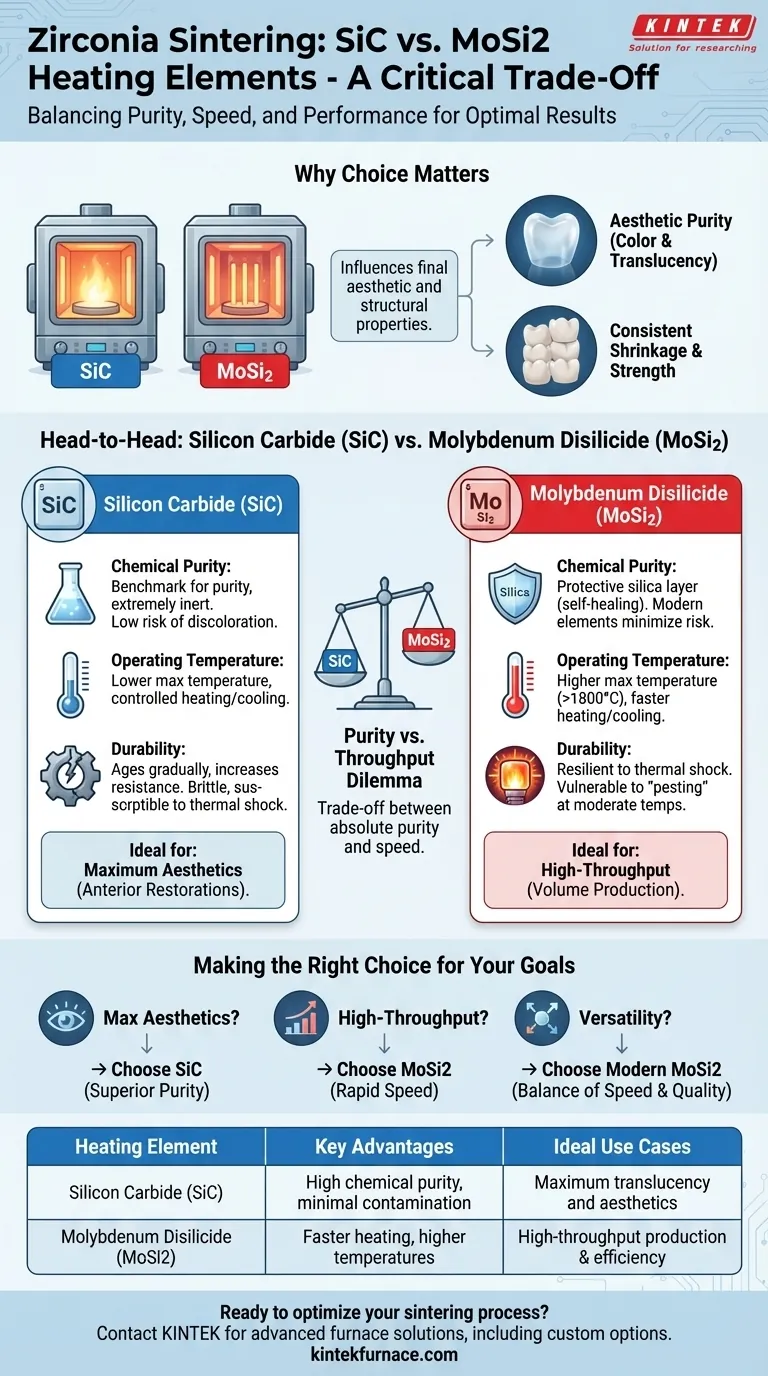
For zirconia sintering, the choice of heating element narrows to two primary materials: Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2). Both are used in modern sintering furnaces, but they are preferred for different reasons related to chemical compatibility, performance, and the desired final characteristics of the zirconia restoration. The ideal choice depends on the specific priorities of your laboratory or manufacturing process.
While both SiC and MoSi2 elements are capable of sintering zirconia, the decision hinges on a critical trade-off. SiC is often favored for its exceptional chemical purity, crucial for high-translucency results, while MoSi2 is valued for its faster heating rates and higher temperature capabilities.

Why Heating Element Choice is Critical for Zirconia Quality
The selection of a heating element is not merely a technical detail; it directly influences the final aesthetic and structural properties of the sintered zirconia. The wrong element or poor element quality can compromise the entire process.
The Impact on Color and Translucency
Zirconia, especially the high-translucency variants used for aesthetic anterior restorations, is highly sensitive to contamination at high temperatures.
Heating elements can release microscopic particles or oxides into the furnace chamber. If these contaminants land on the zirconia surface, they can cause discoloration, graying, or spotting, ruining the aesthetic outcome.
Ensuring Consistent Shrinkage and Strength
The sintering process relies on precise and uniform temperature control to achieve predictable shrinkage and final density.
High-quality heating elements provide stable and even heat distribution, ensuring that every unit in the batch is sintered under identical conditions. This consistency is fundamental to achieving the material's specified flexural strength and marginal fit.
A Head-to-Head Comparison: SiC vs. MoSi2
Both SiC and MoSi2 are the industry standards, but they possess different characteristics that make them suitable for different goals.
Chemical Purity and Contamination Risk
Silicon Carbide (SiC) is widely regarded as the benchmark for purity. It is extremely inert and has a very low risk of releasing contaminants that could discolor zirconia. This makes it a preferred choice for furnaces dedicated to high-aesthetic, anterior-grade zirconia.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements are coated in a protective layer of silica glass. While generally stable, older or lower-quality elements can sometimes "shed" this silica, which may interact with the zirconia surface. However, modern, high-purity MoSi2 elements have significantly minimized this risk.
Operating Temperature and Speed
MoSi2 elements have a distinct advantage in performance. They can typically reach higher maximum temperatures (over 1800°C) and can be heated and cooled much more rapidly than SiC elements.
SiC elements have a lower maximum operating temperature and require more controlled, gradual heating and cooling cycles to prevent thermal shock and ensure a long service life.
Durability and Lifespan
Both element types are designed for long service life but have different failure modes.
SiC elements gradually age, increasing their electrical resistance over time. They are robust but can be brittle and susceptible to fracture from mechanical or thermal shock.
MoSi2 elements are more resistant to thermal shock and can "self-heal" their protective silica layer at high temperatures. However, they are vulnerable to a form of rapid oxidation known as "pesting" if held at moderate temperatures (around 400-700°C) for extended periods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing the ideal characteristics of each element type against your lab's practical needs and budget.
The Purity vs. Throughput Dilemma
The core trade-off is often between the absolute purity of SiC and the speed of MoSi2.
A furnace with SiC elements is a safe investment for achieving the best possible aesthetics, but the cycles will be longer. This may limit the number of batches you can run per day.
A furnace with MoSi2 elements enables faster cycles, increasing throughput and efficiency, which is a major advantage for high-volume production labs.
Total Cost of Ownership
Initial furnace cost is only part of the equation. You must also consider element replacement costs and potential downtime.
MoSi2 elements can offer a very long lifespan if operated correctly. SiC elements are consumables that will need periodic replacement as they age, which should be factored into operating budgets.
Making the Right Choice for Your Sintering Goals
Your decision should be driven by the primary focus of your work.
- If your primary focus is maximum translucency and aesthetics: The superior chemical purity of Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements is the most reliable choice to prevent discoloration in sensitive zirconia materials.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production and speed: The rapid heating rates and robust performance of Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements offer a significant advantage for efficiency.
- If your primary focus is versatility for a range of zirconia types: Look for a furnace with modern, high-purity MoSi2 elements, as they increasingly offer a balance of speed and quality that meets the demands of most dental restorations.
Understanding this distinction empowers you to select a furnace that aligns perfectly with your production needs and quality standards.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element | Key Advantages | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | High chemical purity, minimal contamination risk | Maximum translucency and aesthetics for anterior restorations |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Faster heating rates, higher temperature capabilities | High-throughput production and efficiency in labs |
Ready to optimize your zirconia sintering process? Contact KINTEK today to explore our advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring superior performance, efficiency, and quality for your laboratory. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is using a universal setting for all materials in a dental furnace a mistake? Master Precision Sintering for Perfect Restorations
- Why is accurate temperature control important in dental furnaces? Ensure Perfect Restorations Every Time
- What role does temperature range and accuracy play in dental furnace performance? Ensure Precision for Superior Dental Restorations
- How often should dental furnaces be calibrated? Ensure Precision for Perfect Restorations
- What is the importance of dental furnaces in dentistry? Ensure Strong, Precise Dental Restorations



















