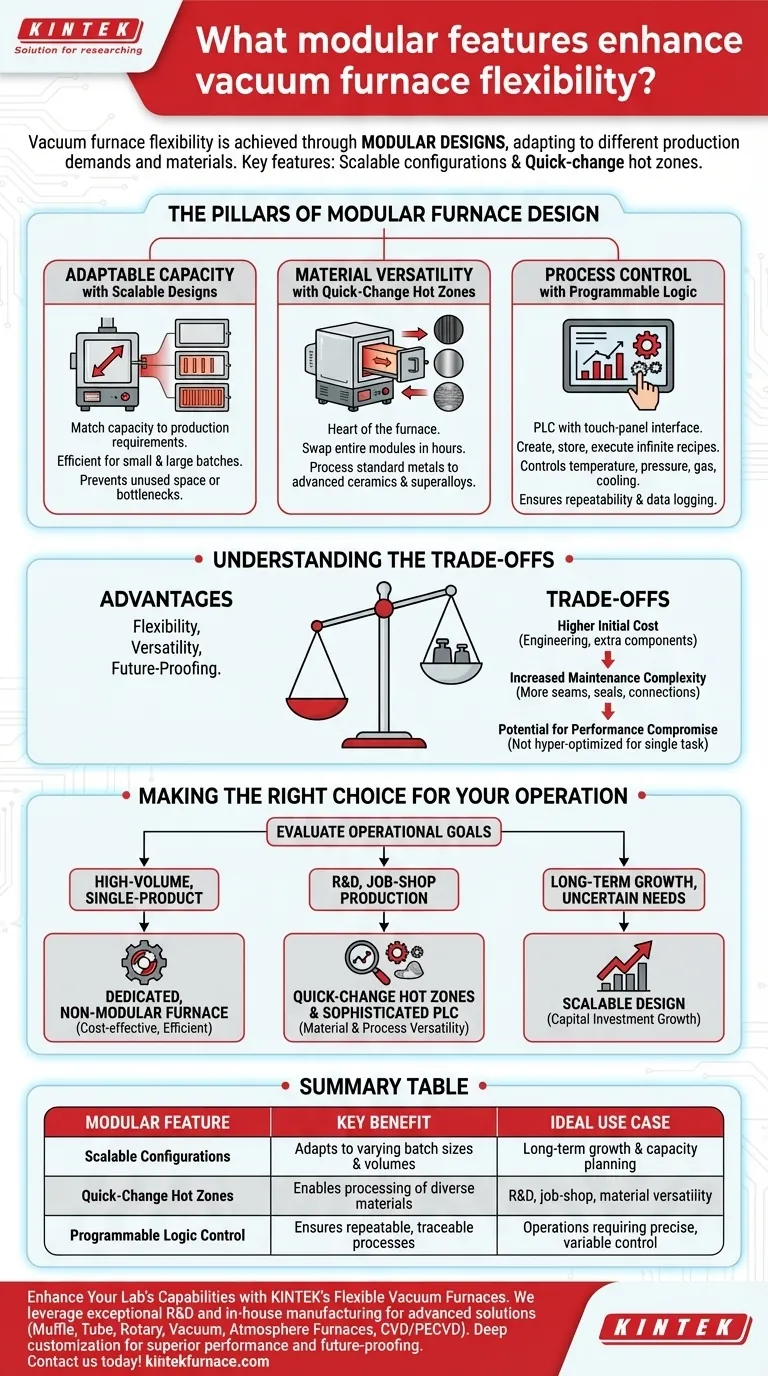
At its core, vacuum furnace flexibility is achieved through modular designs that allow the system to adapt to different production demands and materials. The two most critical modular features are scalable configurations, which adjust for varying batch sizes or continuous processing, and quick-change hot zones, which enable the furnace to process a wide range of materials from standard metals to advanced ceramics and superalloys.
True furnace flexibility is not just about having interchangeable parts. It’s about future-proofing your investment with a system that can evolve alongside your operational needs, new materials, and changing production volumes.

The Pillars of Modular Furnace Design
A truly flexible vacuum furnace is more than a single machine; it's an adaptable platform. This adaptability is built upon a few key modular principles that work together.
Adaptable Capacity with Scalable Designs
A furnace’s physical design dictates its throughput. Modular scalability allows you to match the furnace's capacity to your specific production requirements without over-investing in unused space.
This can mean designing a system with space for future heating chambers or having a furnace that can efficiently handle both small, specialized batches and larger, standard production runs. This prevents the furnace from becoming a bottleneck or an underutilized asset as needs change.
Material Versatility with Quick-Change Hot Zones
The hot zone is the heart of the furnace, and its material composition is critical for achieving desired metallurgical properties and avoiding contamination. Different processes require different hot zone materials.
For example, a graphite-based hot zone is common for many applications, but an all-metal hot zone (typically molybdenum or tungsten) is necessary for processes demanding extreme cleanliness or for materials that react with carbon. A quick-change design allows operators to swap these entire hot zone modules relatively easily, transforming the furnace's capability in hours instead of days and dramatically expanding its material processing range.
Process Control with Programmable Logic
The physical modularity of the furnace is unlocked by its control system. Modern systems use a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) with a simple touch-panel interface.
This allows operators to create, store, and execute an almost infinite number of "recipes." These programs control every variable, including temperature ramps, pressure setpoints, gas backfills, and cooling cycles. This software-driven flexibility ensures that every unique process loaded into the modular hardware is perfectly repeatable and traceable through data logging.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While modularity offers significant advantages, it is essential to approach it with a clear understanding of the associated trade-offs.
The Initial Cost of Versatility
A highly modular vacuum furnace system typically carries a higher upfront investment than a fixed-purpose furnace. You are paying for engineering, additional components (like a spare hot zone), and a more complex design.
Increased Maintenance Complexity
Having interchangeable components, by definition, introduces more seams, seals, and connection points. This can increase the complexity of maintenance routines and may require more highly skilled technicians to manage component swaps and ensure system integrity.
Potential for Performance Compromise
A furnace designed for maximum flexibility may not be as hyper-optimized for a single, repetitive task as a dedicated unit. While the performance is excellent across a wide range, a specialized furnace built for one process may offer slightly faster cycle times or higher efficiency for that specific task.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Selecting the right features depends entirely on your operational goals. Evaluate your current and anticipated needs to determine the appropriate level of modularity.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, single-product manufacturing: A dedicated, non-modular furnace optimized for one specific process will likely be the most cost-effective and efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is research, development, or job-shop production: Prioritize a system with quick-change hot zones and a sophisticated PLC to provide the material and process versatility you need.
- If your primary focus is long-term growth with uncertain future needs: A scalable design is your most critical feature, as it allows your capital investment to grow with your business.
Ultimately, the right choice is a furnace that not only solves today's challenges but also provides a clear and adaptable path for the future.
Summary Table:
| Modular Feature | Key Benefit | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Scalable Configurations | Adapts to varying batch sizes and production volumes | Long-term growth and capacity planning |
| Quick-Change Hot Zones | Enables processing of diverse materials (e.g., metals, ceramics) | R&D, job-shop production, material versatility |
| Programmable Logic Control | Ensures repeatable, traceable processes with custom recipes | Operations requiring precise, variable control |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a flexible vacuum furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve superior performance and future-proof your operations. Contact us today to discuss how our modular designs can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















