In materials science, a box furnace serves as a high-temperature chamber designed to melt individual metals into a unified liquid. This process is fundamental to creating alloys—new materials engineered with specific properties like increased strength, corrosion resistance, or a lower melting point than their constituent elements. Its primary role is to provide a stable, controlled thermal environment.
The true function of a box furnace in alloy melting is not just to supply heat, but to provide precision and purity. Its value lies in its ability to precisely control the temperature and isolate the material, ensuring the final alloy meets exact specifications.
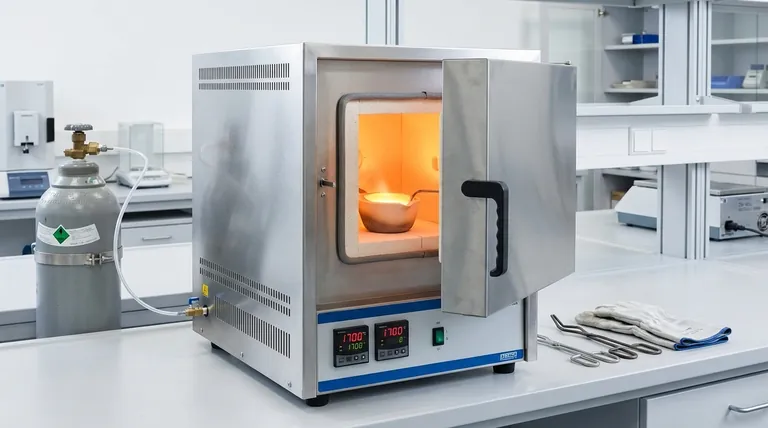

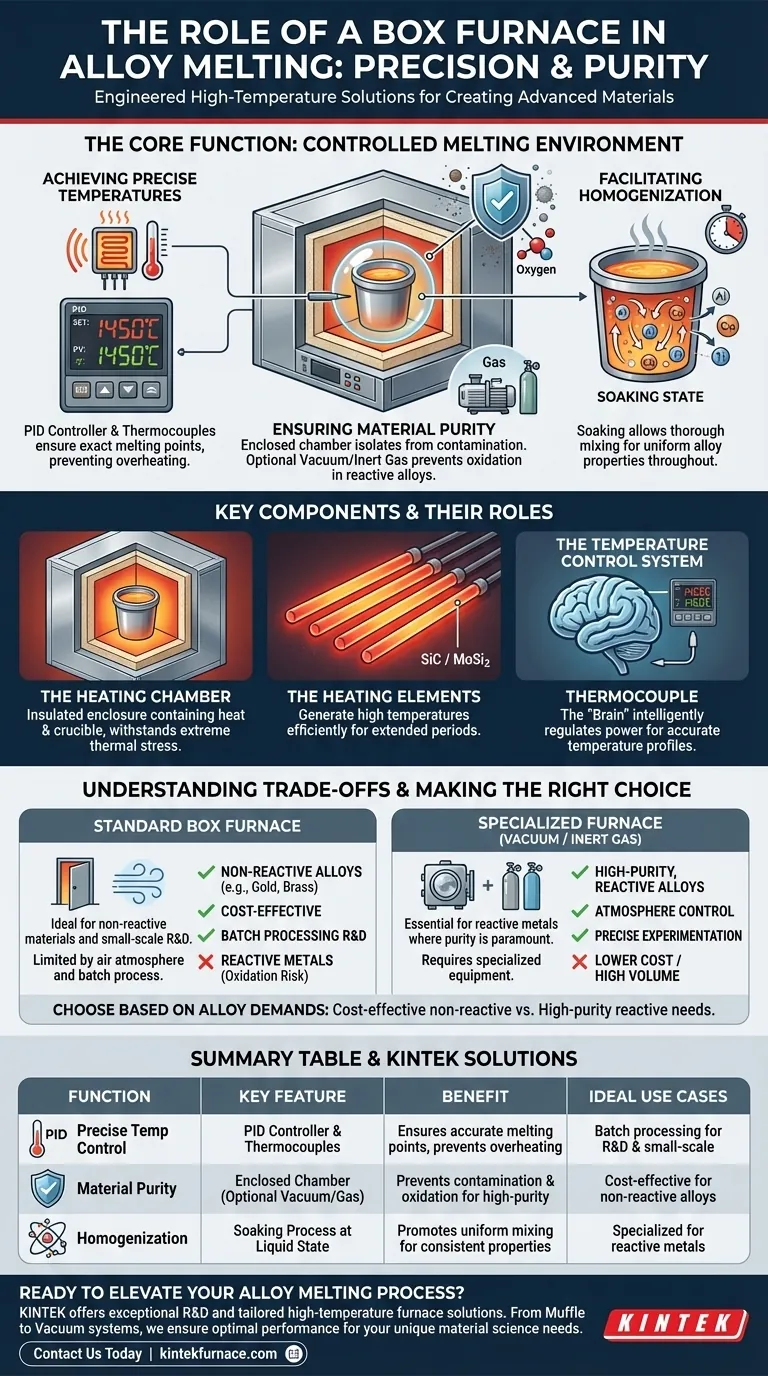
The Core Function: A Controlled Melting Environment
Creating a successful alloy depends entirely on controlling the conditions under which its base metals are combined. A box furnace provides this control through several key functions.
Achieving Precise Temperatures
The temperature control system is the heart of the furnace's operation. It uses sensors, like thermocouples, to measure the internal temperature in real time.
This data allows a controller to precisely regulate the power to the heating elements. This ensures the furnace can hit and hold the specific melting points required for different metal combinations, preventing under-heating or damaging overheating.
Ensuring Material Purity
The furnace body creates an enclosed chamber that isolates the molten metal from the outside environment. This is critical for preventing contamination from dust or other airborne particles.
For alloys made with reactive metals (like aluminum or titanium), even the oxygen in the air can be a contaminant, forming unwanted oxides. In these cases, a specialized box furnace that allows for a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere is used to create a pure, non-reactive environment.
Facilitating Homogenization
Simply melting the metals together is not enough. The furnace must hold the mixture at a liquid state for a specific period, a process known as "soaking."
This allows the different atoms to diffuse and mix thoroughly, creating a homogenous liquid. Without this step, the final solidified alloy could have inconsistent properties throughout its structure.
Key Components and Their Roles
Understanding the furnace's construction clarifies how it achieves a controlled melting environment.
The Heating Chamber
This is the insulated enclosure that contains the heat and the crucible holding the metal. It's typically built from high-temperature refractory materials that can withstand extreme thermal stress without breaking down.
The Heating Elements
These are the components that generate the heat. They are made from materials like silicon carbide or molybdenum disilicide, which can operate at very high temperatures for extended periods when electricity is passed through them.
The Temperature Control System
As mentioned, this system is the furnace's brain. It consists of a thermocouple to measure temperature and a PID controller (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) that intelligently adjusts the heating elements to follow a programmed temperature profile with high accuracy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While versatile, a standard box furnace is not the universal solution for all alloy melting. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Challenge of Atmosphere
A basic box furnace operates with a normal air atmosphere. This is perfectly acceptable for non-reactive metals like gold or certain brasses, but it will cause significant oxidation and impurities in more sensitive alloys.
Batch Processing Limitations
Box furnaces are inherently batch processors. They are ideal for research and development, prototyping, or small-scale production runs where precision is paramount.
They are not suited for the high-volume, continuous production seen in large industrial foundries, where induction or arc furnaces are more common.
When to Choose a Specialized Furnace
If your work involves metals that readily react with oxygen or nitrogen, a standard box furnace is the wrong tool. You must use a vacuum furnace or an inert gas furnace to protect the material's integrity during the melting process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Alloy
Selecting the correct furnace configuration is critical for achieving your desired material properties.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective melting of non-reactive alloys: A standard atmospheric box furnace with precise temperature control is an excellent and reliable tool.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity, reactive alloys: You must invest in a furnace with atmosphere control, such as a vacuum or inert gas model, to prevent oxidation.
- If your primary focus is research and small-batch experimentation: A versatile laboratory box furnace offers the ideal platform for developing and testing new alloy compositions with high precision.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is about matching the equipment's environmental controls to the chemical demands of your alloy.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Precise Temperature Control | PID controller and thermocouples | Ensures accurate melting points and prevents overheating |
| Material Purity | Enclosed chamber with optional vacuum/gas | Prevents contamination and oxidation for high-purity alloys |
| Homogenization | Soaking process at liquid state | Promotes uniform mixing for consistent alloy properties |
| Ideal Use Cases | Batch processing for R&D and small-scale | Cost-effective for non-reactive alloys; specialized for reactive metals |
Ready to elevate your alloy melting process? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for materials science laboratories. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're developing new alloys or ensuring high-purity results, our expertise ensures optimal performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific needs and drive innovation in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















