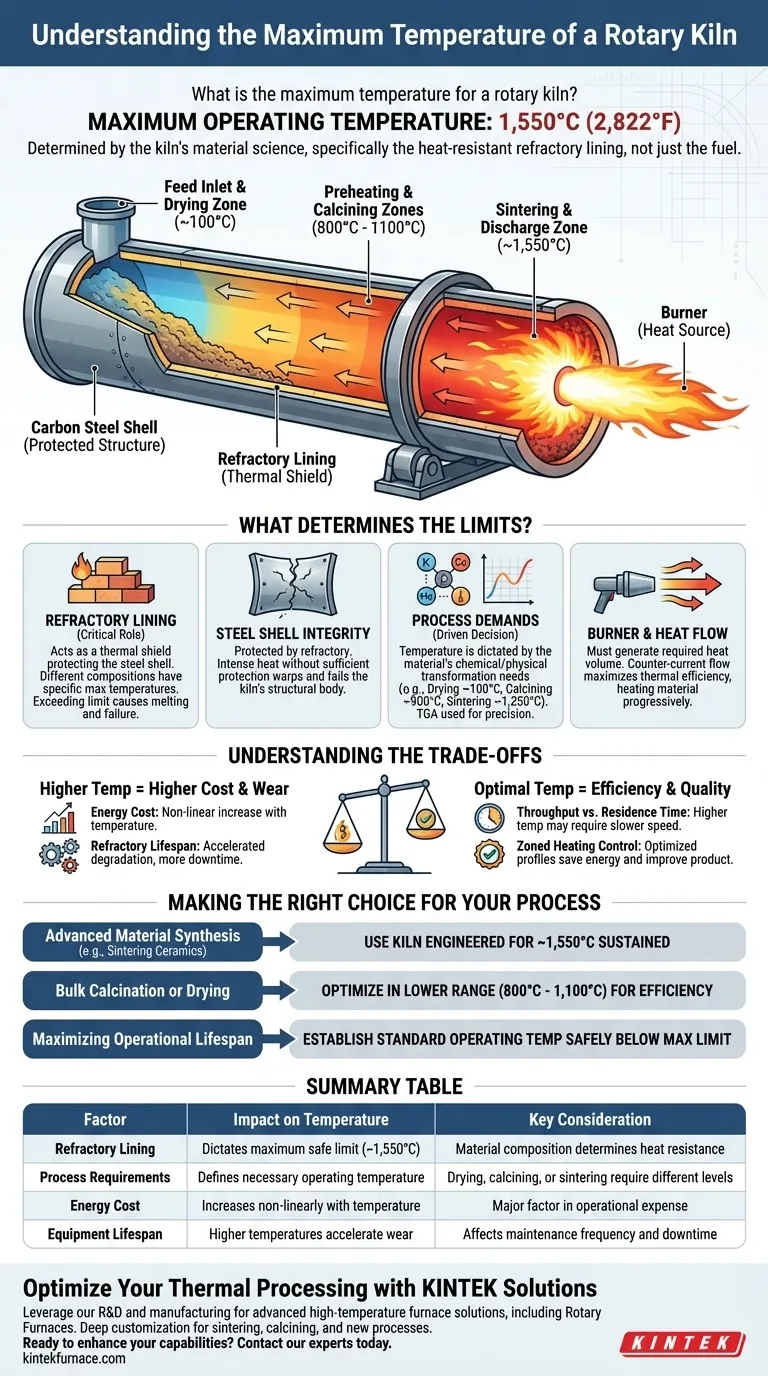
The maximum operating temperature for a high-performance, direct-heated industrial rotary kiln is typically 1,550°C (2,822°F). This upper limit is not determined by the fuel or burner, but by the material science of the kiln's construction, specifically the heat-resistant refractory lining that protects its structural steel shell from catastrophic failure.
The key takeaway is that a kiln's maximum temperature is a fundamental design constraint dictated by its refractory materials. While a kiln may be rated for 1,550°C, the optimal operating temperature is almost always lower, defined instead by the specific thermal requirements of the process and the economic trade-off between heat and operational cost.
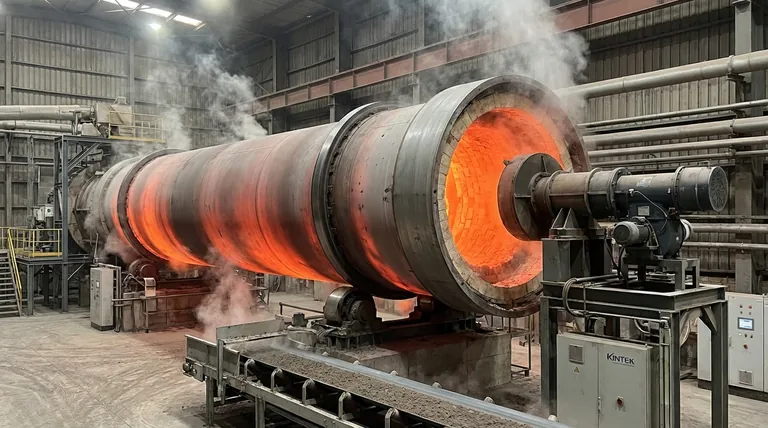

What Determines a Kiln's Maximum Temperature?
The theoretical maximum temperature is an engineering limit. The practical operating temperature is a process-driven decision. Several core factors work together to define these limits.
The Critical Role of the Refractory Lining
The inside of the kiln is lined with bricks or castable refractory material. This lining is the single most important factor determining the kiln's temperature rating. It acts as a thermal shield, protecting the outer steel shell.
Different refractory compositions (e.g., high-alumina, magnesia-chrome) have different maximum service temperatures. Pushing a kiln beyond the temperature limit of its specific refractory will cause the lining to melt or crumble, leading to immediate and severe damage.
The Integrity of the Steel Shell
The refractory lining protects the carbon steel shell that forms the kiln's body. If the refractory fails or is insufficient, the intense heat will cause the steel shell to warp, lose its structural integrity, and ultimately fail. The entire system is designed to keep this shell at a safe temperature.
The Demands of the Process
The process itself dictates the necessary temperature. You only use the heat required for the chemical or physical transformation of the material inside.
For example, drying free water only requires temperatures around 100°C. Calcining limestone to produce lime requires around 900°C. Sintering certain advanced ceramics may push the kiln closer to its 1,550°C limit. Techniques like Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA) are used to precisely identify the temperatures at which these reactions occur.
The Burner and Heat Flow
The burner, located at the discharge end, must be capable of generating the required volume of heat. For maximum thermal efficiency, most kilns use a counter-current flow, where the hot gases from the burner travel up the kiln against the flow of the material moving down the slope. This ensures the material is progressively heated as it moves toward the hottest zone.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Operating a kiln is a constant balance between performance, cost, and longevity. Running at the absolute maximum temperature is rarely the most effective strategy.
Energy Cost vs. Temperature
Achieving and maintaining higher temperatures requires a non-linear increase in energy consumption. The fuel cost to run a kiln at 1,500°C is dramatically higher than running it at 1,000°C. This is often the primary limiting factor from a business perspective.
Refractory Lifespan and Maintenance
Consistently operating near the maximum rated temperature significantly accelerates the wear and degradation of the refractory lining. This leads to more frequent and costly downtime for inspection and relining, directly impacting production capacity.
Throughput vs. Residence Time
To ensure the material inside the kiln is heated uniformly to a target temperature, it must remain in the kiln for a specific duration, known as residence time. Pushing for a higher temperature may require slowing the material's feed rate or the kiln's rotation speed to achieve the desired result, potentially lowering overall throughput.
Zoned Heating Control
Modern kilns are not single-temperature vessels. They are divided into distinct zones—typically drying, preheating, calcining, and cooling—each with separately controllable temperature settings. This allows for an optimized temperature profile that applies heat efficiently only where and when it is needed, saving energy and improving product quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your target temperature should be dictated by your end goal, not by the kiln's maximum technical rating.
- If your primary focus is advanced material synthesis (e.g., sintering technical ceramics): You must use a kiln specifically engineered with premium refractories rated for sustained operation near the 1,550°C limit.
- If your primary focus is bulk calcination or drying: Operating in a lower, optimized temperature range (e.g., 800°C - 1,100°C) will deliver the required transformation while drastically reducing energy costs and mechanical wear.
- If your primary focus is maximizing operational lifespan: Establish a standard operating temperature safely below the kiln's absolute maximum to reduce thermal stress on the refractory lining and mechanical components like riding rings and trunnion wheels.
Ultimately, the correct operating temperature is the one that most efficiently and economically achieves your specific process goal.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Temperature | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Refractory Lining | Dictates maximum safe limit (e.g., ~1,550°C) | Material composition determines heat resistance |
| Process Requirements | Defines the necessary operating temperature | Drying, calcining, or sintering require different heat levels |
| Energy Cost | Increases non-linearly with temperature | Major factor in operational expense |
| Equipment Lifespan | Higher temperatures accelerate wear on linings and shell | Affects maintenance frequency and downtime |
Optimize Your Thermal Processing with KINTEK Solutions
Choosing the right operating temperature is critical for your process efficiency, product quality, and bottom line. At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, tailored to your specific needs.
Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique thermal requirements, whether you are sintering advanced ceramics, calcining materials, or developing new processes.
Ready to enhance your lab's or production line's capabilities? Contact our experts today to discuss how our reliable and efficient heating solutions can drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















