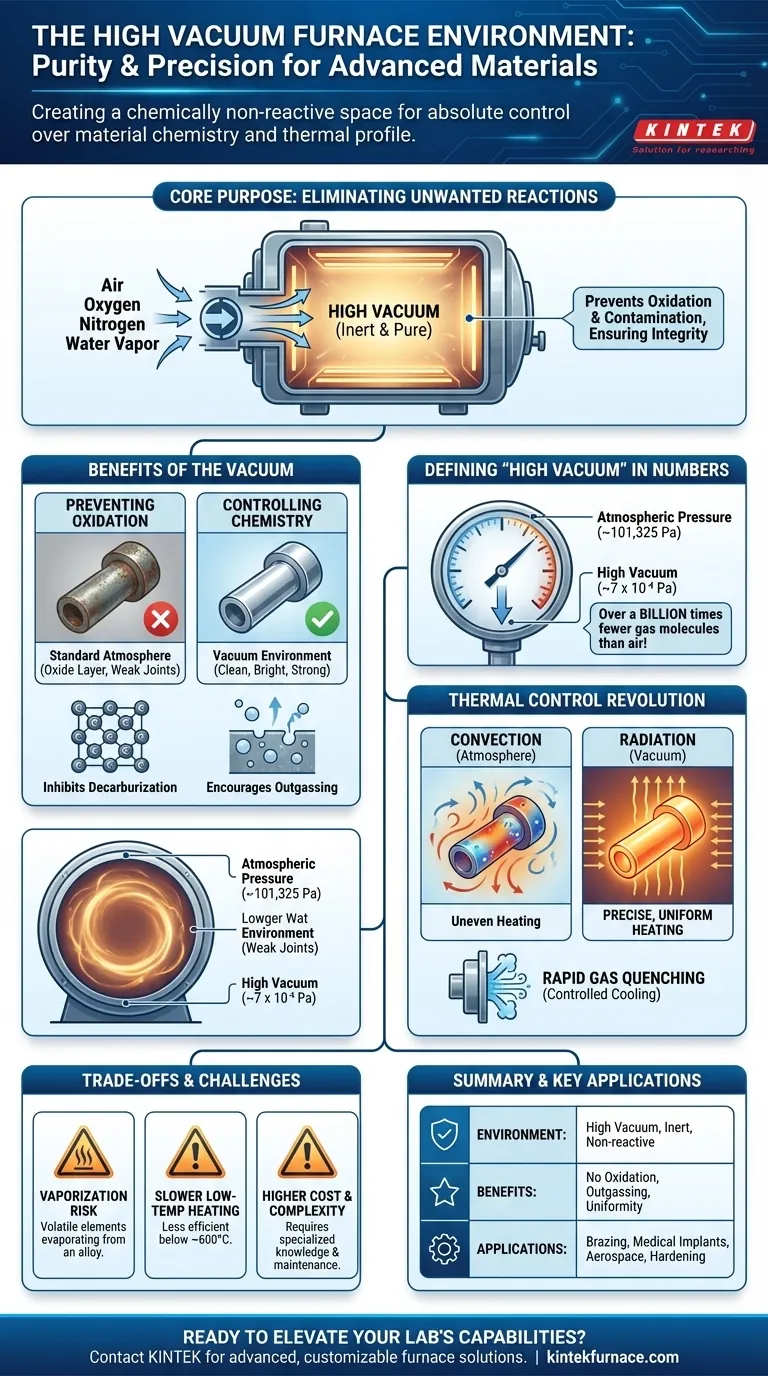
At its core, a high vacuum furnace creates an exceptionally pure and chemically non-reactive environment by removing nearly all atmospheric gases. This inert space is critical for high-temperature processes, as it prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation and eliminates sources of contamination that would otherwise compromise the integrity of the material being treated.
The true purpose of a high vacuum furnace is not simply to remove air, but to gain absolute control over a material's chemistry and thermal profile. It creates a pristine environment where heat can be applied without introducing impurities or causing unintended reactions.

The Purpose of a Vacuum: Eliminating Unwanted Reactions
The primary function of creating a vacuum is to remove gases—specifically oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor—that readily react with materials at elevated temperatures. In a standard atmosphere, these reactions are unavoidable.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At high temperatures, most metals will instantly react with oxygen, forming a layer of oxide on their surface. This can ruin the part's finish, weaken brazed joints, and alter its fundamental properties.
A high vacuum environment starves the process of these reactive gases, ensuring parts emerge from the furnace clean, bright, and free of contamination.
Controlling Material Chemistry
Beyond preventing surface reactions, a vacuum can actively improve a material's purity. Processes like decarburization, where carbon is undesirably removed from a steel's surface, are completely inhibited.
Furthermore, the low-pressure environment encourages outgassing, a process where trapped impurities and dissolved gases within the material itself are pulled out, leading to a purer, higher-quality finished product.
Defining "High Vacuum" in Numbers
The term "high vacuum" refers to a specific, measurable level of pressure. Many industrial high vacuum furnaces operate at pressures as low as 7 x 10⁻⁴ Pascals (Pa).
To put this in perspective, standard atmospheric pressure is roughly 101,325 Pa. The environment inside the furnace, therefore, contains over a billion times fewer gas molecules than the air we breathe.
Beyond Chemistry: The Impact on Thermal Control
The absence of a gaseous atmosphere fundamentally changes how heat behaves, providing significant advantages for precise thermal processing.
Enabling Precise Temperature Uniformity
In a normal furnace, air currents create hot and cold spots, a phenomenon known as convection. This leads to uneven heating.
In a vacuum, heat transfer occurs primarily through radiation. This is a much more direct and uniform method, allowing the entire part—even complex geometries—to reach the target temperature with exceptional consistency.
Facilitating Rapid Heating and Cooling
Since there is no air to heat up or cool down, the furnace's energy is focused almost entirely on the workpiece. This results in faster temperature ramp rates and more efficient energy use.
When the heating cycle is complete, introducing an inert gas like argon or nitrogen can be used to cool the part rapidly and uniformly in a process known as gas quenching, all while maintaining a contamination-free environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a vacuum environment is not without its challenges. Understanding its limitations is key to successful implementation.
The Challenge of Vaporization
At very low pressures and high temperatures, certain elements in an alloy (like zinc in brass or chromium in some steels) can turn directly into a vapor and be pulled out by the vacuum system. This phenomenon, known as vaporization, must be carefully managed to maintain the desired alloy composition.
Limitations on Heat Transfer
While radiation is excellent for uniformity at high temperatures, it is less efficient than convection at lower temperatures (below approximately 600°C / 1100°F). This can sometimes slow down the initial heating phase of a process cycle.
Cost and Complexity
High vacuum furnaces are sophisticated systems. They require more rigorous maintenance, specialized knowledge to operate, and have a higher initial investment cost compared to standard atmospheric furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Ultimately, the decision to use a high vacuum furnace depends on the specific outcome you need to achieve for your material.
- If your primary focus is clean, strong joints: A vacuum environment is essential for high-purity brazing, as it prevents oxides that would otherwise inhibit the flow of the brazing alloy.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material purity: Use a high vacuum for applications like medical implants or aerospace components, where outgassing contaminants is critical.
- If your primary focus is precise hardness and microstructure: A vacuum furnace offers unparalleled control over heating and cooling cycles for processes like hardening and annealing, ensuring consistent results.
Choosing a high vacuum furnace is a decision to prioritize material integrity and process control above all else.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Environment Type | High vacuum, inert, and non-reactive |
| Key Benefits | Prevents oxidation, enables outgassing, ensures uniform heating |
| Typical Pressure | As low as 7 x 10⁻⁴ Pa |
| Heat Transfer | Primarily radiation for precise temperature control |
| Common Applications | Brazing, medical implants, aerospace components, hardening |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with a high vacuum furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization ensures your unique experimental needs are met precisely. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your material integrity and process control!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion



















