Induction-based ultrasonic atomization is highly effective for a broad range of electrically conductive materials. This includes volatile metals like tin, zinc, and aluminum alloys, as well as materials with high thermal conductivity such as copper, silver, and gold alloys. The process is also well-suited for producing powders from various steels, titanium, silicon, and other precious metals.
The defining characteristic for material compatibility is not the element itself, but its electrical conductivity for induction melting and its fluid properties once molten. This process excels where precise control over particle size is needed for conductive metals that can be effectively melted and then shattered by ultrasonic vibrations.
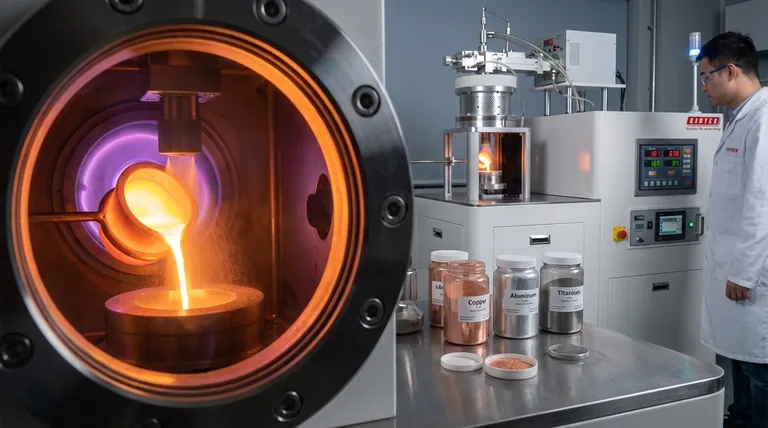

The Principles of Material Selection
To understand which materials are suitable, you must consider the two core technologies involved: induction heating and ultrasonic atomization. A material must be compatible with both stages of the process.
The Role of Electrical Conductivity
The process begins with induction heating. This method uses an electromagnetic field to generate eddy currents within the material, causing it to heat rapidly and efficiently from the inside out.
Therefore, the fundamental requirement is that the material must be electrically conductive. This is why the process is a match for virtually all metals and conductive composites but is unsuitable for non-conductive materials like ceramics.
Melting and Fluid Dynamics
Once the material reaches its melting point, it must flow as a liquid to the ultrasonic emitter, or sonotrode. The material's properties as a liquid—specifically its viscosity and surface tension—directly impact the atomization process.
The ultrasonic vibrations must be able to overcome these forces to break the liquid stream into fine droplets, which then solidify into powder.
Why Volatile and High-Conductivity Metals Excel
The references specifically highlight two groups of materials that are particularly well-suited for this process.
Volatile materials (e.g., Sn, Zn, Mg) have relatively low melting and boiling points, making them easy to melt with induction heating without requiring extreme energy inputs.
High thermal conductivity materials (e.g., Cu, Ag, Au) distribute heat very evenly. This prevents localized overheating and ensures a uniform melt temperature, which leads to more consistent droplet formation and powder characteristics.
Key Process Parameters That Influence Material Choice
The equipment and environment place practical constraints on which materials can be processed successfully.
Induction Power and Crucible Interaction
The material is melted inside a container, typically a graphite crucible. This means the target material's melting point must be manageable within the thermal limits of the crucible.
Furthermore, the material must be chemically compatible with graphite at high temperatures to avoid contamination or degradation of the melt.
The Ultrasonic Atomization Step
The sonotrode vibrates at a high frequency (typically 20-60 kHz) to shatter the molten metal into droplets. The properties of the liquid metal determine the resulting particle size.
This process is known for producing a relatively narrow particle size distribution, often in the 35 to 80 µm range, which is ideal for applications like additive manufacturing and thermal spray coatings.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
The entire process is performed under a vacuum or in an inert gas environment (like argon). This is critical for preventing the hot, molten metal from oxidizing.
This control is especially vital for reactive metals such as aluminum, magnesium, and titanium, which would otherwise form unwanted oxide layers, compromising the purity and quality of the final powder.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While versatile, induction-based ultrasonic atomization is not without its challenges.
Material Reactivity
Even with an inert atmosphere, highly reactive metals like titanium can be challenging. They can potentially react with trace impurities in the gas or with the crucible material itself, requiring very high-purity environments and specialized equipment.
Ultra-High Melting Point Materials
Refractory metals like tungsten or tantalum have extremely high melting points. While induction can melt them, it requires immense power and specialized systems capable of handling extreme temperatures, pushing the limits of standard equipment.
Non-Conductive Materials
This is the most fundamental limitation. Ceramics, polymers, and other non-conductive materials cannot be melted directly with induction. They are incompatible with this process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your material selection should be guided by the final goal of your powder production.
- If your primary focus is producing powders for electronics or brazing: Materials with high conductivity and lower melting points, such as tin, silver, or specific copper alloys, are excellent choices.
- If your primary focus is lightweight structural components: Aluminum, magnesium, and titanium alloys are the primary candidates, but they require strict atmosphere control to ensure high purity.
- If your primary focus is developing novel alloys or research: The process offers flexibility for nearly any conductive metal, provided you can manage its melting point and reactivity within the system's constraints.
Ultimately, success with this method depends on matching the material's conductive and fluid properties to the capabilities of the induction and ultrasonic systems.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Examples | Key Characteristics for Atomization |
|---|---|---|
| Volatile Metals | Tin (Sn), Zinc (Zn), Aluminum Alloys | Low melting point, easy to melt and atomize |
| High Thermal Conductivity Metals | Copper (Cu), Silver (Ag), Gold (Au) alloys | Excellent heat distribution, uniform melt |
| Steels & Titanium | Various steel alloys, Titanium (Ti) | Requires strict atmosphere control to prevent oxidation |
| Other Conductive Materials | Silicon (Si), Precious Metals | Must be electrically conductive to be induction melted |
Unlock the Potential of Your Metal Powders with KINTEK
Do you work with conductive metals like aluminum, copper, titanium, or precious alloys and need to produce high-quality powders with a narrow particle size distribution (typically 35-80 µm) for applications such as additive manufacturing or thermal spray coatings?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements for processes like induction-based ultrasonic atomization.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our tailored solutions can help you achieve precise control over your powder production process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does MPCVD achieve high growth rates for diamond synthesis? Unlock Rapid, High-Quality Diamond Growth
- Why is MPCVD considered a cornerstone of modern materials science and engineering? Unlock High-Purity Materials for Innovation
- In which industries is the microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition system commonly used? Unlock High-Purity Material Synthesis
- What is the basic principle of operation for the microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition system? Unlock High-Purity Material Growth
- What are the two main methods of synthetic diamond production? Discover HPHT vs. CVD for Lab-Grown Gems



















