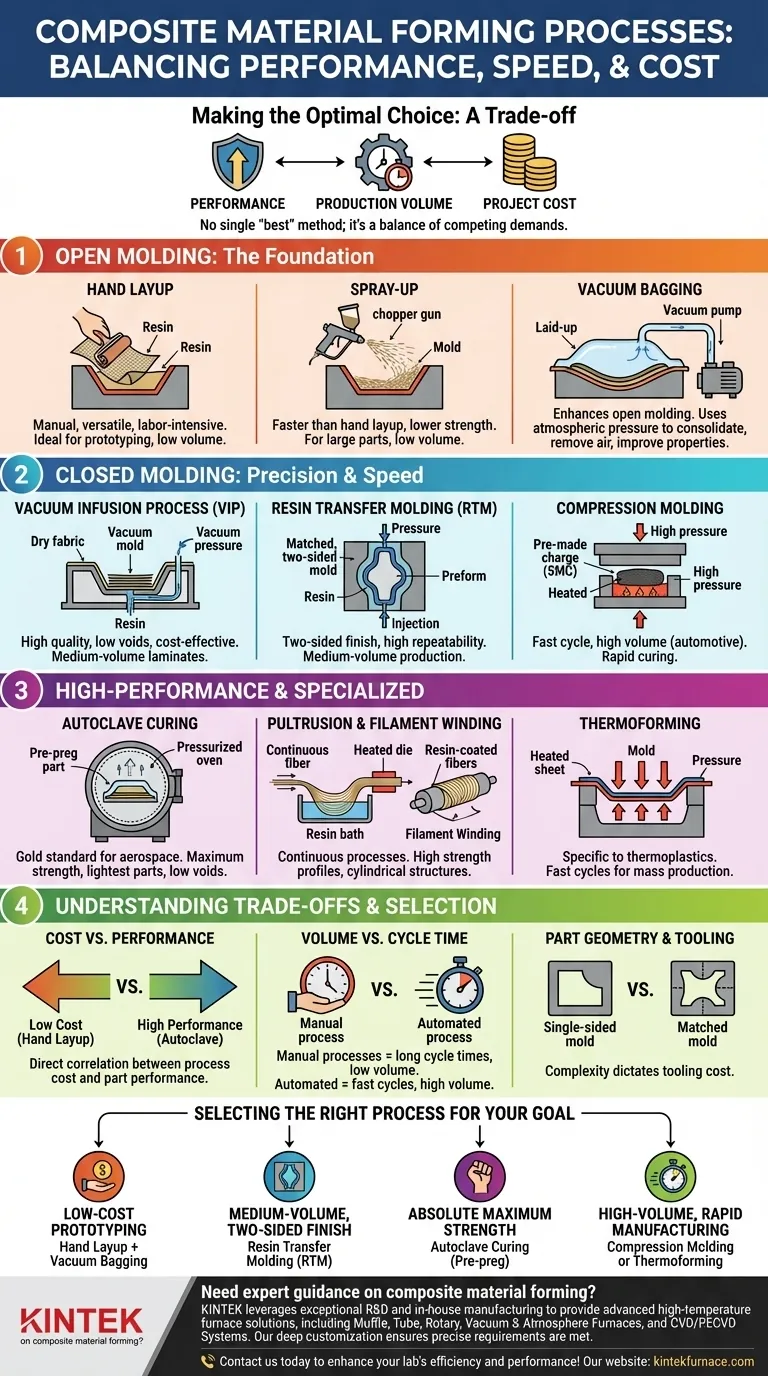
The manufacturing process for a composite part is chosen from a wide spectrum of techniques, ranging from simple manual methods to highly automated, high-pressure systems. While processes like thermoforming and vacuum forming exist, they are primarily used for thermoplastic composites. The broader field, especially for high-performance thermoset materials like carbon fiber epoxy, relies on methods such as hand layup, vacuum infusion, resin transfer molding (RTM), and autoclave curing to achieve specific performance and production goals.
The selection of a composite forming process is a critical engineering decision that balances three factors: the required performance of the final part, the desired production volume and speed, and the overall project cost. There is no single "best" method; the optimal choice is always a trade-off between these competing demands.
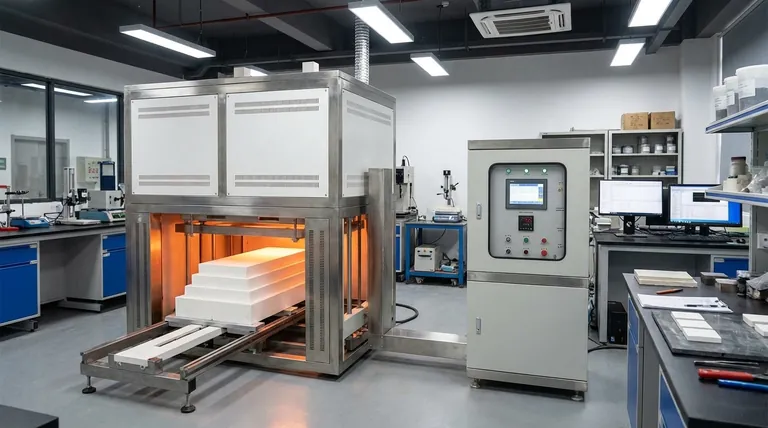

Open Molding: The Foundation of Composites
Open molding processes use a single-sided mold, which is open to the atmosphere. These methods are foundational, offering flexibility and low initial tooling costs, making them ideal for prototyping and low-volume production.
Hand Layup
Hand layup is the most fundamental composite manufacturing process. Dry reinforcement fabrics (like carbon fiber or fiberglass) are placed into a mold, and a liquid resin is applied manually with brushes and rollers. This process is highly versatile but labor-intensive and dependent on technician skill for quality.
Spray-Up
A variation of open molding, the spray-up process uses a special "chopper gun." This gun simultaneously chops continuous fibers into short lengths and sprays them onto the mold along with a catalyzed resin. It is faster than hand layup for large parts but typically results in lower strength due to the shorter, randomly oriented fibers.
Vacuum Bagging
Vacuum bagging is not a standalone process but a critical enhancement to open molding. After a part is laid up and saturated with resin, a flexible bag is sealed over the part and a vacuum is applied. The resulting atmospheric pressure (up to 14.7 psi) consolidates the laminate, removes trapped air, and squeezes out excess resin, significantly improving the fiber-to-resin ratio and mechanical properties.
Closed Molding: Gaining Precision and Speed
Closed molding processes use a two-part, matched mold or a rigid mold with a flexible bag. These methods enclose the material, offering better control, higher repeatability, and improved surface finishes on all sides of the part.
Vacuum Infusion Process (VIP)
In vacuum infusion, dry reinforcement fabrics are placed into a mold and sealed under a vacuum bag. Resin is then introduced through carefully placed ports and drawn through the dry fabric by the vacuum. This method produces high-quality laminates with excellent fiber content and very low voids, serving as a cost-effective alternative to more complex processes.
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM)
RTM uses a matched, two-sided mold. A dry fiber "preform" is placed inside, the mold is clamped shut, and resin is injected under pressure. RTM is excellent for producing parts with a good surface finish on both sides at medium production volumes, offering high repeatability.
Compression Molding
This process is dominant in high-volume automotive applications. A pre-made charge of composite material, often Sheet Molding Compound (SMC), is placed into a heated metal mold. A press closes the mold under immense pressure, forcing the material to fill the cavity and curing it rapidly. Cycle times can be as short as a few minutes.
High-Performance and Specialized Processes
These processes are engineered to create parts with the highest possible mechanical properties or to enable continuous, automated production of specific shapes.
Autoclave Curing
This is the gold standard for aerospace, military, and elite motorsport applications. Parts are made with "pre-preg"—fabric pre-impregnated with a latent resin. After layup, the part is vacuum-bagged and cured inside an autoclave, which is essentially a pressurized oven. The combination of high pressure and precise temperature control creates the strongest, lightest, and most void-free parts possible.
Pultrusion and Filament Winding
These are continuous manufacturing processes. Pultrusion pulls fibers through a resin bath and then a heated die to form constant cross-section profiles, like I-beams, rods, and tubes. Filament winding wraps resin-coated fibers around a rotating mandrel to create high-strength cylindrical or convex structures like pressure vessels and drive shafts.
Thermoforming
This process is specific to thermoplastic composites. A pre-consolidated, rigid sheet of thermoplastic composite material is heated until it becomes soft and pliable. It is then quickly transferred to a mold where it is shaped using vacuum pressure, air pressure, or a mechanical press. It offers very fast cycle times suitable for mass production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right process requires a clear understanding of the compromises between quality, cost, and speed. A process that is ideal for a prototype is rarely suitable for mass production.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between process cost and part performance. Hand layup has very low tooling costs but produces parts with lower fiber content and potential for voids. At the other extreme, autoclave curing requires a multi-million dollar investment but produces parts with unparalleled strength and lightness.
Volume vs. Cycle Time
Manual processes like hand layup and autoclave curing have very long cycle times, measured in hours or even days, making them suitable only for low-volume production. Automated processes like compression molding and pultrusion have cycle times measured in minutes, enabling the production of thousands or millions of parts per year.
Part Geometry and Tooling
The complexity of the part dictates the tooling. Simple, open shapes can use inexpensive single-sided molds. Parts requiring a finished surface on both sides demand more expensive matched tooling, as seen in RTM and compression molding. Continuous profiles are uniquely suited for pultrusion.
Selecting the Right Process for Your Goal
Your project's primary objective is the most important factor in selecting a manufacturing method.
- If your primary focus is low-cost prototyping or one-off custom parts: Hand layup, enhanced with vacuum bagging, offers the best balance of accessibility and quality.
- If your primary focus is medium-volume production with a good two-sided finish: Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) is the ideal choice for its excellent repeatability and aesthetic quality.
- If your primary focus is absolute maximum strength and minimal weight: Pre-preg materials cured in an autoclave are the undisputed standard for mission-critical applications.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, rapid manufacturing of consumer or automotive parts: Compression molding (for thermosets) or thermoforming (for thermoplastics) provides the necessary speed and cost-efficiency.
Understanding this spectrum of processes empowers you to make strategic manufacturing decisions that are as critical as the material itself.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Features | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Hand Layup | Manual, low cost, versatile | Prototyping, low-volume parts |
| Vacuum Infusion | High fiber content, low voids | Medium-volume, high-quality laminates |
| Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) | Two-sided finish, repeatable | Medium-volume production |
| Autoclave Curing | Maximum strength, low voids | Aerospace, high-performance applications |
| Compression Molding | Fast cycle, high volume | Automotive, mass production |
| Pultrusion/Filament Winding | Continuous, high strength | Profiles, cylindrical parts |
Need expert guidance on composite material forming? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















