In standard applications, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements can reliably operate at surface temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F). While higher temperatures are technically possible for specific processes, the element's operational lifespan and stability are maximized within this range.
The absolute maximum temperature is only part of the story. The true performance and longevity of a silicon carbide element are determined by the operating atmosphere, power management, and the physical stresses it endures.
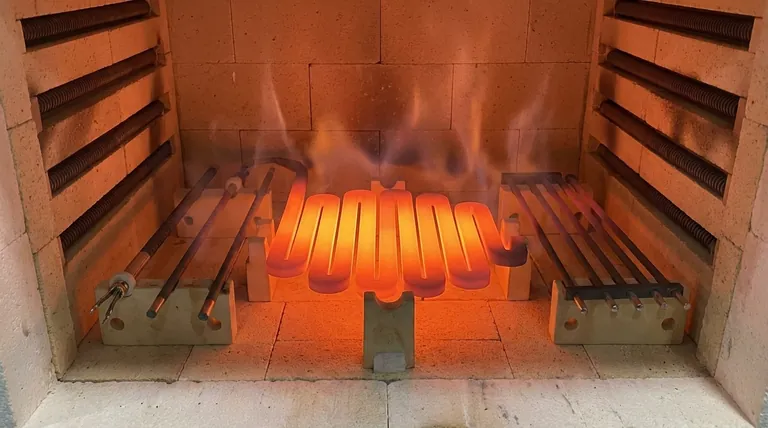
Why SiC Excels at High Temperatures
Silicon carbide's utility as a high-temperature heating element comes from a unique combination of intrinsic material properties. Understanding these characteristics is key to deploying them effectively.
Inherent Material Strength
Unlike many metals that soften significantly as they approach their melting point, SiC retains very high mechanical strength even at extreme temperatures. This structural integrity prevents sagging or deformation within the furnace.
Superior Thermal Properties
SiC possesses excellent thermal conductivity, allowing it to heat up quickly and distribute that heat uniformly across its surface. It is also highly resistant to thermal shock, meaning it can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking, which is critical for cycling applications.
Chemical Inertness
In many industrial environments, SiC elements show remarkable resistance to chemical attack. This makes them a reliable choice for processes involving harsh or corrosive atmospheres where other elements might quickly degrade.
Factors That Define the True Operating Limit
The "1600°C" figure is a benchmark, not a universal constant. Several real-world factors dictate the practical and sustainable temperature limit for your specific application.
The Role of the Operating Atmosphere
The atmosphere inside the furnace has a significant impact on element life. SiC elements perform exceptionally well in reducing atmospheres. However, certain oxidizing environments or contaminants can accelerate a process known as "aging."
The Impact of Power and Voltage
To prolong service life, it is best practice to operate the furnace at the lowest possible voltage that still achieves the target temperature. Applying excessive power to reach temperatures faster can unnecessarily stress the element.
The Concept of "Aging"
Over time, SiC elements naturally oxidize, which causes their electrical resistance to increase. This is a normal process called aging. To compensate, the power supply must be capable of delivering progressively higher voltage to maintain the same heat output, a crucial consideration for long-term system design.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While extremely capable, SiC elements are not without their limitations. Acknowledging these trade-offs is crucial for proper design and handling.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
Like most ceramics, SiC elements are brittle at room temperature and must be handled with care to avoid mechanical shock or impact. Careful installation and furnace maintenance are essential.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
While generally inert, the presence of certain chemicals, particularly water vapor at high temperatures or alkali metals, can significantly shorten the element's operational life. The furnace atmosphere must be controlled.
System Power Requirements
Because of aging, the power supply connected to SiC elements must have enough "headroom" to increase its voltage output over the element's life. This requirement can influence the initial cost and complexity of the control system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select and operate your SiC elements based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is reaching the absolute maximum temperature: Plan for a shorter element lifespan and ensure your power supply can handle the high demand and subsequent aging.
- If your primary focus is maximizing lifespan and reliability: Operate at least 50-100°C below the maximum rating and use a control system that applies power smoothly and accurately.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and cooling cycles: SiC is an excellent choice due to its thermal shock resistance, but you must ensure the elements are properly supported to avoid mechanical stress.
Ultimately, viewing a silicon carbide element as a component within a larger system is the key to unlocking its full potential.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 1600°C (2912°F) in standard applications |
| Key Properties | High mechanical strength, excellent thermal conductivity, thermal shock resistance, chemical inertness |
| Factors Affecting Limit | Operating atmosphere, power management, aging process, mechanical handling |
| Trade-offs | Brittleness at room temperature, atmosphere sensitivity, power supply requirements for aging |
| Best Practices | Operate 50-100°C below max for longevity, use smooth power control, handle with care to avoid shock |
Unlock the full potential of your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable silicon carbide heating elements and custom furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and durability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications and maximize performance!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















