The effective operating range for DM Type Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements is between 1200°C and 1400°C. This specific window is where the material provides the best balance of thermal efficiency, structural integrity, and operational lifespan. Operating outside this range can significantly compromise performance and lead to premature failure.
Understanding the 1200-1400°C range is not about knowing a simple limit; it's about recognizing the optimal performance window dictated by the element's material science and physical design. Respecting this window is critical for both efficiency and longevity.
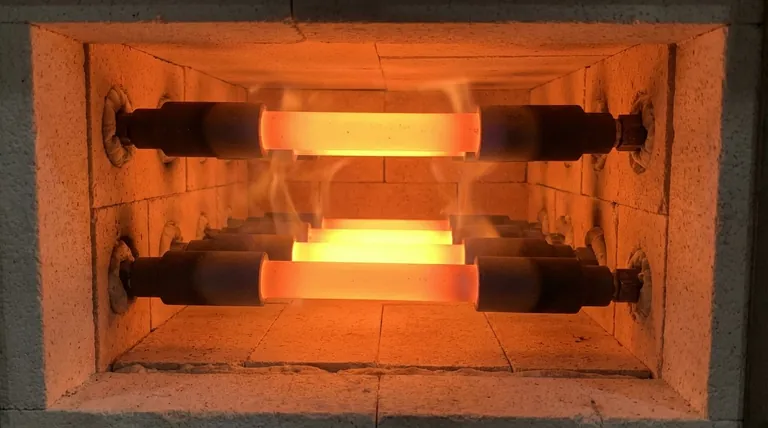
Why This Specific Temperature Range?
The specified operating range is a direct result of the fundamental properties of silicon carbide. It is not an arbitrary number but a carefully defined window for optimal function.
The Material: Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon carbide is a high-performance ceramic known for its exceptional strength and stability at very high temperatures. Its high density (3.2 g/cm³) and extreme hardness (9.5 Mohs) allow it to withstand the harsh conditions inside an industrial furnace.
However, its electrical and physical behaviors change dramatically with temperature, dictating its ideal operating conditions.
Below 1200°C: The Risk of Increased Oxidation
While the elements can function at lower temperatures, prolonged operation below 1200°C is not recommended. At these "cooler" high temperatures, a form of oxidation can occur that gradually degrades the material and increases its electrical resistance at an accelerated rate, shortening its useful life.
Above 1400°C: The Point of Accelerated Aging
Exceeding the 1400°C maximum temperature subjects the silicon carbide to thermal stress that significantly accelerates material degradation. This drastically shortens the element's lifespan and increases the risk of mechanical failure.
Understanding the DM Type Design
The "DM Type" designation refers to a specific physical construction that is optimized for furnace applications. Each feature serves a distinct purpose.
The Hollow Tube: Efficient Heat Radiation
The main body of the element is a hollow tube. This design maximizes the surface area, allowing it to radiate heat uniformly and efficiently into the furnace chamber. This is crucial for applications like ceramic firing and metal treatment where even heating is paramount.
The Thickened Ends: Cool and Safe Connections
The element features thickened solid ends, often called "cold ends." These ends have a larger cross-sectional area, which lowers their electrical resistance compared to the hollow "hot zone."
As a result, the ends remain significantly cooler. This design allows the element to pass through the furnace wall insulation and connect to the electrical supply without overheating the terminals or the furnace structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, SiC elements have specific characteristics that users must manage to ensure reliable operation.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
The same hardness that makes SiC durable at high temperatures also makes it very brittle at room temperature. The elements must be handled with extreme care during shipping, storage, and installation. Mechanical shock or impact can easily cause a fracture.
Resistance Increase Over Time
All silicon carbide heating elements age, and a key characteristic of this aging is a gradual increase in electrical resistance. Your power supply system must be able to compensate for this change by delivering increased voltage over time to maintain the desired power output and temperature.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
The atmosphere inside the furnace can impact the element's lifespan. While robust, certain chemical vapors or highly reducing atmospheres can react with the silicon carbide and accelerate its degradation, even when operating within the correct temperature range.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Choosing and using these elements correctly requires matching their properties to your specific operational goals.
- If your primary focus is metal heat treatment or ceramic production: Strictly maintain your process temperature within the 1200-1400°C window to ensure maximum element life and consistent heating.
- If your primary focus is semiconductor manufacturing: Precise temperature control is paramount, so plan for a power control system that can adjust for the element's natural change in resistance over its life.
- If you are installing or replacing elements: Always remember their fragility at ambient temperatures and handle them carefully to prevent breakage before they are ever used.
By understanding these principles, you can leverage the unique properties of DM Type SiC elements to achieve stable and efficient high-temperature processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Optimal Temperature Range | 1200°C to 1400°C |
| Material | Silicon Carbide (SiC) |
| Key Design | Hollow tube for heat radiation, thickened cold ends |
| Key Considerations | Brittle at room temperature, resistance increases over time, sensitive to atmospheres |
| Applications | Metal heat treatment, ceramic production, semiconductor manufacturing |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise fit for your unique experimental needs, such as optimizing DM Type SiC heating elements for superior performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















