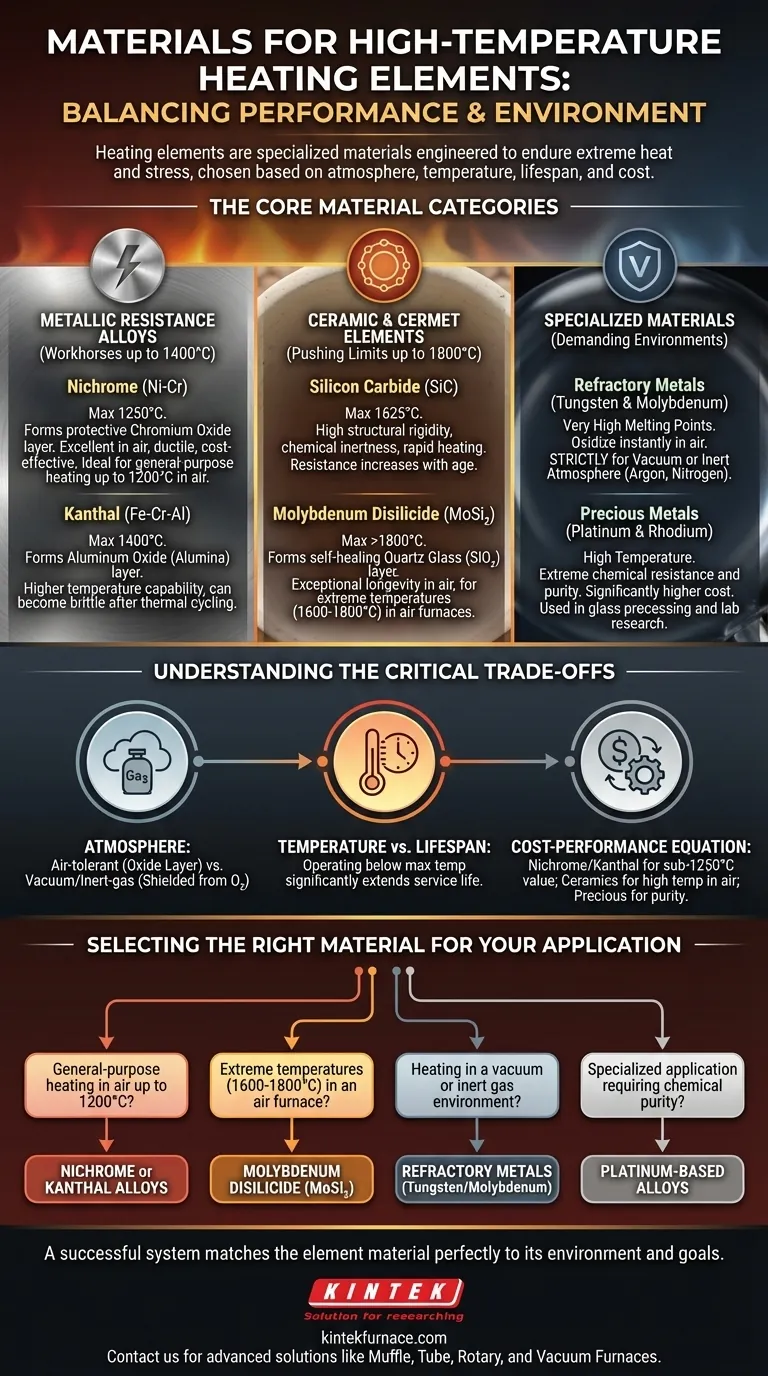
In high-temperature applications, heating elements are not made from common conductors but from specialized materials engineered to endure extreme heat and stress. These materials primarily fall into three categories: metallic resistance alloys like Nichrome and Kanthal, advanced ceramics like silicon carbide, and refractory metals like tungsten, each chosen for a unique combination of heat resistance, durability, and environmental stability.
The selection of a heating element material is not about finding the single "best" option. It is a precise engineering decision that balances the maximum required temperature against the operating atmosphere, lifespan, and overall system cost.
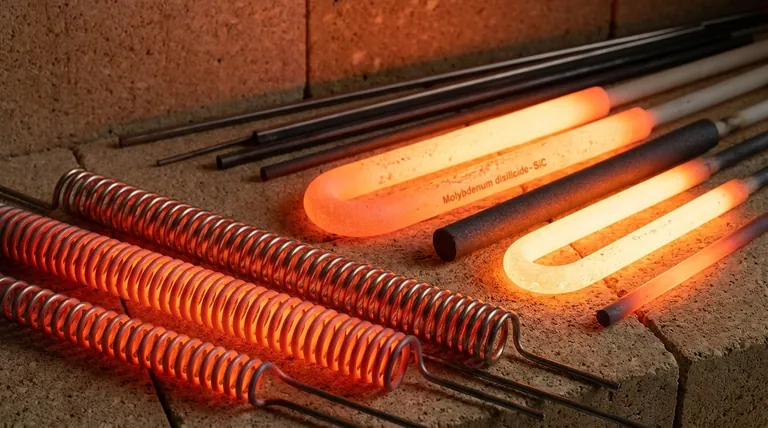

The Workhorses: Metallic Resistance Alloys
Metallic alloys are the most common choice for industrial and commercial heating up to approximately 1250°C (2280°F). They offer an excellent balance of performance, workability, and cost.
Nickel-Chromium (Nichrome)
Nichrome, typically an alloy of 80% nickel and 20% chromium, is often considered the industry standard. Its key strength is the formation of a protective, adherent outer layer of chromium oxide when heated.
This oxide layer prevents the material underneath from oxidizing further, giving Nichrome excellent performance and a long lifespan in air. It is also highly ductile and easy to form into coils.
Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (Kanthal)
Kanthal (a brand name for Fe-Cr-Al alloys) is a leading alternative to Nichrome, capable of reaching even higher temperatures, sometimes up to 1400°C (2550°F).
Instead of a chromium oxide layer, Fe-Cr-Al forms an aluminum oxide (alumina) layer. This layer provides superior protection at higher temperatures but can make the material more brittle after thermal cycling compared to Nichrome.
Pushing the Limits: Ceramic and Cermet Elements
For temperatures beyond the capabilities of metallic alloys, ceramic-based elements are required. These materials can operate reliably in air at temperatures where even the best alloys would fail.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂)
MoSi₂ is a ceramic-metallic composite (cermet) used for the most demanding high-temperature air furnaces, capable of operating above 1800°C (3270°F).
When heated, it forms a protective quartz glass (silicon dioxide) layer on its surface. This layer is self-healing; if it cracks, the underlying material re-oxidizes to seal the gap, providing exceptional element longevity.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon Carbide elements are known for their high structural rigidity and chemical inertness, allowing them to be used in various processes without contaminating the product.
They can operate at very high temperatures (up to 1625°C / 2957°F) and have high thermal conductivity, allowing for rapid heating. However, their electrical resistance tends to increase with age, which must be accounted for in the power supply design.
Specialized Materials for Demanding Environments
Some applications have unique constraints, such as the absence of oxygen or the need for extreme purity, which requires another class of materials.
Refractory Metals (Tungsten & Molybdenum)
Tungsten and Molybdenum have exceptionally high melting points but will oxidize and fail almost instantly if heated in the presence of air.
Their use is therefore strictly limited to vacuum furnaces or those with a controlled inert atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen). In these environments, they provide stable and reliable high-temperature heating.
Precious Metals (Platinum & Rhodium)
Platinum and its alloys with rhodium are used in highly specialized applications, such as in the glass industry or laboratory research.
Their primary advantage is extreme chemical resistance and stability, which prevents contamination of the material being heated. This performance comes at a significantly higher cost, limiting their use to applications where purity is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong material is a common and costly mistake. The decision hinges on three factors: atmosphere, temperature, and cost.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
This is the most important factor. Using a material like tungsten in an air furnace will lead to immediate failure.
Air-tolerant materials like Nichrome, Kanthal, SiC, and MoSi₂ are designed to form a protective oxide layer. Vacuum/inert-gas materials like Tungsten and Molybdenum lack this ability and must be shielded from oxygen.
Balancing Temperature vs. Lifespan
Every heating element has a maximum recommended operating temperature. However, running an element consistently at its absolute peak temperature will dramatically shorten its service life.
For optimal lifespan and reliability, it is best practice to select a material whose maximum temperature is significantly higher than your intended operating temperature.
The Cost-Performance Equation
Cost often dictates the final choice. Nichrome and Kanthal offer the best performance for their cost in the sub-1250°C range.
Ceramic elements like SiC and MoSi₂ represent a higher initial investment but are necessary for achieving higher temperatures in air. Precious metals and refractory metals are reserved for applications where their unique properties are non-negotiable.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Use your primary goal to guide your selection.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating in air up to 1200°C: Nichrome or Kanthal alloys are your most reliable and cost-effective choices.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (1600-1800°C) in an air furnace: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) is the superior material due to its self-healing properties.
- If your primary focus is heating in a vacuum or inert gas environment: Refractory metals like Tungsten or Molybdenum are necessary to prevent oxidative failure.
- If your primary focus is a specialized application requiring chemical purity, like glass processing: Platinum-based alloys are the standard, despite their high cost.
Ultimately, a successful high-temperature system is defined by selecting the element material that is perfectly matched to its operating environment and performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Materials | Max Temperature (°C) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic Alloys | Nichrome, Kanthal | Up to 1400 | Good oxidation resistance, cost-effective, ductile |
| Ceramics/Cermets | SiC, MoSi₂ | Up to 1800 | High temp in air, self-healing, rigid |
| Refractory Metals | Tungsten, Molybdenum | Very high | For vacuum/inert gas, high melting point |
| Precious Metals | Platinum, Rhodium | High | Extreme purity, chemical resistance |
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processes? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet the unique requirements of diverse laboratories. Contact us today to discuss how our heating elements can enhance your efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















