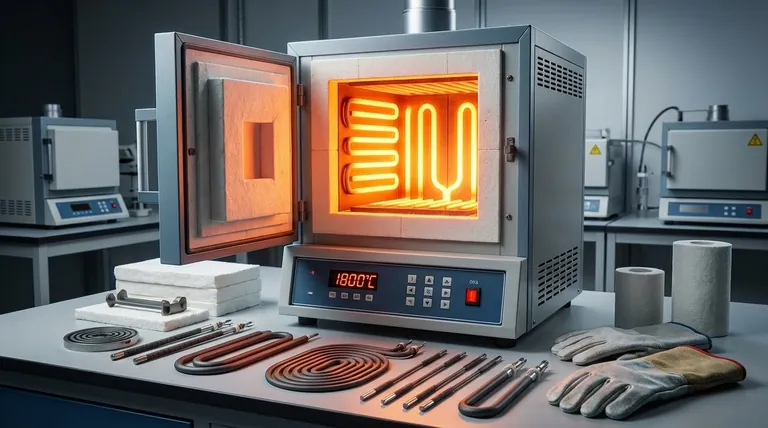
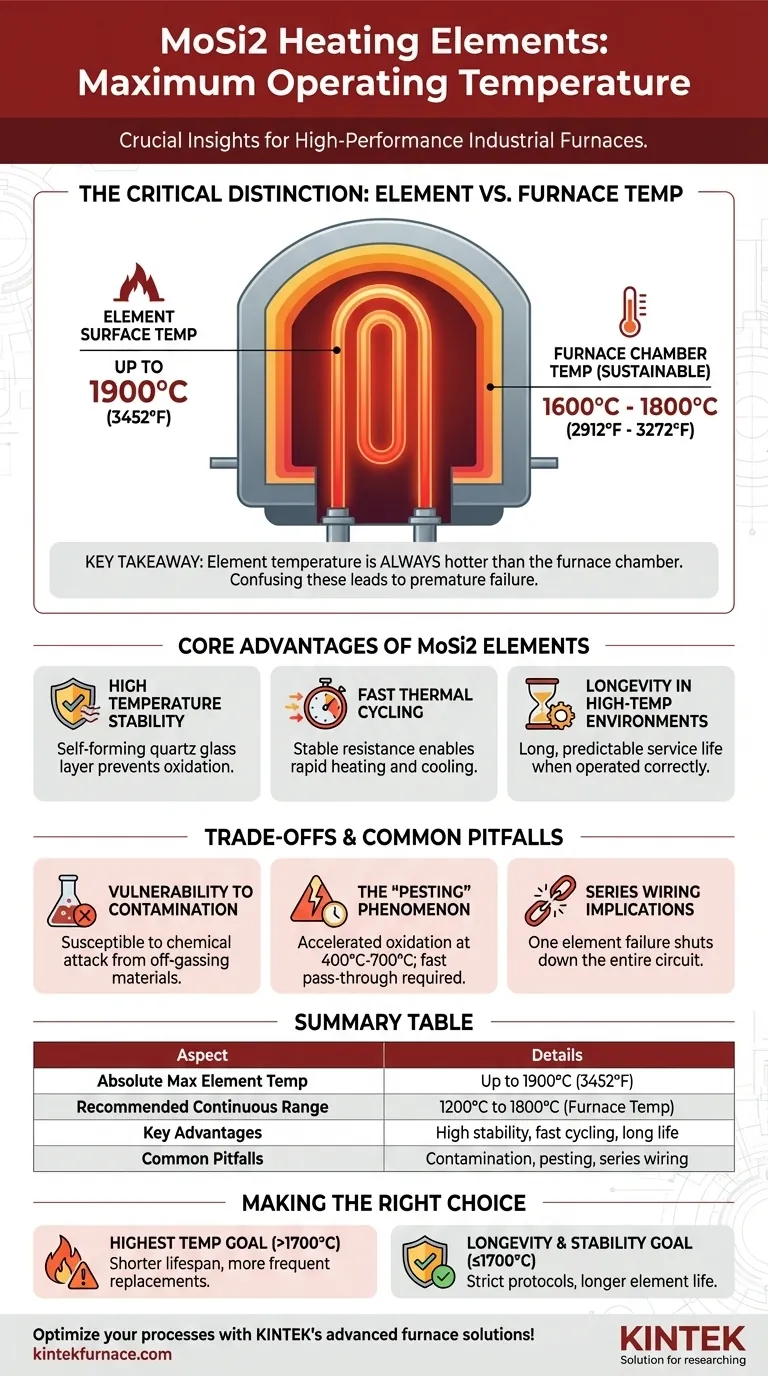
In practice, the maximum element temperature for Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements can reach up to 1900°C (3452°F). However, the sustainable operating temperature within a furnace is typically lower, falling within the range of 1600°C to 1800°C (2912°F to 3272°F) for most industrial applications.
The key takeaway is that an element's maximum rated temperature is not the same as the furnace's maximum operating temperature. Understanding this distinction, along with the material's environmental vulnerabilities, is critical for achieving both high performance and long service life.

Understanding MoSi2 Temperature Ratings
MoSi2 elements are a benchmark for high-temperature electric heating, but their temperature ratings must be interpreted correctly to ensure reliable operation.
The Critical Difference: Element vs. Furnace Temperature
A heating element's surface is always hotter than the furnace chamber it is heating. For MoSi2, the element surface can be operating at 1800°C to 1900°C to maintain a stable furnace temperature of 1600°C to 1700°C.
Confusing these two values is a common cause of premature element failure. Pushing the furnace atmosphere to the element's absolute maximum temperature will drastically shorten its life.
Absolute Maximum Element Temperature
The material's physical limit is approximately 1900°C (3452°F). Operating at or near this temperature should be considered a peak, intermittent capability rather than a continuous operating point.
Recommended Continuous Operating Range
For optimal balance between performance and longevity, most industrial processes use MoSi2 elements to maintain furnace temperatures between 1200°C and 1800°C. Operating consistently above 1500°C is where these elements provide a significant lifespan advantage over alternatives like Silicon Carbide (SiC).
Core Advantages of MoSi2 Elements
The ability to operate at extreme temperatures stems from several key material properties that make MoSi2 uniquely suited for demanding applications.
High Temperature Stability
MoSi2 elements develop a protective outer layer of quartz glass (silica) when heated. This self-forming layer prevents the underlying material from oxidizing, allowing it to remain stable at temperatures that would destroy most other metals.
Fast Thermal Cycling
The elements' resistance remains relatively stable across their operating temperature range. This allows them to be heated and cooled rapidly without suffering significant damage, making them ideal for processes that require fast thermal cycles.
Longevity in High-Temperature Environments
When operated correctly within their recommended range and kept free of contaminants, MoSi2 elements have a very long and predictable service life. This reduces furnace downtime and maintenance costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While powerful, MoSi2 elements are not indestructible. Their reliability depends on understanding their specific vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability to Contamination
These elements are highly susceptible to chemical attack. Technicians must ensure that materials placed in the furnace, such as painted or colored zirconia, are fully dried and cured to prevent off-gassing that can contaminate and destroy the elements.
The "Pesting" Phenomenon
At lower temperatures, typically between 400°C and 700°C (750°F to 1300°F), MoSi2 can suffer from accelerated oxidation, a phenomenon known as "pesting." This causes the element to rapidly disintegrate into a powder. Furnaces must be designed to pass through this temperature range quickly during both heat-up and cool-down.
Series Wiring Implications
MoSi2 elements are often wired in series. This means that if one element fails, the entire circuit is broken, which can shut down a section of the furnace. This design simplifies power control but makes troubleshooting an individual failed element more critical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your target operating temperature should be determined by your primary objective—balancing maximum performance against long-term reliability.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible process temperature: You can design your furnace to operate near 1800°C, but you must accept a shorter element lifespan and budget for more frequent replacements.
- If your primary focus is element longevity and process stability: Limit your maximum continuous operating temperature to 1700°C or lower and implement strict protocols for furnace cleanliness and maintenance.
- If your process requires frequent cycling: Ensure your control system is programmed to move through the 400°C-700°C "pesting" range as rapidly as possible to protect the elements.
Ultimately, harnessing the full potential of MoSi2 heating elements comes from treating them as a component of a complete thermal system.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Absolute Max Element Temperature | Up to 1900°C (3452°F) |
| Recommended Continuous Operating Range | 1200°C to 1800°C for furnace temperature |
| Key Advantages | High temperature stability, fast thermal cycling, long service life |
| Common Pitfalls | Vulnerability to contamination, pesting at 400°C-700°C, series wiring implications |
Optimize your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored heating systems. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance performance and longevity in your thermal applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















