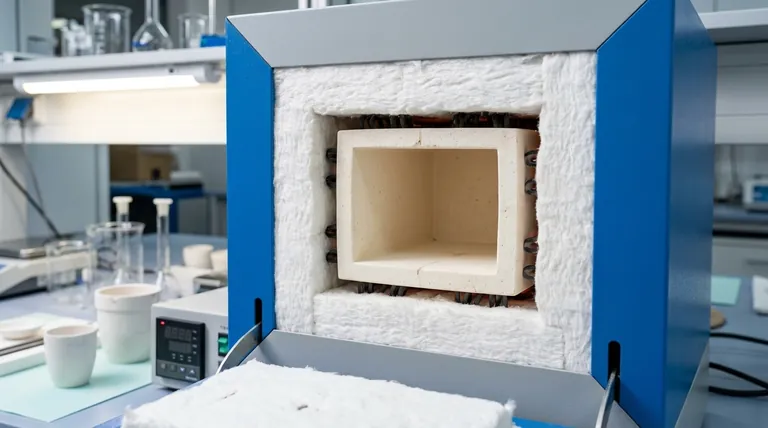
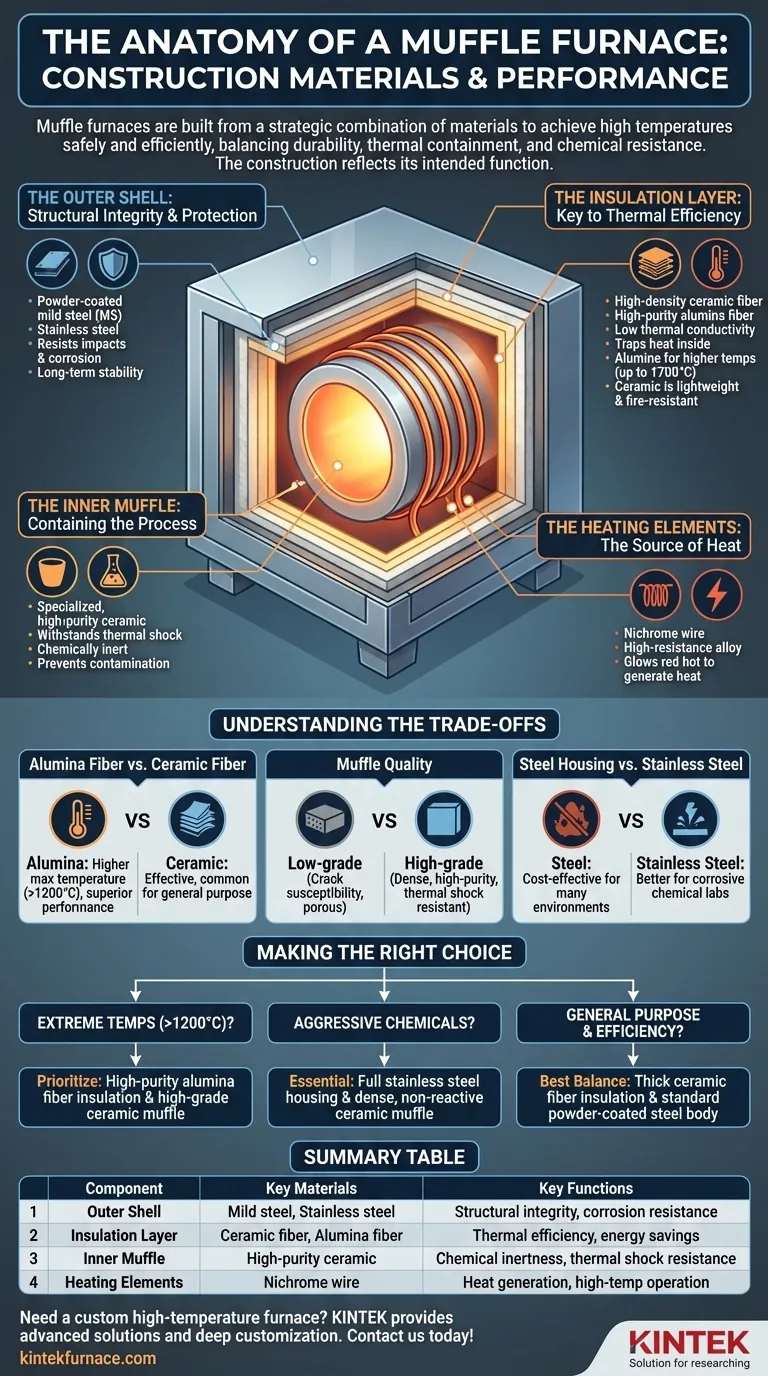
At their core, muffle furnaces are built from a strategic combination of materials chosen for thermal performance and durability. Construction typically involves a protective outer steel body, an advanced insulation layer made of ceramic or alumina fiber, and a high-purity inner chamber designed to contain extreme heat and reactive processes. Each material serves a distinct purpose in achieving high temperatures safely and efficiently.
The material selection in a muffle furnace is a direct reflection of its intended function. The goal is to create a system that expertly balances structural durability, thermal containment, and chemical resistance, with the insulation layer dictating efficiency and the inner muffle defining the purity of the process.

The Anatomy of a Muffle Furnace: A Material-by-Material Breakdown
Understanding how a muffle furnace is built requires looking at it as a system of layers, each with a specific job. The choice of material for each layer directly impacts the furnace's maximum temperature, energy use, and longevity.
The Outer Shell: Structural Integrity and Protection
The outermost layer provides the furnace's structure and protects its delicate internal components.
This shell is typically constructed from powder-coated mild steel (MS) or, for superior durability, stainless steel. This housing resists physical impacts and environmental corrosion, ensuring the furnace's long-term stability.
The Insulation Layer: The Key to Thermal Efficiency
Between the outer shell and the inner chamber lies the most critical material for performance: the insulation. This is often a double-layer structure.
The primary materials used are high-density ceramic fiber or high-purity alumina fiber. Both are exceptional insulators with very low thermal conductivity, which is essential for trapping heat inside the chamber and keeping the outer shell cool.
Alumina fiber is often preferred for higher-temperature applications, as it can withstand up to 1700°C while providing excellent electrical insulation. Ceramic fiber is also highly effective, known for being lightweight and fire-resistant. This layer is the single biggest factor in the furnace's energy efficiency.
The Inner Muffle: Containing the Process
The "muffle" itself is the inner chamber that holds the sample. It serves a crucial dual purpose: it protects the sample from direct contact with the heating elements and protects the heating elements from any aggressive gases or vapors released by the sample.
This chamber is almost always made from a specialized, high-purity ceramic. This material is chosen for its ability to withstand extreme thermal shock and for being chemically inert, which prevents it from reacting with the substances being heated and contaminating the experiment.
The Heating Elements: The Source of the Heat
Wrapped around the outside of the ceramic muffle, within the insulation layer, are the heating elements.
These are commonly made from Nichrome wire, a high-resistance alloy that glows red hot when electricity passes through it. This resistive heating is what generates the furnace's extreme temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Not all muffle furnaces are created equal, and the differences often come down to the quality and type of materials used. Recognizing these distinctions is key to evaluating a unit's performance.
Alumina Fiber vs. Ceramic Fiber Insulation
While both are excellent insulators, alumina fiber generally offers a higher maximum service temperature and superior performance in the most demanding applications. A furnace built with alumina fiber is engineered for work consistently pushing above 1200°C. Standard ceramic fiber is a highly effective and more common choice for general-purpose work.
The Importance of Muffle Quality
A low-grade ceramic muffle is susceptible to cracking under rapid temperature changes (thermal shock). It may also be more porous, potentially absorbing or reacting with materials, which can compromise the purity of your results. A dense, high-purity muffle is a hallmark of a high-quality furnace.
Steel Housing vs. Stainless Steel
A powder-coated steel body is perfectly adequate for many environments and is a cost-effective choice. However, in laboratories where corrosive chemicals are frequently used, a stainless steel housing provides significantly better long-term protection against rust and degradation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific application should guide your evaluation of a furnace's construction materials.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperatures (above 1200°C): Prioritize a furnace with high-purity alumina fiber insulation and a robust, high-grade ceramic muffle.
- If your primary focus is working with aggressive chemicals: A furnace with a full stainless steel housing and a dense, non-reactive ceramic muffle is essential.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating and energy efficiency: A well-built unit with thick ceramic fiber insulation and a standard powder-coated steel body offers the best balance of performance and value.
Ultimately, understanding these core materials empowers you to select a furnace that will perform reliably and deliver the accurate results your work depends on.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Materials | Key Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Shell | Powder-coated mild steel, Stainless steel | Structural integrity, corrosion resistance |
| Insulation Layer | Ceramic fiber, Alumina fiber | Thermal efficiency, energy savings |
| Inner Muffle | High-purity ceramic | Chemical inertness, thermal shock resistance |
| Heating Elements | Nichrome wire | Heat generation, high-temperature operation |
Need a custom high-temperature furnace for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for enhanced performance and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















