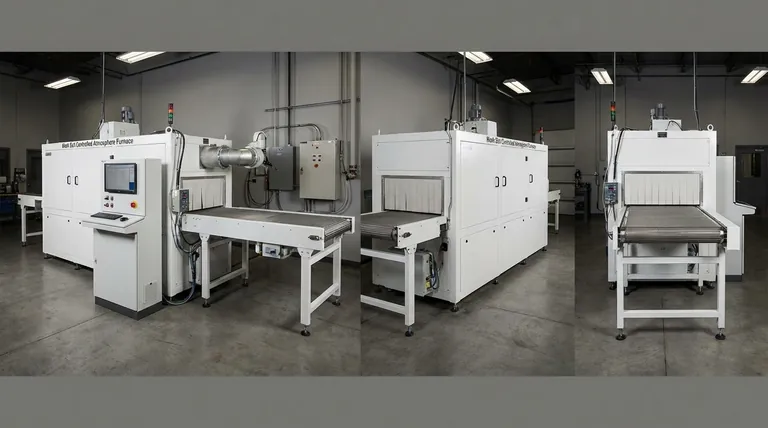
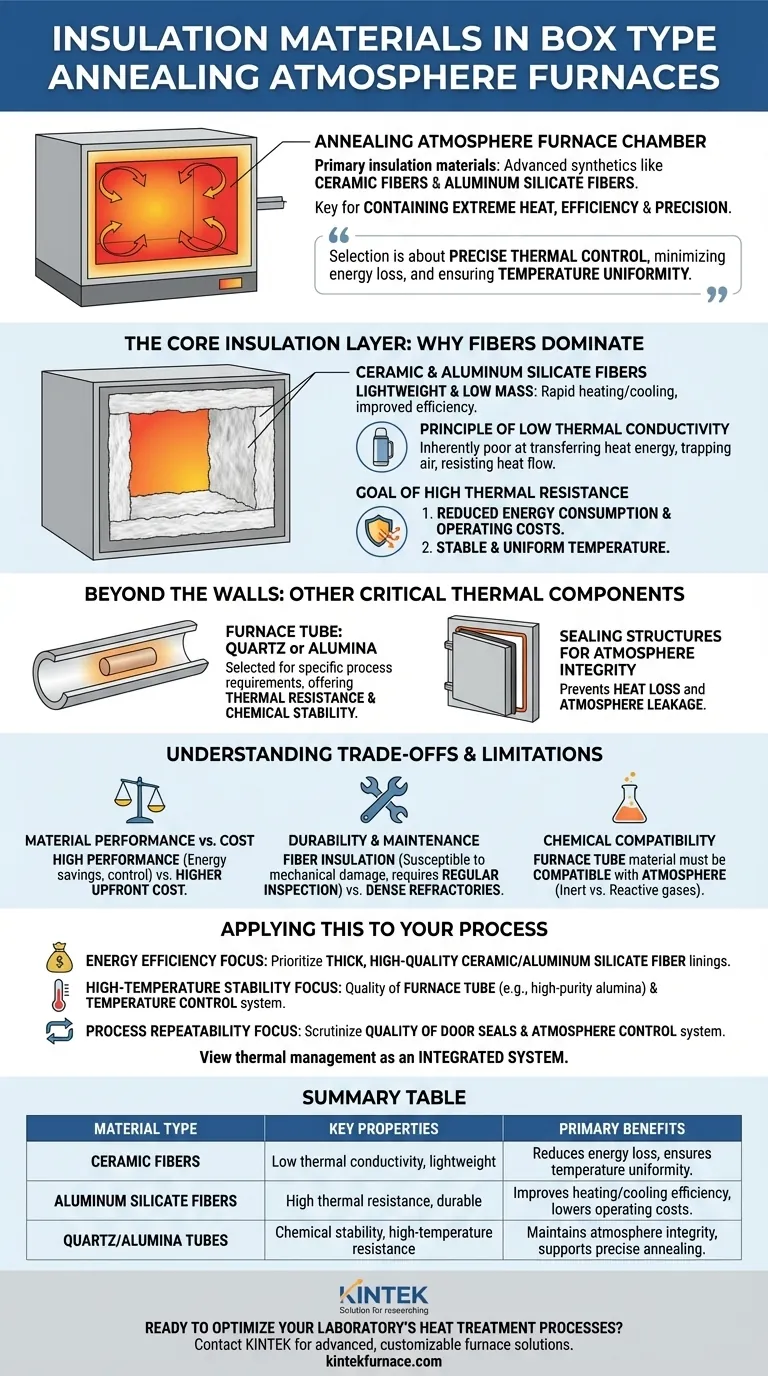
In a box type annealing atmosphere furnace, the primary insulation materials are advanced synthetics like ceramic fibers and aluminum silicate fibers. These materials are specifically chosen for their exceptional ability to contain extreme heat, which is fundamental to the furnace's efficiency and the precision of the annealing process.
The selection of insulation is not just about containing heat; it's about achieving precise thermal control. High-performance materials like ceramic fibers are used because they minimize energy loss and ensure the temperature uniformity required for successful heat treatment.

The Core Insulation Layer: Why Fibers Dominate
The main body of the furnace, often called the furnace chamber, requires insulation that can withstand high temperatures while preventing heat from escaping into the surrounding environment. This is where specialized fiber materials are critical.
Ceramic and Aluminum Silicate Fibers
The inner walls of the furnace are lined with materials like ceramic fibers and aluminum silicate fibers. These are the workhorses of modern furnace insulation.
They are lightweight and have a very low mass, meaning they don't absorb and store much heat themselves. This allows the furnace to heat up and cool down more rapidly when needed, improving operational efficiency.
The Principle of Low Thermal Conductivity
These fibers are effective because they exhibit low thermal conductivity. This means they are inherently poor at transferring heat energy from one point to another.
Think of it like a high-quality thermos. The vacuum layer prevents heat from easily passing through, and similarly, the structure of these fibers traps air and resists the flow of heat, keeping it inside the furnace where it belongs.
The Goal of High Thermal Resistance
The result of low conductivity is high thermal resistance. The insulation layer actively blocks heat from escaping, which provides two major benefits.
First, it dramatically reduces energy consumption and operating costs. Second, it helps maintain a stable and uniform temperature inside the furnace, which is essential for consistent and predictable annealing results.
Beyond the Walls: Other Critical Thermal Components
While the fiber lining provides the primary insulation, other components are crucial for thermal management and maintaining the integrity of the controlled atmosphere.
The Furnace Tube: Quartz or Alumina
Inside the main insulated chamber, a furnace tube often contains the workpiece and the controlled atmosphere. The material for this tube is selected based on the specific process requirements.
Common choices include quartz or alumina. Alumina, for example, offers excellent thermal resistance and chemical stability at very high temperatures, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Sealing Structures for Atmosphere Integrity
An often-overlooked aspect of thermal management is the seal. The furnace door must have a reliable sealing structure to prevent two problems at once: heat loss and atmosphere leakage.
A poor seal allows heat to escape via convection and enables the controlled atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen, argon, or hydrogen) to leak out, compromising the entire annealing process.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Selecting materials for a furnace involves balancing performance, cost, and operational realities. There is no single perfect solution for every application.
Material Performance vs. Cost
High-performance insulation like ceramic fiber offers superior energy savings and thermal control. However, these advanced materials typically have a higher upfront cost compared to traditional refractory bricks. The decision often hinges on balancing initial investment against long-term operational savings.
Durability and Maintenance
While effective, fiber-based insulation can be more susceptible to mechanical damage than dense refractories. Regular inspection and maintenance, including cleaning the furnace interior and checking for any degradation, are necessary to ensure long-term performance.
Chemical Compatibility
The choice of internal components, especially the furnace tube, is dictated by the gases used. The atmosphere, which can range from inert gases like nitrogen and argon to reactive ones like hydrogen, must be chemically compatible with the tube material (quartz or alumina) to prevent degradation at high temperatures.
Applying This to Your Process
Your choice and evaluation of a furnace should be guided by your specific heat treatment goals. The insulation system is a key part of that decision.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Prioritize furnaces with thick, high-quality ceramic or aluminum silicate fiber linings, as this directly impacts operating costs.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability: The quality and material of the furnace tube (e.g., high-purity alumina) and the precision of the temperature control system are as important as the external insulation.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: Scrutinize the quality of the door seals and the atmosphere control system, as leaks are a primary source of inconsistent results.
Ultimately, viewing the furnace's thermal management as an integrated system—from the insulation to the seals to the internal tube—is the key to achieving efficient and reliable performance.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Properties | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Fibers | Low thermal conductivity, lightweight | Reduces energy loss, ensures temperature uniformity |
| Aluminum Silicate Fibers | High thermal resistance, durable | Improves heating/cooling efficiency, lowers operating costs |
| Quartz/Alumina Tubes | Chemical stability, high-temperature resistance | Maintains atmosphere integrity, supports precise annealing |
Ready to optimize your laboratory's heat treatment processes? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored insulation solutions can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance



















