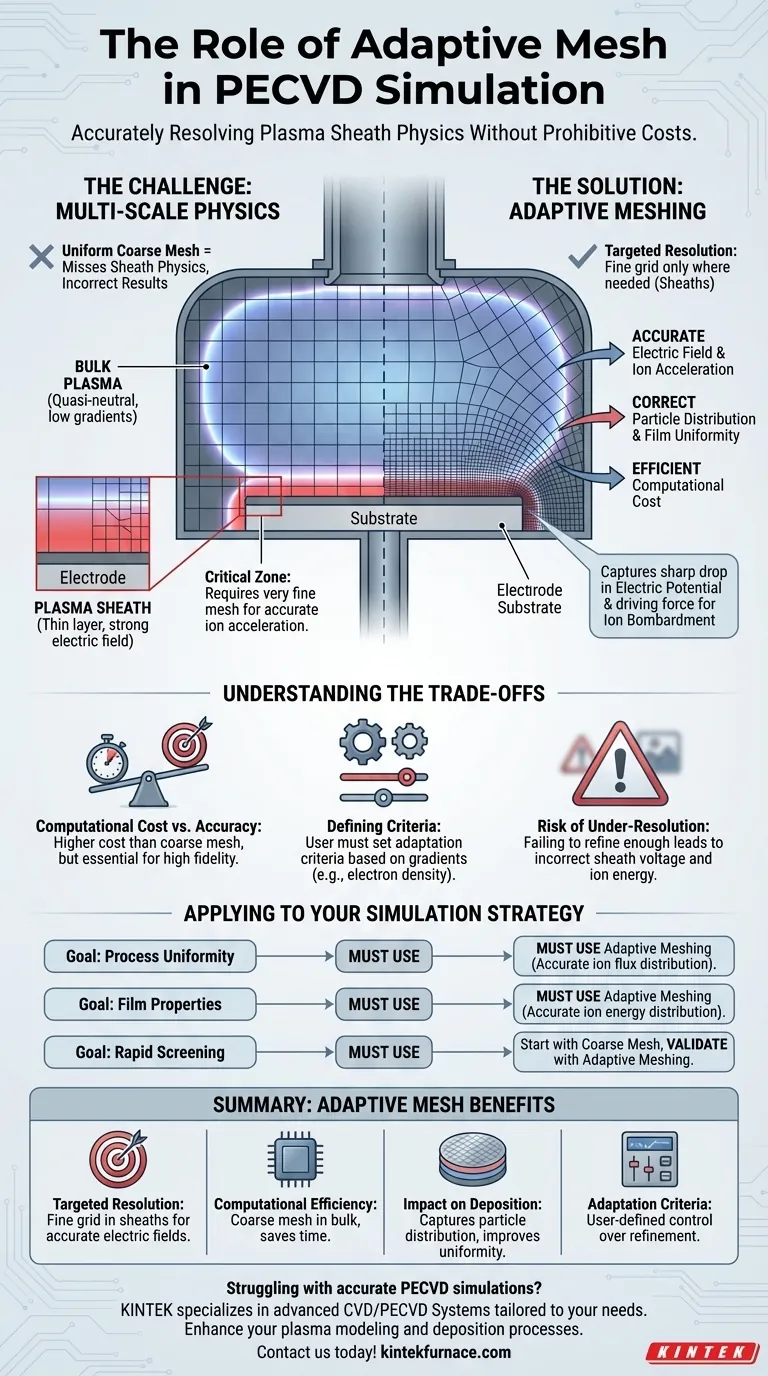
In PECVD simulation, the fundamental role of adaptive mesh is to apply a very fine computational grid specifically in the thin, critical regions near electrodes. This allows the model to accurately resolve the physics of the plasma sheath, which would be computationally impossible if such a fine mesh were used across the entire simulation domain.
The core challenge in PECVD simulation is accurately modeling phenomena that occur at vastly different physical scales. Adaptive meshing is the essential tool that enables high-fidelity results in critical zones, like plasma sheaths, without incurring the prohibitive computational cost of a globally fine mesh.

The Challenge: Multi-Scale Physics in PECVD
To understand the value of adaptive mesh, you must first understand the dual nature of the plasma environment inside a PECVD chamber. The plasma is not a uniform entity; it has distinct regions with dramatically different characteristics.
The Bulk Plasma
The vast majority of the plasma volume is the bulk plasma. This region is quasi-neutral, meaning the densities of positive ions and negative electrons are roughly equal.
Physical gradients in this area are relatively small. As a result, a coarse computational mesh is often sufficient to capture the physics of the bulk plasma without sacrificing accuracy.
The Plasma Sheath: The Critical Zone
Near the surfaces of the electrodes and the substrate lies the plasma sheath. This is an extremely thin boundary layer, often just a few millimeters thick or less.
Within the sheath, a strong electric field develops. This field is responsible for accelerating ions from the bulk plasma toward the surface, a process that is fundamental to the thin-film deposition that gives PECVD its name.
The Simulation Dilemma
This creates a dilemma. To accurately calculate the electric field and ion acceleration in the thin sheath, you need an extremely fine mesh. However, applying that same fine mesh to the large bulk plasma region would make the simulation time-consuming to the point of being impractical.
Using a coarse mesh everywhere would miss the sheath physics entirely, leading to incorrect calculations for ion energy, particle distribution, and ultimately, deposition rate and film quality.
How Adaptive Meshing Solves the Problem
Adaptive meshing provides an elegant and efficient solution to this multi-scale problem by concentrating computational effort only where it is most needed.
Targeted Resolution
An adaptive mesh algorithm automatically refines the grid—creating much smaller cells—in areas where key physical quantities are changing rapidly. In a PECVD simulation, this is predominantly within the plasma sheaths.
The bulk plasma, where conditions are more uniform, is left with a coarser mesh, saving significant computational resources.
Capturing Key Physics
By resolving the sheath, the simulation can accurately calculate the sharp drop in electric potential that occurs there. This is the driving force behind ion bombardment on the substrate.
Without this resolution, the model cannot correctly determine the energy and angle at which ions strike the surface, rendering the simulation's predictions about film properties unreliable.
Impact on Particle Distribution
Accurate sheath physics directly translates to an accurate calculation of particle distribution. The strength and shape of the electric field in the sheath dictate the uniformity of ion flux across the wafer.
This means adaptive meshing is not just a numerical convenience; it is directly linked to correctly predicting real-world outcomes like deposition uniformity and film density.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, adaptive meshing is not a magic bullet. Its effective use requires a clear understanding of the trade-offs involved.
Computational Cost vs. Accuracy
The primary trade-off is always between speed and fidelity. Enabling adaptive meshing increases computational cost compared to a purely coarse mesh, but it is an investment that yields vastly more accurate and physically meaningful results.
Defining the Adaptation Criteria
The simulation software does not inherently know what a "sheath" is. The user must guide it by setting adaptation criteria. This typically involves instructing the solver to refine the mesh in regions with high gradients of a specific variable, such as electron density or electric potential.
Setting these criteria too loosely may fail to adequately resolve the sheath, while setting them too aggressively can create an unnecessarily dense mesh that slows down the calculation.
Risk of Under-Resolution
The most significant pitfall is failing to refine the mesh enough. If the sheath region is not resolved with a sufficiently fine mesh, the calculated sheath voltage and ion energy will be incorrect. This can mislead process development and chamber design decisions.
Applying This to Your Simulation
Your strategy for using adaptive mesh should align directly with your engineering or research goals.
- If your primary focus is process uniformity: You must use adaptive meshing to accurately capture the sheath structure, as this directly controls the ion flux distribution across the substrate.
- If your primary focus is predicting film properties: Accurate calculation of the ion energy distribution, which is entirely dependent on a well-resolved sheath, is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is rapid, qualitative screening: You might begin with a coarse mesh to get a directional sense of plasma behavior, but any conclusions must be validated with a follow-up simulation using adaptive meshing.
Ultimately, mastering adaptive meshing transforms it from a simple feature into a strategic tool for balancing accuracy and efficiency in your PECVD analysis.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role in PECVD Simulation | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Targeted Resolution | Applies fine grid in plasma sheath regions | Accurate modeling of electric fields and ion acceleration |
| Computational Efficiency | Uses coarse mesh in bulk plasma | Reduces simulation time without sacrificing accuracy |
| Impact on Deposition | Captures particle distribution and ion flux | Improves predictions of film uniformity and density |
| Adaptation Criteria | User-defined based on gradients (e.g., electron density) | Enables precise control over mesh refinement for critical zones |
Struggling with accurate PECVD simulations for your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to meet your unique experimental needs. With our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing capabilities, we offer deep customization to enhance your plasma modeling and thin-film deposition processes. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your laboratory's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is keeping maintenance records important for MPCVD equipment? Ensure Reliability and Quality in Crystal Growth
- What is the basic principle of operation for the microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition system? Unlock High-Purity Material Growth
- Why is the temperature control system important in MPCVD equipment? Ensure Precise Diamond Growth and Process Stability
- Why is maintaining gas pipelines important in MPCVD equipment? Ensure Purity and Safety in Crystal Growth
- What are some challenges associated with MPCVD? Overcome High Costs and Complexity for Diamond Synthesis



















