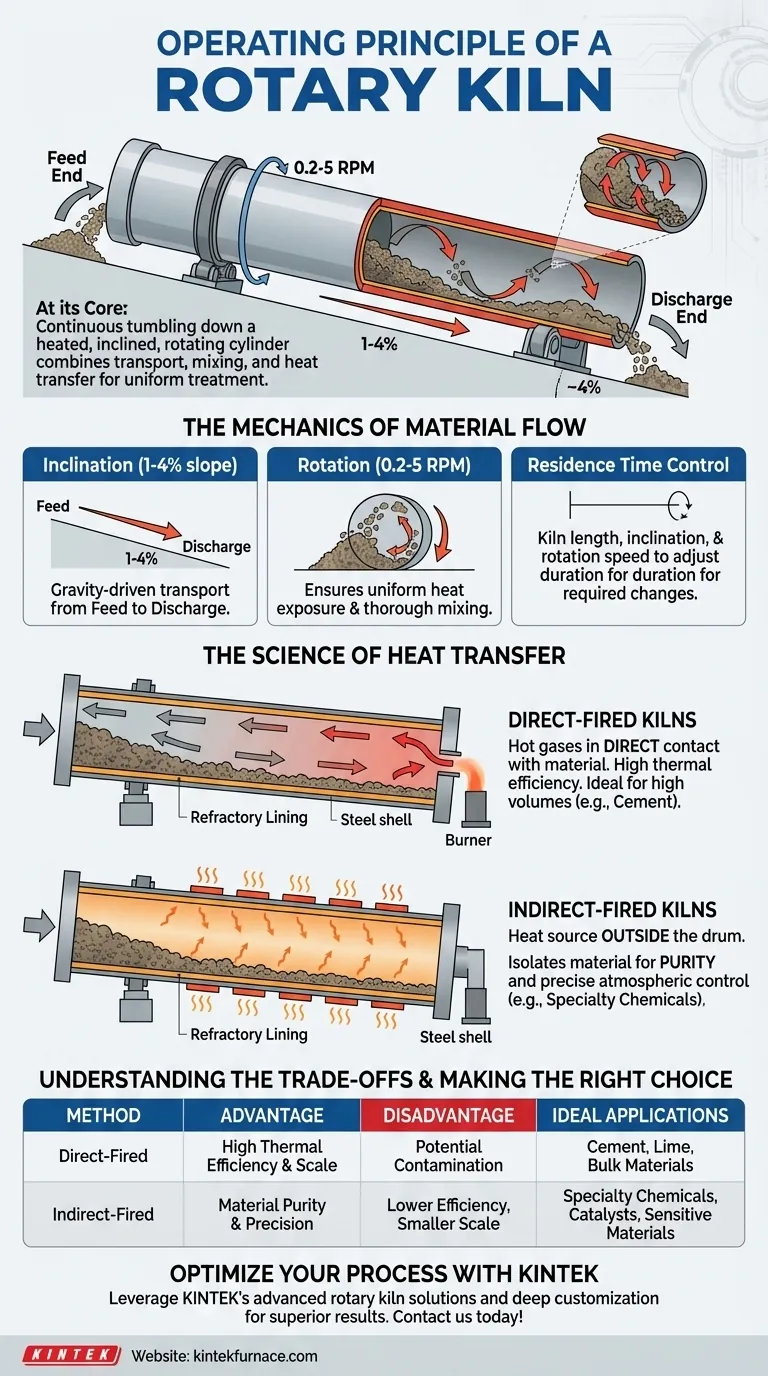
At its core, a rotary kiln operates by continuously tumbling material down a heated, slowly rotating, and slightly inclined cylinder. This simple yet effective mechanism combines material transport, mixing, and heat transfer into a single process. The combination of the kiln's slope and its rotation speed dictates how the material moves and how long it is exposed to heat, allowing for a precise and uniform thermal treatment.
The fundamental principle of the rotary kiln is its ability to achieve continuous and uniform thermal processing. It achieves this by using gravity and rotation to move and mix materials through a controlled, high-temperature environment, making it a cornerstone of heavy industry.

The Mechanics of Material Flow
The genius of the rotary kiln is how it uses simple physics to manage a complex industrial process. The movement of material is not arbitrary; it is a carefully controlled variable.
The Role of Inclination
The entire kiln vessel is set at a slight downward angle, typically between 1% and 4% from the horizontal.
This slope is the primary driver of material transport. Material fed into the higher, or "feed," end naturally travels toward the lower, or "discharge," end due to gravity.
The Impact of Rotation
The kiln rotates slowly on its longitudinal axis, usually between 0.2 and 5 revolutions per minute (RPM).
This rotation lifts the material partway up the kiln's inner wall before it tumbles back down into the bed of material. This tumbling action is critical for ensuring uniform heat exposure and thorough mixing, which prevents hot spots and promotes consistent chemical reactions.
Controlling Residence Time
The "residence time"—the total time material spends inside the kiln—is a function of the kiln's length, its inclination, and its rotation speed.
By adjusting the slope and rotational speed, operators can precisely control this duration to ensure the material undergoes the required physical or chemical changes.
The Science of Heat Transfer
Getting heat into the material is the kiln's ultimate purpose. This is achieved through two primary methods, each with distinct advantages.
Direct-Fired Kilns
In a direct-fired system, a burner is typically located at the discharge end of the kiln, generating hot gases that flow directly through the cylinder.
These gases come into direct contact with the material, transferring heat efficiently. Most large industrial kilns use a counter-current flow, where the hot gas flows in the opposite direction of the material, maximizing thermal efficiency.
Indirect-Fired Kilns
In an indirect-fired system, the heat source is located outside the rotating drum. The drum is heated externally, and this heat radiates inward to the material.
This design is crucial when the material must not be contaminated by combustion byproducts or when a specific internal atmosphere (e.g., inert or reducing) is required. Electric rotary kilns are a common example of this, using electric heating elements for precise, clean heat.
The Critical Refractory Lining
The inside of the kiln's steel shell is protected by a refractory lining, a layer of heat-resistant brick or castable material.
This lining serves two purposes: it insulates the steel shell from extreme process temperatures and minimizes heat loss to the surrounding environment, improving overall efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Direct vs. Indirect Heating
The choice between direct and indirect heating is the most fundamental design decision and depends entirely on the process requirements.
Direct Heating: Efficiency and Scale
Direct-fired kilns are more thermally efficient because heat is transferred straight from the flame and gases to the material. This makes them ideal for processing huge volumes of bulk materials, such as in the manufacturing of cement.
The primary drawback is the potential for the material to be contaminated by byproducts of fuel combustion, such as ash or sulfur.
Indirect Heating: Purity and Precision
Indirect-fired kilns are the superior choice when material purity is paramount. By isolating the material from the heat source, any risk of contamination is eliminated.
This method also allows for absolute control over the kiln's internal atmosphere. While less thermally efficient and often smaller in scale, the precision of indirect heating is essential for producing specialty chemicals, calcining catalysts, or processing sensitive materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Understanding these operating principles allows you to select and optimize a kiln for a specific industrial goal.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost processing (like cement or lime): A direct-fired, counter-current kiln is the most thermally and economically efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is material purity or a controlled atmosphere (like specialty chemicals): An indirect-fired kiln, potentially an electric one, provides the necessary process isolation and precision.
- If your primary focus is a specific chemical reaction: Controlling residence time and the temperature profile across the kiln's different zones (drying, preheating, calcining) is the most critical factor.
By mastering the interplay of rotation, inclination, and heat flow, any thermal processing challenge can be effectively engineered and controlled.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Material Flow | Controlled by kiln inclination (1-4% slope) and rotation (0.2-5 RPM) for gravity-driven transport and mixing. |
| Heat Transfer | Direct-fired for efficiency; indirect-fired for purity and controlled atmospheres. |
| Residence Time | Adjustable via slope and rotation to ensure uniform thermal treatment and chemical reactions. |
| Applications | Ideal for cement, lime, specialty chemicals, and catalyst calcination. |
Optimize your thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced rotary kiln solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to your unique needs. Whether you're in cement production or specialty chemicals, our deep customization ensures precise control for superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules



















