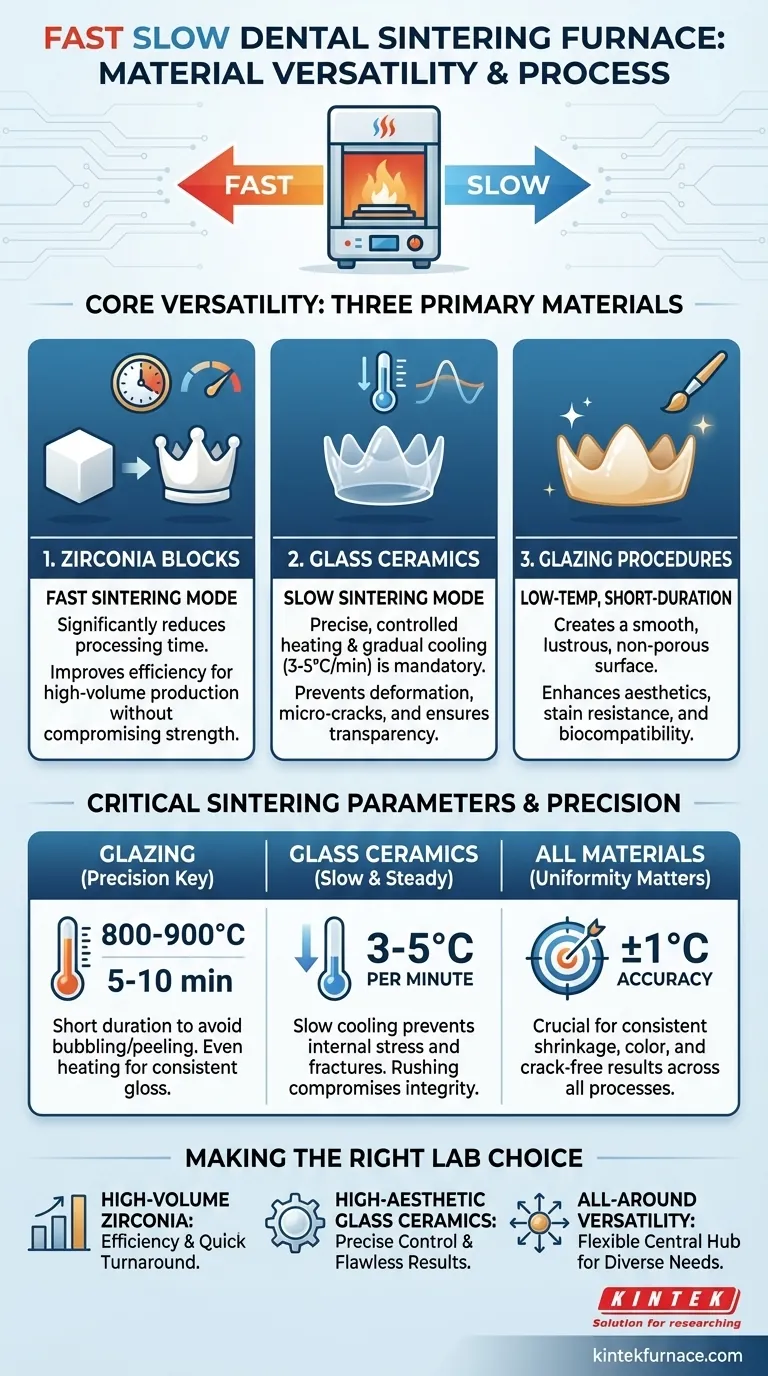
At its core, the Fast Slow Dental Sintering Furnace is designed to process three primary categories of dental materials. It can successfully sinter high-strength zirconia blocks, fire delicate glass ceramics, and perform final glazing procedures. This versatility makes it a comprehensive tool for a modern dental laboratory's workflow.
The true value of this furnace is not just the materials it supports, but its specialized dual-mode functionality. Its ability to perform both rapid, high-temperature cycles for zirconia and precise, slow-cooling cycles for glass ceramics is what defines its role in producing high-quality dental restorations.

A Versatile Furnace for Modern Dental Materials
The furnace's design acknowledges that different dental materials have fundamentally different thermal processing requirements. It addresses this by providing distinct programs and control capabilities for each category.
Sintering Zirconia Blocks
The "fast" sintering mode is primarily engineered for zirconia. This allows laboratories to significantly reduce the processing time for zirconia crowns and bridges, improving efficiency and patient turnaround time without compromising the material's strength.
Processing Glass Ceramics
Glass ceramics, such as lithium disilicate, require a much more delicate approach. The furnace's "slow" sintering mode is essential for this application.
This mode uses a controlled, gradual heating and cooling cycle. This precision is critical to prevent the uneven flow of the glass phase, which can cause deformation or reduce the final restoration's transparency.
Performing Glazing
The furnace is also equipped for the final glazing stage of a restoration. This is a low-temperature, short-duration process that creates a smooth, lustrous, and non-porous surface on the final crown.
Proper glazing enhances aesthetics, improves stain resistance, and increases the biocompatibility of the restoration.
Understanding the Critical Sintering Parameters
Successfully using the furnace depends on understanding and respecting the specific parameters for each material. Using the wrong program can lead to failed restorations.
For Glazing: Precision is Key
When glazing, you must use a low-temperature program, typically between 800-900°C, for a short duration of 5-10 minutes.
Exceeding these parameters can cause the glaze to bubble or peel, while uneven heating can result in color differences and a blotchy, uneven gloss on the final restoration.
For Glass Ceramics: Slow and Steady is Non-Negotiable
The physical integrity of glass ceramics depends on managing internal stress during the cooling phase. A slow cooling rate of 3-5°C per minute is mandatory to prevent the formation of micro-cracks.
Rushing this process by using a fast-cooling cycle will almost certainly compromise the restoration, leading to fractures either immediately or after placement in the patient's mouth.
For All Materials: Temperature Uniformity Matters
The furnace's ability to maintain a uniform temperature with an accuracy of ±1°C is not a minor feature; it is crucial for predictable outcomes.
For zirconia, this ensures consistent shrinkage and color. For glass ceramics, it prevents deformation. For glazing, it ensures an even, aesthetic finish.
Making the Right Choice for Your Lab's Needs
Your laboratory's primary focus will determine which feature of the furnace is most valuable to your workflow.
- If your primary focus is high-volume zirconia production: The efficiency of the fast-sintering mode is a significant advantage, allowing for quicker case completion.
- If your primary focus is high-aesthetic glass ceramic restorations: The precise control, slow-sintering programs, and managed cooling rates are essential for achieving flawless, crack-free results.
- If your primary focus is all-around versatility: The ability to switch between these demanding protocols for different materials makes the furnace a flexible central hub for a full-service lab.
Understanding these capabilities allows you to harness the furnace's full potential for consistent, high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Sintering Parameters | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Zirconia Blocks | Fast mode, high temperature | Reduced processing time, improved strength |
| Glass Ceramics | Slow mode, controlled cooling (3-5°C/min) | Prevents cracks, ensures transparency |
| Glazing | Low temperature (800-900°C), short duration (5-10 min) | Enhances aesthetics, stain resistance |
Upgrade your dental lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced sintering solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace expertise. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization to meet your unique needs. Whether you focus on zirconia, glass ceramics, or versatile workflows, our furnaces deliver precise temperature control and reliable performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your sintering processes and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the recommended maintenance practices for dental furnaces? Ensure Precision and Longevity for Your Lab
- What is the working principle of a dental furnace? Mastering Precision Sintering & Firing for Crowns
- Why is using a universal setting for all materials in a dental furnace a mistake? Master Precision Sintering for Perfect Restorations
- What are the primary functions of ceramic dental furnaces? Achieve Precision and Durability in Dental Restorations
- Why is temperature range important when selecting a dental furnace? Unlock Material Compatibility and Precision



















