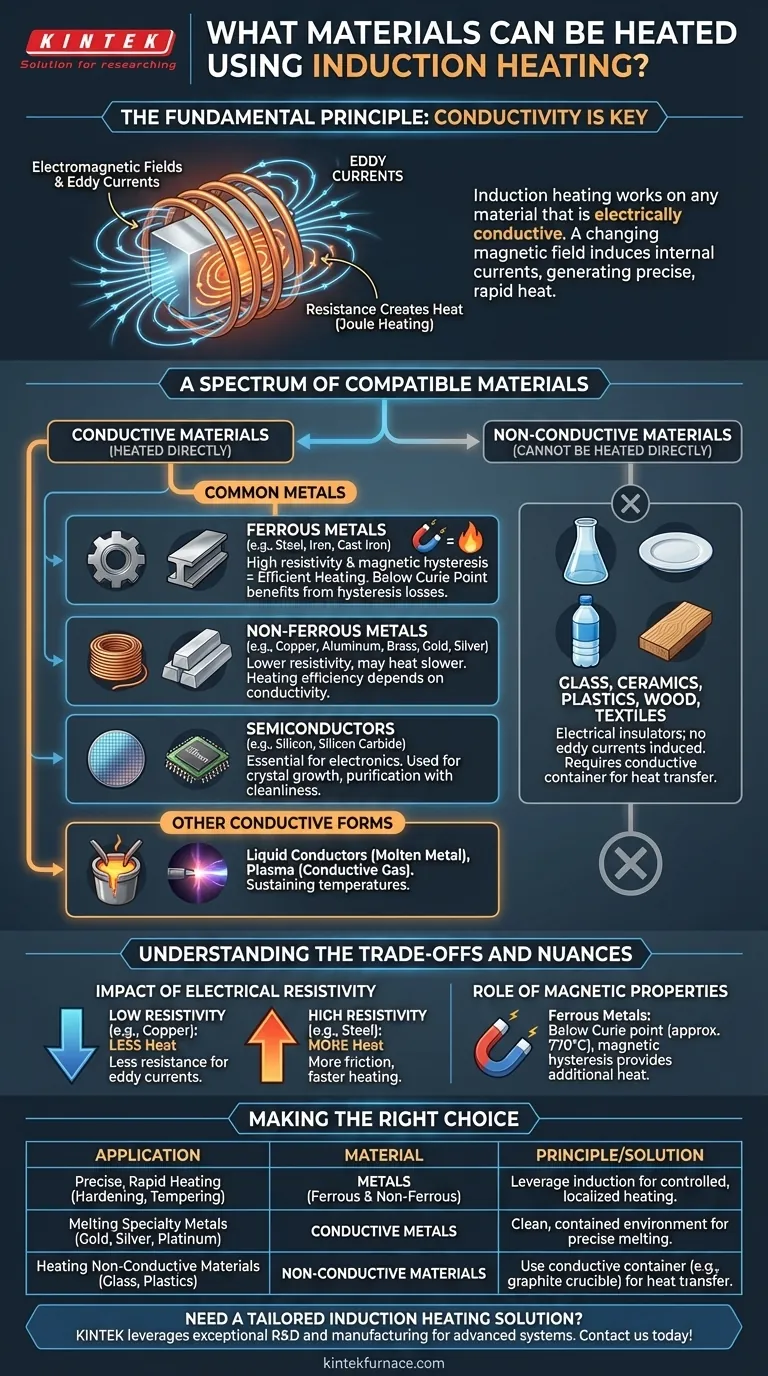
At its core, induction heating works on any material that is electrically conductive. This includes a wide range of metals such as steel, iron, copper, aluminum, brass, gold, and silver. It is also effective on semiconductors like silicon and carbide, and even on conductive liquids and gases like molten metal or plasma.
The key takeaway is not the specific material, but its fundamental electrical property. If a material can conduct electricity, a changing magnetic field can induce internal currents within it, generating precise and rapid heat from the inside out.
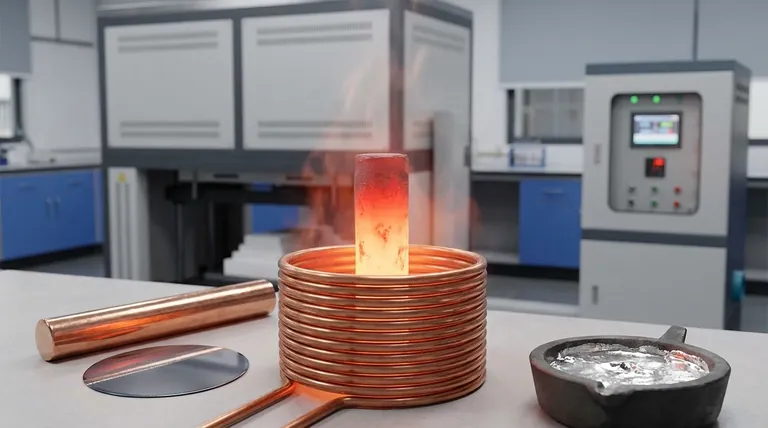

The Fundamental Principle: Why Conductivity is Key
To truly understand which materials work, you must first understand how induction heating operates. It's a non-contact method that uses the principles of electromagnetism.
Electromagnetic Fields and Eddy Currents
An induction coil generates a powerful, rapidly alternating magnetic field. When an electrically conductive material is placed within this field, the field induces circular electrical currents inside the material itself. These are known as eddy currents.
Resistance Creates Heat
Every conductive material has some natural resistance to the flow of electricity. As these eddy currents swirl through the material, they overcome this resistance, and this friction generates highly localized and instantaneous heat. This is the same principle (Joule heating) that causes any electrical wire to warm up.
A Spectrum of Compatible Materials
While the principle is simple, its application spans a vast range of materials, each with unique characteristics.
Common Metals (Ferrous and Non-Ferrous)
This is the most frequent application for induction. It works exceptionally well on ferrous metals like carbon steel, stainless steel, and cast iron. It also heats non-ferrous metals like copper, aluminum, and brass, though their heating characteristics differ based on their conductivity.
Semiconductors
Materials like silicon and silicon carbide are essential in the electronics industry. Induction is used to heat them for processes like crystal growth and purification, where cleanliness and precision are paramount.
Other Conductive Forms
The principle is not limited to solids. Liquid conductors, such as molten metals in a foundry, can be held at temperature or further heated using induction. In scientific applications, it can even be used to generate and sustain plasma, which is a conductive gas.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Simply being "conductive" is not the full story. The efficiency and effectiveness of induction heating depend on several interacting factors.
The Impact of Electrical Resistivity
Paradoxically, materials with extremely high conductivity, like pure copper, can be more difficult to heat efficiently. The eddy currents flow with very little resistance, generating less friction and thus less heat. Materials with higher resistivity, like steel, often heat up much faster and more easily.
The Role of Magnetic Properties
Ferrous metals (like iron and steel) benefit from a second heating effect at temperatures below their Curie point (approx. 770°C). Their magnetic nature causes hysteresis losses—additional heat generated as the material's magnetic domains rapidly flip in response to the AC field. This makes them exceptionally easy to heat with induction.
What Cannot Be Heated Directly
It's equally important to know what doesn't work. Electrical insulators cannot be heated by induction because they do not conduct electricity. This includes materials like glass, ceramics, plastics, wood, and textiles. No eddy currents can be induced, so no heat is generated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these principles allows you to select induction heating for the right task.
- If your primary focus is precise, rapid heating of metals: Induction is an unparalleled choice for applications like case hardening, tempering, brazing, and annealing where control is critical.
- If your primary focus is melting specialty metals: Induction provides the clean, contained, and controllable environment needed for melting gold, silver, platinum, and high-grade stainless steel.
- If your primary focus is heating a non-conductive material: Direct induction is not an option, but you can use it to heat a conductive container (like a graphite crucible) which then transfers heat to the non-conductive material inside.
By matching the material's properties to the principles of induction, you can leverage this technology with precision and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Examples | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Ferrous Metals | Steel, Iron | High resistivity, magnetic hysteresis for efficient heating |
| Non-Ferrous Metals | Copper, Aluminum | Lower resistivity, heats slower |
| Semiconductors | Silicon, Carbide | Used in electronics for precise, clean heating |
| Conductive Liquids/Gases | Molten Metal, Plasma | Effective for sustaining temperatures |
| Non-Conductive Materials | Glass, Plastics | Cannot be heated directly; requires conductive containers |
Need a tailored high-temperature solution for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced induction heating systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet unique experimental requirements for materials like metals and semiconductors. Contact us today to enhance your efficiency and precision!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















