In industrial heating, the significance of high power density in silicon carbide (SiC) elements is their ability to deliver a massive amount of heat from a minimal physical footprint. This core characteristic allows for the design of smaller, more responsive, and more energy-efficient furnaces. It is the key factor that enables faster production cycles and higher throughput in demanding thermal processes.
High power density is not merely a technical specification; it is the enabler of process intensification. It translates directly into smaller equipment, faster heating cycles, and greater operational efficiency, solving the core industrial challenges of space, time, and energy consumption.

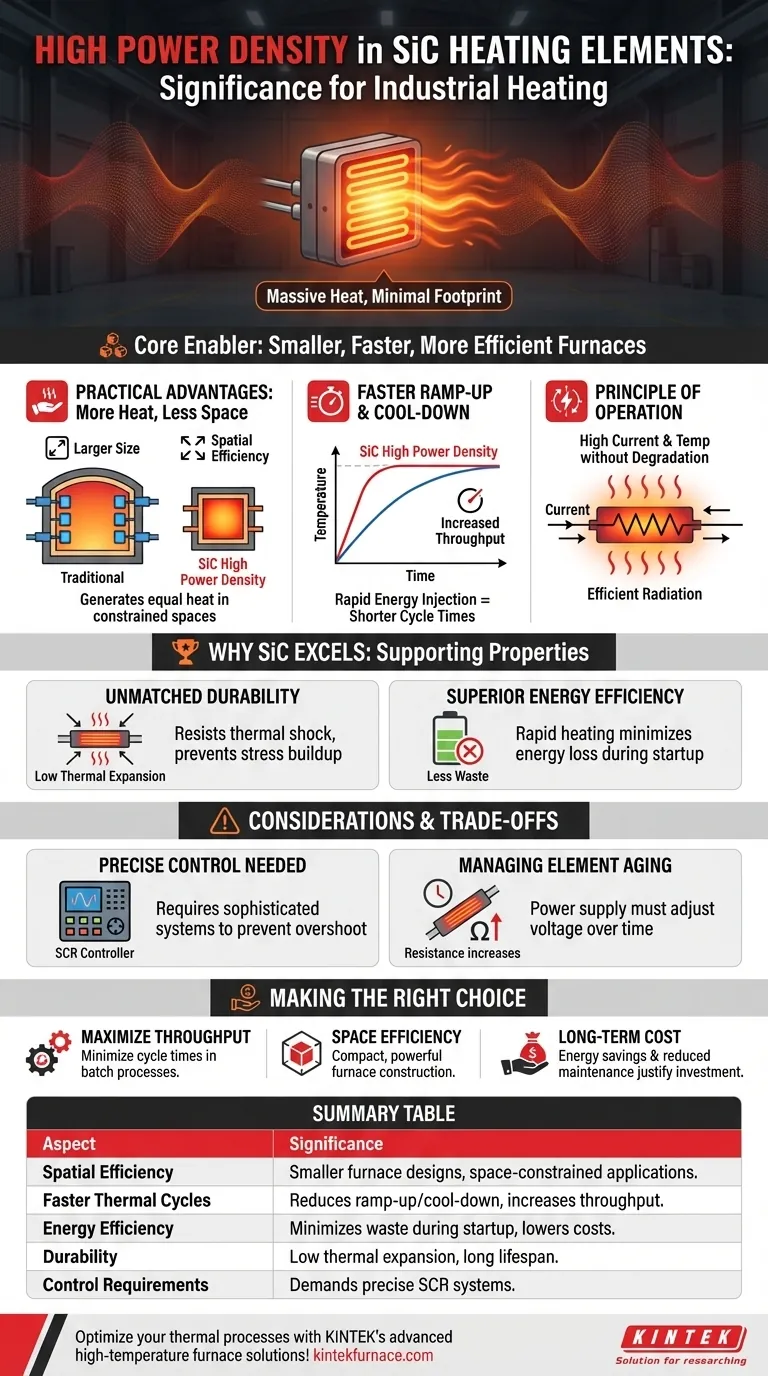
What High Power Density Means in Practice
High power density refers to the amount of thermal energy (watts) that an element can emit per unit of its surface area (cm² or in²). For SiC, this value is exceptionally high, leading to tangible operational advantages.
More Heat, Less Space
The most direct benefit is spatial efficiency. A high power density element can generate the same amount of heat as a much larger, lower-density element, or multiple smaller ones.
This is critical in applications where furnace dimensions are restricted or when retrofitting a furnace to increase its heating capacity without changing its size.
Faster Ramp-Up and Cool-Down Times
High power density allows for a rapid injection of energy into the furnace chamber. This significantly shortens the time required to reach the target process temperature.
For industries that rely on batch processing, such as in heat treatment, these faster thermal cycles directly translate to increased throughput and productivity.
The Principle of Operation
SiC elements function by passing an electrical current through the material, which generates heat due to its inherent electrical resistance.
High power density signifies that the material can withstand a very high current and temperature in a compact form without degrading, efficiently radiating this intense heat to the workpiece.
The Broader Context: Why SiC Excels in Demanding Environments
Power density is the headline feature, but it is supported by other intrinsic properties of silicon carbide that make it a uniquely robust solution.
Unmatched Durability
Silicon carbide has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it does not expand or contract significantly when its temperature changes.
This stability prevents the buildup of internal mechanical stress during the rapid heating and cooling cycles enabled by its high power density, dramatically enhancing its durability and lifespan.
Superior Energy Efficiency
The ability to heat up quickly means less energy is wasted during non-productive startup phases.
By delivering heat rapidly and precisely, SiC elements ensure that energy is consumed for the process itself, not for slowly bringing a massive thermal system up to temperature, which is a common issue with lower-density elements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly advantageous, leveraging high power density requires a well-engineered system. It is not a "drop-in" solution without considering the implications.
The Need for Precise Control
The ability to inject heat quickly also creates the risk of overshooting the target temperature. A system with high power density demands a sophisticated control system.
Simple on/off controllers are often inadequate. Proportional control using Silicon Controlled Rectifiers (SCRs) is typically necessary to precisely manage the power output and ensure process stability.
Managing Element Aging
Like all high-temperature elements, SiC elements age, causing their electrical resistance to gradually increase over time.
To maintain constant power output (and thus consistent heating), the power supply must be able to compensate by increasing the voltage. This often requires a multi-tap transformer or a voltage-adjusting power controller, which must be factored into the initial system design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a heating strategy depends entirely on your operational priorities. High power density is not always necessary, but it is transformative when applied to the right problem.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: The high power density of SiC is ideal for minimizing cycle times in batch processes where every minute saved increases output.
- If your primary focus is space efficiency: SiC allows for more compact and powerful furnace construction, solving challenges related to facility footprint or equipment size limitations.
- If your primary focus is long-term operational cost: SiC's combination of rapid heating and durability offers significant energy savings and reduced maintenance that often justifies a higher initial investment.
By understanding power density, you move from simply choosing a component to designing a more efficient and productive heating process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Significance |
|---|---|
| Spatial Efficiency | Enables smaller furnace designs, ideal for space-constrained applications. |
| Faster Thermal Cycles | Reduces ramp-up and cool-down times, increasing throughput in batch processes. |
| Energy Efficiency | Minimizes energy waste during startup, lowering operational costs. |
| Durability | Low thermal expansion ensures long lifespan under rapid temperature changes. |
| Control Requirements | Demands precise systems like SCR controllers to prevent overshooting. |
Optimize your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable heating systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance efficiency, save space, and boost productivity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions



















