When operating a heating system cyclically, the most critical factor to consider is the physical stress caused by thermal expansion and contraction. Each time the heating element is energized, it expands, and each time it cools, it contracts. This constant movement must be properly managed in the system's mechanical design to prevent physical binding, localized overheating, and premature failure.
The cyclic nature of an application is a primary driver of heating element failure. While accommodating the element's physical expansion is a fundamental requirement, true system longevity depends on understanding and mitigating the cumulative material degradation caused by repeated heating and cooling cycles.
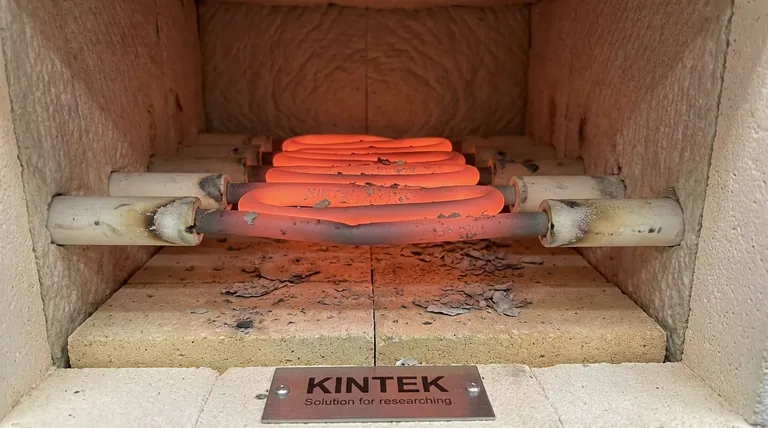

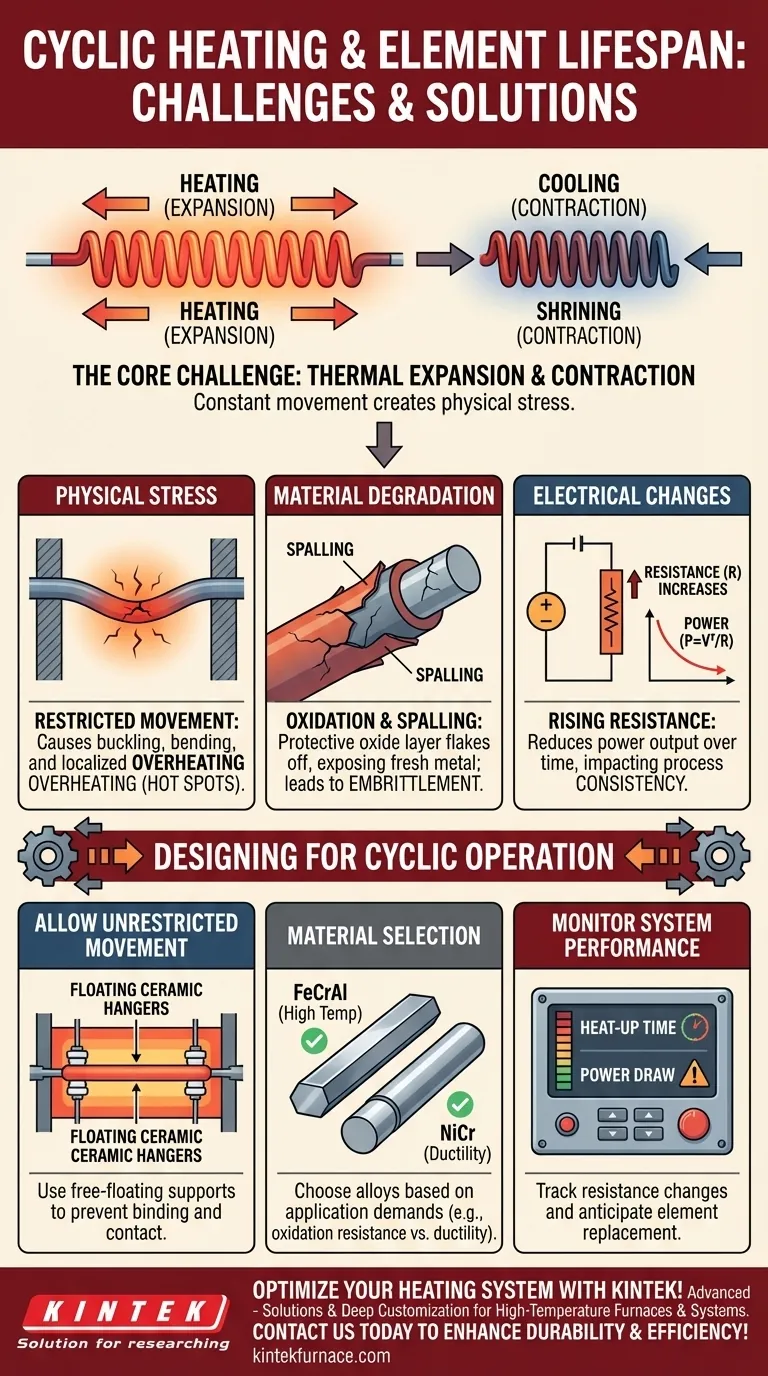
The Core Challenge: Thermal Expansion and Contraction
The most immediate effect of on/off cycling is the physical movement of the element. This is not a minor detail; it is a fundamental mechanical behavior that dictates the design of the element's supports.
How Cycling Causes Element Movement
Every material has a coefficient of thermal expansion. When a heating element goes from room temperature to its operating temperature (which can exceed 1000°C), it will physically grow in length. This growth is predictable and significant. When the power is cut, it shrinks back to its original size.
The Critical Need for Unrestricted Movement
Because of this growth and shrinkage, heating elements must never be rigidly fixed at both ends. They must be installed on hangers, grooves, or supports that allow them to move freely along their length. If this movement is restricted, the element will buckle or bend, creating immense internal stress.
The Danger of Physical Contact
If an expanding element is placed too close to a furnace wall or a refractory shelf, it may make contact as it heats up. This contact prevents heat from radiating away from that specific point, creating a hot spot. This localized overheating dramatically accelerates oxidation and will cause the element to fail at that point.
Beyond Movement: The Hidden Stresses of Cycling
While managing physical movement is crucial, repeated cycling introduces other, less obvious stresses that degrade the element over time.
Material Oxidation and Embrittlement
Most heating element alloys, like iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl), rely on forming a stable, protective oxide layer to prevent rapid degradation. Each heat cycle exposes the element to oxygen, contributing to this layer.
However, the repeated expansion and contraction can cause this protective oxide layer to flake off—a process called spalling. This exposes fresh metal underneath, which then oxidizes, effectively thinning the element wire over time and reducing its lifespan.
Changes in Electrical Resistance
As an element oxidizes and its cross-sectional area decreases, its electrical resistance increases. In a voltage-controlled system, this rising resistance will cause the power output (P = V²/R) to drop.
This means that over thousands of cycles, the system may take longer to reach its target temperature or struggle to maintain it, impacting process consistency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Designing for a cyclic application requires balancing performance with longevity. Ignoring these trade-offs often leads to frequent and costly maintenance.
Faster Cycling vs. Element Lifespan
There is a direct correlation: the more frequent the on/off cycles, the shorter the element's operational life. An element run continuously at a stable temperature will last significantly longer than one cycled frequently, even if the total "on-time" is the same. The stress comes from the transition.
Material Selection is Key
Different element alloys behave differently under cyclic conditions. FeCrAl alloys are generally excellent for high temperatures but can become brittle over time. Nickel-chromium (NiCr) alloys often exhibit better ductility and resistance to cyclic stress, though they may have lower maximum operating temperatures. The right choice depends entirely on the application's demands.
The Myth of "Saving" the Element
It's a common misconception that turning an element off "saves" its life. In highly cyclic applications, the opposite is often true. The temperature change itself is the primary source of wear and tear, not the time spent at a steady temperature.
Designing for Cyclic Operation
Your design and operational strategy should be directly informed by the demands of your process. Use these points as a guide.
- If your primary focus is maximum lifespan and reliability: Ensure elements have ample, unrestricted space to expand and contract, and select an alloy known for superior oxidation resistance and ductility in cyclic conditions.
- If your primary focus is consistent thermal performance: Monitor the system's heat-up times and power draw to anticipate the effects of increasing element resistance and plan for eventual replacement.
- If you are troubleshooting frequent failures: Immediately inspect for any signs of physical binding, sagging that leads to contact with insulation, or excessive flaking of the element's surface.
By anticipating the mechanical and material stresses of cycling, you can design a robust heating system built for endurance.
Summary Table:
| Consideration | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Thermal Expansion | Allow free movement to prevent binding, buckling, and hot spots from expansion/contraction. |
| Material Degradation | Oxidation, spalling, and embrittlement reduce lifespan; select alloys like FeCrAl or NiCr for durability. |
| Electrical Changes | Resistance increases over cycles, affecting power output and temperature consistency. |
| Design Strategies | Use supports for movement, balance cycle frequency vs. lifespan, and monitor for failures. |
Optimize your heating system for cyclic applications with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, enhancing durability and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific requirements and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















