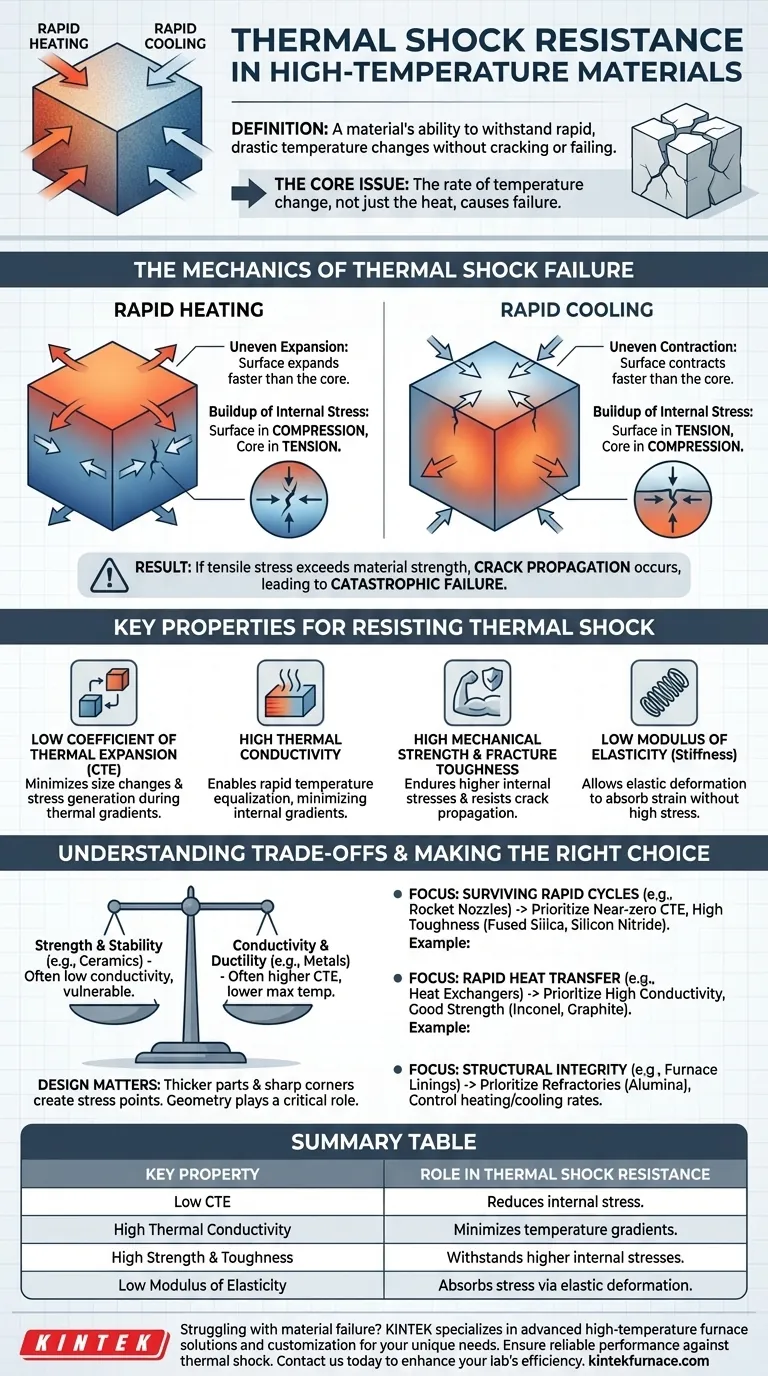
Thermal shock resistance is a material's ability to withstand rapid, drastic changes in temperature without cracking, fracturing, or otherwise failing. This property is critically important for materials used in high-temperature environments because uneven heating or cooling creates powerful internal mechanical stresses that can easily exceed a material's strength, leading to catastrophic failure.
The core issue is not simply heat, but the rate of temperature change. A material fails from thermal shock when one part of it tries to expand or contract much faster than another part, creating internal forces that literally tear it apart.
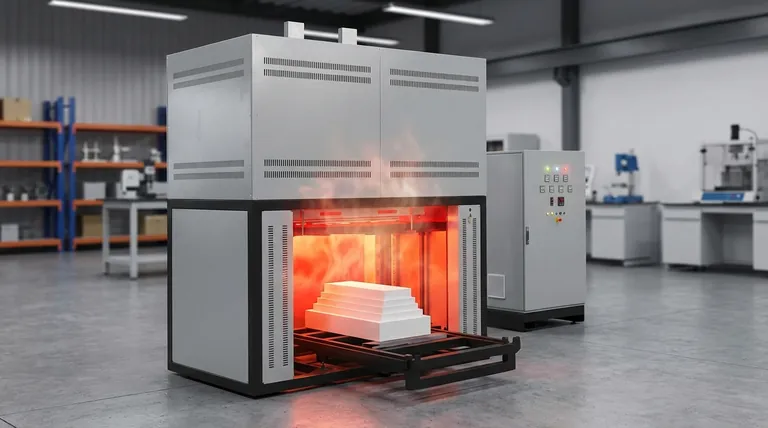

The Mechanics of Thermal Shock Failure
To understand why thermal shock resistance matters, you must first understand the physics of the failure it prevents. The process is a direct result of a material's physical properties interacting under thermal stress.
Uneven Expansion and Contraction
When an object is heated or cooled rapidly, its surface temperature changes much faster than its internal or "core" temperature.
Because materials expand when heated and contract when cooled, the surface layer tries to change its size while the core has not yet caught up.
The Buildup of Internal Stress
This difference in expansion or contraction between the surface and the core creates powerful internal forces.
During rapid heating, the expanding surface is constrained by the cool, unexpanded core, putting the surface in compression and the core in tension. During rapid cooling, the contracting surface pulls on the hot, expanded core, putting the surface in tension.
From Stress to Fracture
Most brittle materials, like ceramics, are far weaker in tension than in compression. If the tensile stress generated during rapid cooling (or from the core during heating) exceeds the material's inherent strength, a crack will form and propagate, leading to failure.
Key Properties for Resisting Thermal Shock
A material's resistance to thermal shock is not a single value but an outcome of several interconnected physical properties. Improving these factors increases a material's durability against thermal cycling.
Low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE)
This is arguably the most important factor. A material with a low CTE expands and contracts very little with temperature changes. This directly reduces the amount of strain and subsequent stress generated during a thermal gradient.
High Thermal Conductivity
A material with high thermal conductivity can transfer heat quickly and efficiently. This allows the temperature to equalize more rapidly throughout the object, minimizing the temperature difference between the surface and the core and thus reducing stress.
High Mechanical Strength and Fracture Toughness
A material that is inherently strong (high tensile strength) and resistant to crack propagation (high fracture toughness) can simply endure higher levels of internal stress before it fails.
Low Modulus of Elasticity
The Modulus of Elasticity measures a material's stiffness. A material with a lower modulus is more "flexible" and can accommodate some internal strain by deforming elastically without generating as much stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material for a high-temperature application is an exercise in balancing competing properties. There is no single "perfect" material for all situations.
No Single Solution
Materials with the best high-temperature stability, like many advanced ceramics, often have low thermal conductivity, making them inherently vulnerable to thermal shock despite their ability to withstand the heat itself.
Strength vs. Conductivity
Metals typically have excellent thermal conductivity and ductility (which helps absorb stress), but they often have higher CTEs and lower maximum operating temperatures compared to ceramics.
The Critical Role of Geometry
Thermal shock resistance isn't solely a material property; it is also heavily influenced by the component's design. Thicker parts and sharp internal corners create higher stress concentrations and are far more susceptible to failure than thin sections and rounded edges.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right material requires analyzing your specific operational demands and prioritizing the most critical properties.
- If your primary focus is surviving extreme and rapid temperature cycles (e.g., rocket nozzles, ceramic brake discs): Prioritize materials with a near-zero coefficient of thermal expansion and high fracture toughness, such as fused silica or certain silicon nitride ceramics.
- If your primary focus is rapid heat transfer under cyclic conditions (e.g., heat exchangers, welding jigs): Prioritize materials with high thermal conductivity and good strength, such as specific metal alloys (like Inconel) or graphite.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity under slow, predictable thermal changes (e.g., furnace linings): You can often use materials like alumina or other refractories, but you must control the rate of heating and cooling to stay within their thermal shock limits.
Ultimately, designing for thermal shock is a systems-level challenge that requires a deep understanding of both material science and mechanical engineering principles.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Role in Thermal Shock Resistance |
|---|---|
| Low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) | Reduces internal stress from temperature changes |
| High Thermal Conductivity | Minimizes temperature gradients and stress buildup |
| High Mechanical Strength and Fracture Toughness | Withstands higher internal stresses without failure |
| Low Modulus of Elasticity | Allows elastic deformation to absorb stress |
Struggling with material failure in high-temperature environments? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs, ensuring your materials withstand thermal shock and perform reliably. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and durability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do repeat sintering processes and specialized sintering molds address the technical challenges of manufacturing oversized flywheel rotor components? Expand Scale and Integrity
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the conversion of S-1@TiO2? Achieve Precision Calcination of Nanospheres
- Why are precision stirring and drying equipment necessary for photocatalytic materials? Master Microstructure Control
- What is the primary role of a muffle furnace in the annealing process of AlCrTiVNbx alloys? Enhance Alloy Strength
- What role does a muffle furnace play in g-C3N4 synthesis? Mastering Thermal Polycondensation for Semiconductors



















