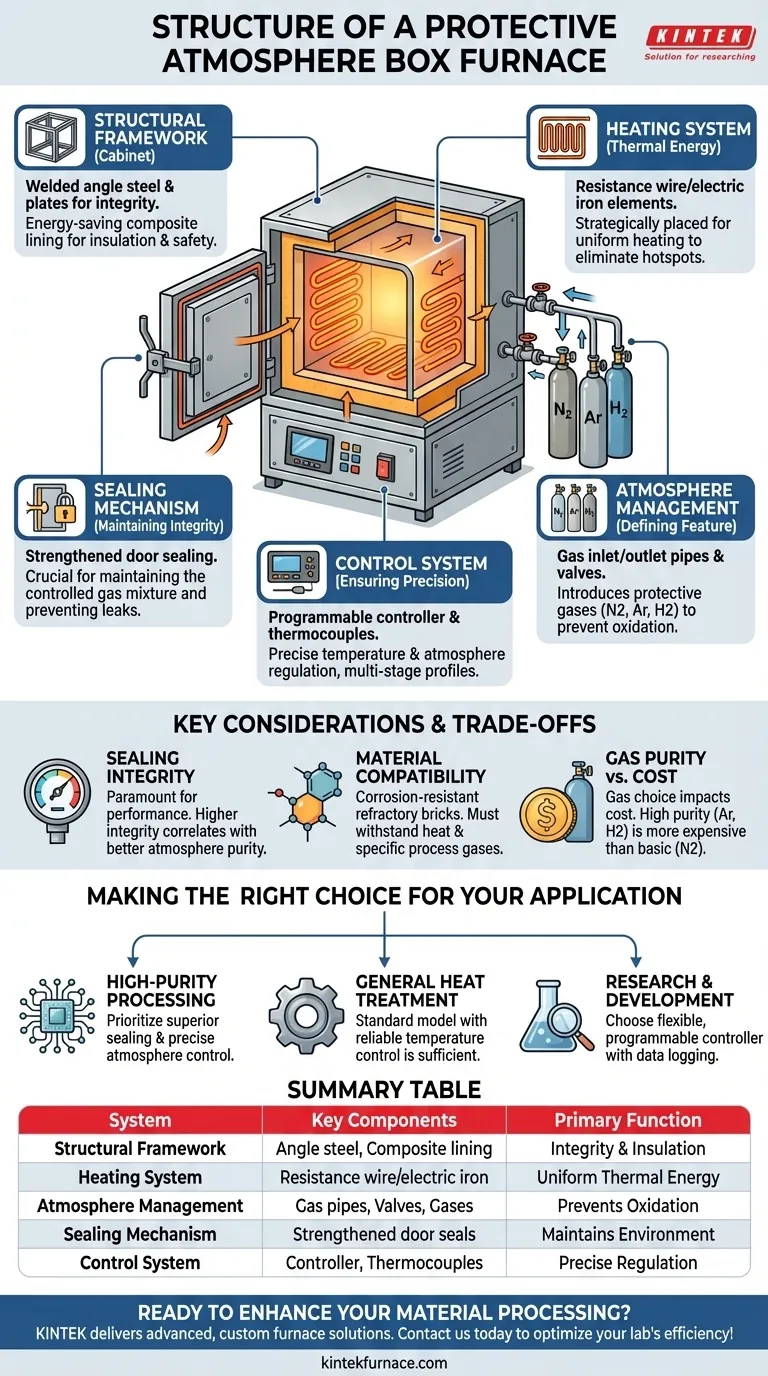
At its core, a protective atmosphere box furnace is a sealed, high-temperature chamber designed around five primary systems. These are the structural framework or cabinet, an internal heating system, a sophisticated temperature control system, a dedicated atmosphere management system for handling gases, and robust sealing mechanisms to maintain the controlled environment.
A protective atmosphere box furnace is more than just a hot box; it is an integrated system where every component serves one of two critical functions: generating precise heat or meticulously managing the internal gas environment to prevent oxidation and contamination. The integrity of the atmospheric seal is just as important as the accuracy of the heating elements.

The Core Systems of an Atmosphere Furnace
To understand the furnace's structure, it's best to think of it as a collection of interdependent systems working together to create a highly controlled processing environment. Each system has a distinct role.
The Structural Framework (The Cabinet)
The outer body, or cabinet, is typically welded from angle steel and steel plates, providing the furnace's structural integrity.
This external shell houses an energy-saving composite lining. This lining consists of high-temperature insulation materials that minimize heat loss, improve energy efficiency, and ensure the outer surface remains safe for operators.
The Heating System (Generating Thermal Energy)
Inside the chamber, heating elements—often made of resistance wire or electric iron—generate the required heat.
These elements are strategically placed to ensure uniform heating throughout the chamber, which is critical for consistent material processing. The goal is to eliminate hot or cold spots that could compromise the final product.
The Atmosphere Management System (The Defining Feature)
This system is what differentiates an atmosphere furnace from a standard one. It includes gas inlet and outlet pipes with precision valves.
These allow for the introduction of specific protective atmospheres, such as inert gases (nitrogen, argon) or reducing gases (hydrogen), to prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation. The system also allows for purging the ambient air before the heating cycle begins.
The Sealing Mechanism (Maintaining Integrity)
A protective atmosphere is useless if it can leak out or if oxygen can leak in. Therefore, the furnace features strengthened door sealing.
This is one of the most critical structural aspects. A high-integrity seal ensures the carefully controlled gas mixture inside the chamber is maintained throughout the entire heating and cooling process.
The Control System (Ensuring Precision)
The brain of the furnace is its temperature and atmosphere control system. This consists of thermocouples to measure the internal temperature and a programmable controller.
Modern systems allow for precise, multi-stage heating profiles. They also integrate with the atmosphere management system to regulate gas flow and mixtures, ensuring the process is both accurate and repeatable. Safety interlocks are often included to prevent operation under unsafe conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
Specifying or operating an atmosphere furnace requires understanding the inherent design trade-offs that impact performance and cost.
Sealing Integrity is Paramount
A minor leak in a door seal or gas fitting can defeat the entire purpose of the furnace. The cost and complexity of the sealing mechanism often correlate directly with the purity of the atmosphere that can be maintained.
Material Compatibility
The internal furnace lining, typically made of special corrosion-resistant refractory bricks, must be chosen carefully. It must not only withstand extreme heat but also resist chemical attack from the protective gases used, especially at high temperatures.
Gas Purity vs. Cost
The type of gas used has significant cost implications. While nitrogen is a common and relatively inexpensive choice for preventing basic oxidation, high-purity processes may require more expensive argon or reactive hydrogen, which also brings additional safety requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace structure depends entirely on your specific material processing goals.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing (e.g., for sensitive electronics or medical alloys): You must prioritize a furnace with superior sealing integrity and a highly precise atmosphere control system.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment (e.g., annealing or sintering non-critical parts): A standard model with reliable temperature control and basic atmosphere management will likely suffice.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Choose a furnace with a flexible, programmable controller and data logging capabilities to ensure process repeatability and analysis.
Understanding this structure empowers you to select the right tool to protect your materials and achieve your desired results.
Summary Table:
| System | Key Components | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Framework | Angle steel cabinet, composite lining | Provides integrity and insulation |
| Heating System | Resistance wire/electric iron elements | Generates uniform thermal energy |
| Atmosphere Management | Gas pipes, valves, inert/reducing gases | Prevents oxidation and contamination |
| Sealing Mechanism | Strengthened door seals | Maintains controlled gas environment |
| Control System | Programmable controller, thermocouples | Ensures precise temperature and atmosphere regulation |
Ready to enhance your material processing with a custom protective atmosphere furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to deliver advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs—whether for high-purity applications, general heat treatment, or R&D. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.



















