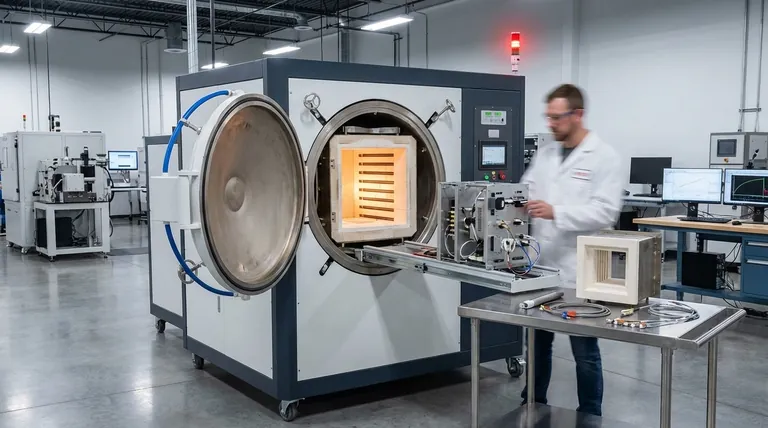
At their core, customized vacuum furnaces are explicitly designed for long-term operational viability through simplified maintenance and planned upgrade paths. Unlike off-the-shelf models, a custom furnace is built with future servicing and adaptation in mind, allowing it to evolve with your production demands rather than becoming a technological dead end.
The decision to customize a vacuum furnace is not just about meeting today's specific process requirements. It is a strategic investment in reducing long-term operational costs, minimizing downtime, and future-proofing your capital equipment against evolving technological and production needs.

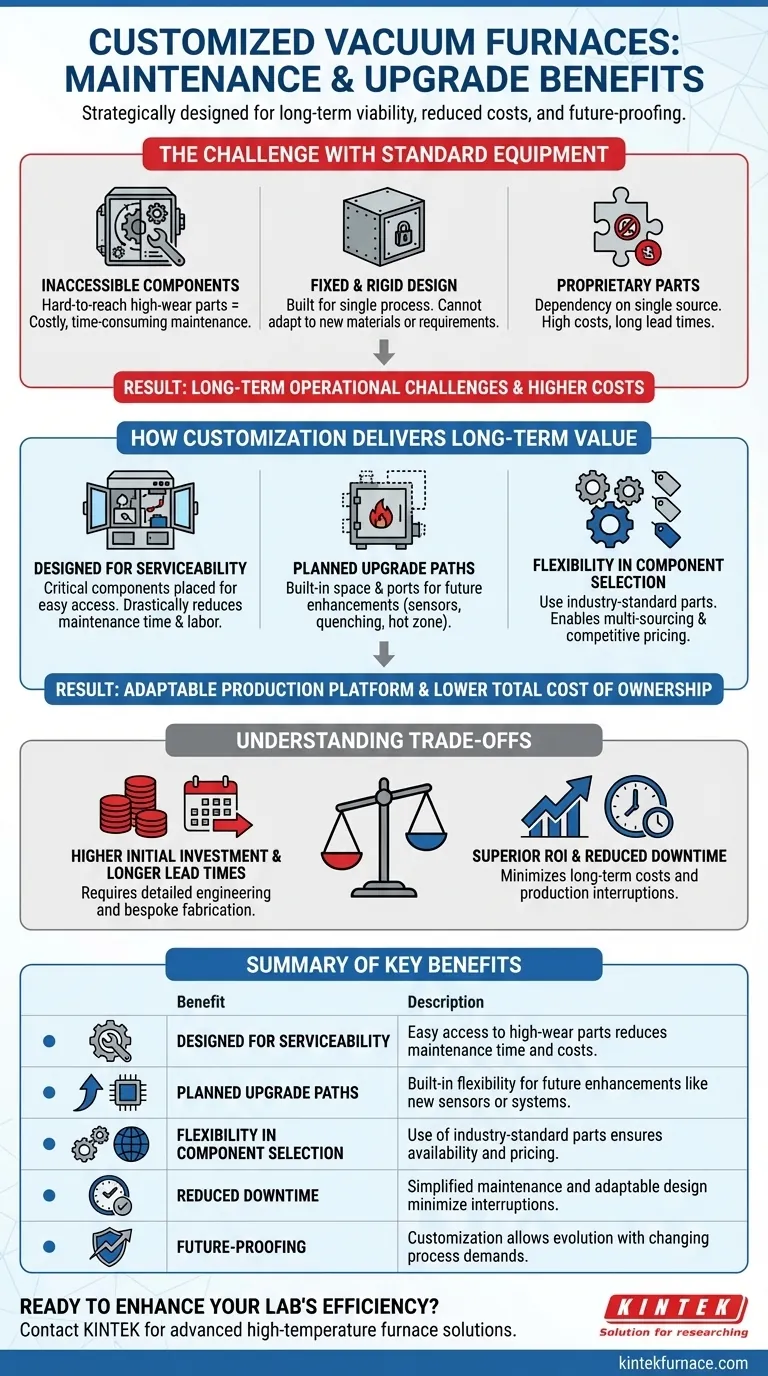
The Challenge with Standard Equipment
Standard, mass-produced furnaces are designed to meet a common denominator of needs at a competitive price point. This design philosophy often creates long-term challenges in maintenance and adaptability.
Inaccessible Core Components
Many standard furnaces prioritize a compact footprint over serviceability. This can place high-wear components like heating elements, vacuum pumps, or thermocouple assemblies in locations that are difficult to access, turning routine maintenance into a costly, time-consuming project.
Fixed and Rigid Design
An off-the-shelf furnace is built for a single, defined process. Its chamber size, port configuration, power supply, and quenching system are fixed. If your material requirements change or you need to adopt a new process, the equipment often cannot adapt, forcing a new capital expenditure.
The "Proprietary Parts" Problem
Some manufacturers of standard equipment use proprietary components that can only be sourced from them. This can lead to high replacement costs, long lead times, and a dependency that puts your production schedule at risk if a single part becomes unavailable.
How Customization Delivers Long-Term Value
A custom design process allows you to address serviceability and future needs from the very beginning. This transforms the furnace from a static piece of equipment into an adaptable production platform.
Designed for Serviceability
During the design phase, you can specify that critical, high-wear components be placed in easily accessible locations. This simple directive drastically reduces the time and labor required for inspections, cleaning, and replacement, directly lowering your operational costs and minimizing downtime.
Planned Upgrade Paths
A key advantage of customization is building for the future. The furnace can be designed with additional space, spare ports, or an overrated power supply to accommodate future enhancements. This makes it feasible to add advanced sensors, introduce a more rapid gas quenching system, or even swap out the entire hot zone years down the line.
Flexibility in Component Selection
With a custom build, you have the authority to request the use of industry-standard, non-proprietary components for items like pumps, valves, and controllers. This ensures you can source spare parts from multiple suppliers, promoting competitive pricing and ensuring parts availability for the life of the furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the long-term benefits are significant, a custom approach requires acknowledging certain realities. Objectivity is crucial when making a major capital investment.
Higher Initial Investment
Customization is a more intensive process involving detailed engineering and bespoke fabrication. This naturally results in a higher upfront cost compared to purchasing a standard, in-stock furnace.
Longer Lead Times
Building a furnace to your exact specifications takes time. The design, approval, sourcing, and manufacturing process for a custom unit is significantly longer than for an off-the-shelf model. This requires more advanced planning.
Dependency on the Builder for Major Upgrades
While you can specify standard parts for maintenance, the furnace's core design DNA belongs to the original builder. For major structural upgrades or complex system integrations, you will likely need to re-engage them, creating a long-term technical relationship.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Choosing between a standard and custom furnace depends entirely on your operational strategy and long-term goals.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible upfront cost for a stable, unchanging process: A standard furnace is likely the most pragmatic choice.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term operational costs and production downtime: A custom furnace designed for ease of maintenance will deliver a superior return on investment.
- If your primary focus is adaptability and future-proofing your investment against new materials or evolving process demands: A custom furnace with built-in upgrade paths is the only way to ensure long-term viability.
Ultimately, investing in a custom furnace is a decision to control the total cost of ownership over the entire lifecycle of the equipment.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Designed for Serviceability | Easy access to high-wear components reduces maintenance time and costs. |
| Planned Upgrade Paths | Built-in flexibility for future enhancements like new sensors or quenching systems. |
| Flexibility in Component Selection | Use of industry-standard parts ensures availability and competitive pricing. |
| Reduced Downtime | Simplified maintenance and adaptable design minimize production interruptions. |
| Future-Proofing | Customization allows the furnace to evolve with changing process demands. |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with a custom vacuum furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, reducing long-term costs and downtime. Contact us today to discuss how we can future-proof your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today



















