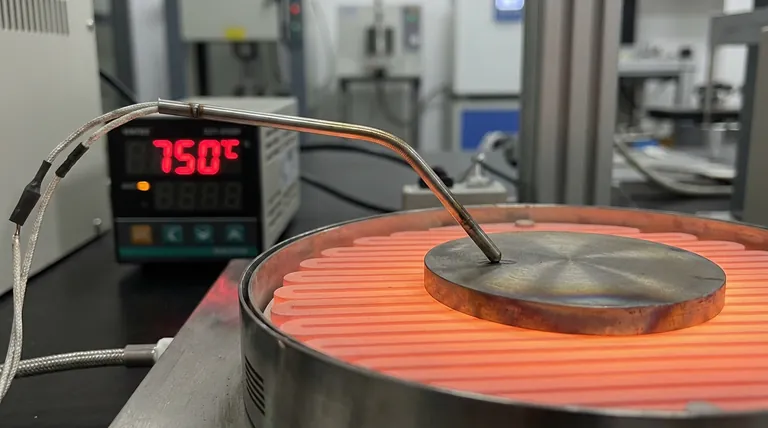
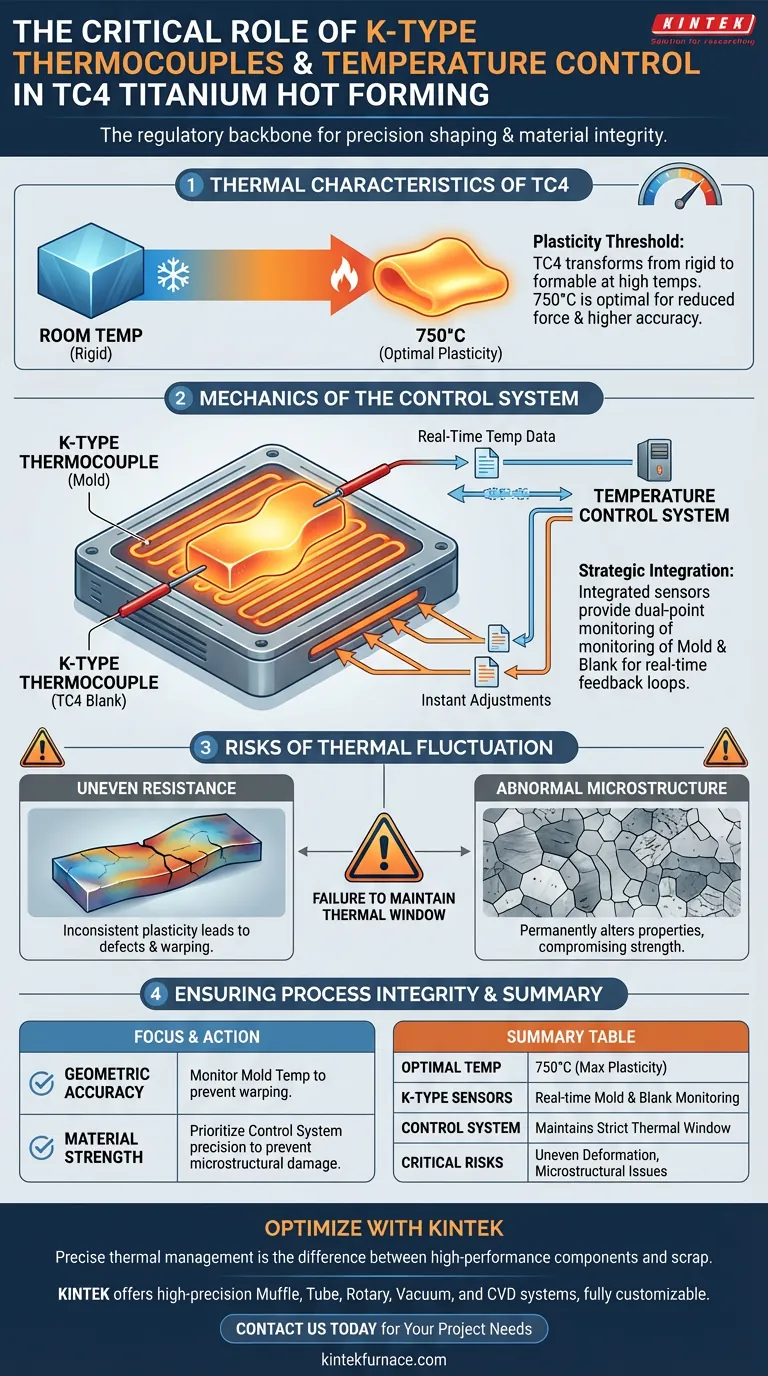
K-type thermocouples and temperature control systems serve as the critical regulatory backbone for the hot forming of TC4 titanium alloy. Integrated directly into the heating platform, these thermocouples provide real-time, high-precision monitoring of both the mold and the titanium blank. This data drives the temperature control system, ensuring the alloy remains within a strict thermal window to maintain the plasticity required for accurate shaping.
TC4 titanium alloy requires a strict thermal window to transform from a rigid metal into a formable state. Without precise control, slight temperature deviations can lead to uneven deformation or compromised material structure.

The Thermal Characteristics of TC4 Titanium
The Plasticity Threshold
At room temperature, TC4 titanium alloy is rigid and difficult to form. However, its material properties change drastically when heated.
The Role of High Temperatures
The primary reference indicates that TC4 exhibits significantly better formability at 750°C. At this specific temperature, the alloy enters a state of high plasticity, allowing it to be shaped with reduced force and higher accuracy.
The Mechanics of the Control System
Strategic Sensor Integration
K-type thermocouples are not merely attached to the surface; they are integrated into the heating platform of the hot forming machine.
Dual-Point Monitoring
Effective control requires monitoring two distinct variables: the temperature of the mold and the temperature of the TC4 blank itself.
Real-Time Feedback Loops
The control system uses the data from the thermocouples to make instant adjustments. This ensures that the heating elements compensate immediately for any thermal loss during the forming process.
Risks of Thermal Fluctuation
The Danger of Uneven Resistance
If the temperature control system fails to maintain the target window, the plasticity of the alloy becomes inconsistent. This leads to uneven forming resistance, where cooler parts of the blank resist shaping while hotter parts deform too easily, causing defects.
Abnormal Microstructural Evolution
Temperature is not just about shape; it is about metallurgy. Fluctuations outside the defined window can trigger abnormal microstructural evolution, permanently altering the physical properties of the finished part and potentially rendering it unusable for high-stress applications.
Ensuring Process Integrity
If your primary focus is Geometric Accuracy:
Ensure your thermocouples monitor the mold temperature to prevent uneven resistance that leads to dimensional warping.
If your primary focus is Material Strength:
Prioritize the precision of the control system to prevent microstructural damage caused by overheating or thermal oscillation.
Precise thermal management is the difference between a high-performance aerospace component and a piece of scrap metal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in TC4 Hot Forming |
|---|---|
| Optimal Temperature | 750°C for maximum plasticity and reduced forming force |
| K-type Thermocouples | Integrated sensors for real-time mold and blank monitoring |
| Control System | Maintains thermal window to prevent uneven deformation |
| Critical Risks | Inconsistent resistance and abnormal microstructural evolution |
Optimize Your Titanium Processing with KINTEK
Precise thermal management is the difference between high-performance components and manufacturing scrap. At KINTEK, we understand the rigorous demands of TC4 titanium alloy forming. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your specific lab or industrial high-temp requirements.
Ensure your material integrity and geometric accuracy with our industry-leading temperature control solutions. Contact us today to discuss your project needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Tao Zhang, Xiaochuan Liu. Deformation Control of TC4 Titanium Alloy in Thin-Walled Hyperbolic Structures During Hot Forming Processes. DOI: 10.3390/ma17246146
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Where are H Type Silicon Carbide Heating Elements commonly used? Ideal for High-Temp Cycling in Glass, Electronics, and Chemicals
- What should be considered regarding the cyclic nature of an application when using heating elements? Ensure Longevity in High-Temp Cycling
- What is the purpose of K-type thermocouples and multi-channel loggers? Validating Thermal Insulation Performance
- What temperature range can silicon carbide heating elements withstand? Up to 1600°C for reliable performance
- What are the main types of alloys used for manufacturing heating elements? Discover the Best Alloys for Your Heating Needs
- Why are alloys used in electrical heating devices? Discover the Key to Durable, Efficient Heat Generation
- What safety measures are incorporated into heating elements? Ensure Reliable Protection for Your Applications
- What is a silicon carbide heating element and how is it made? Discover High-Temp, Durable Heating Solutions











