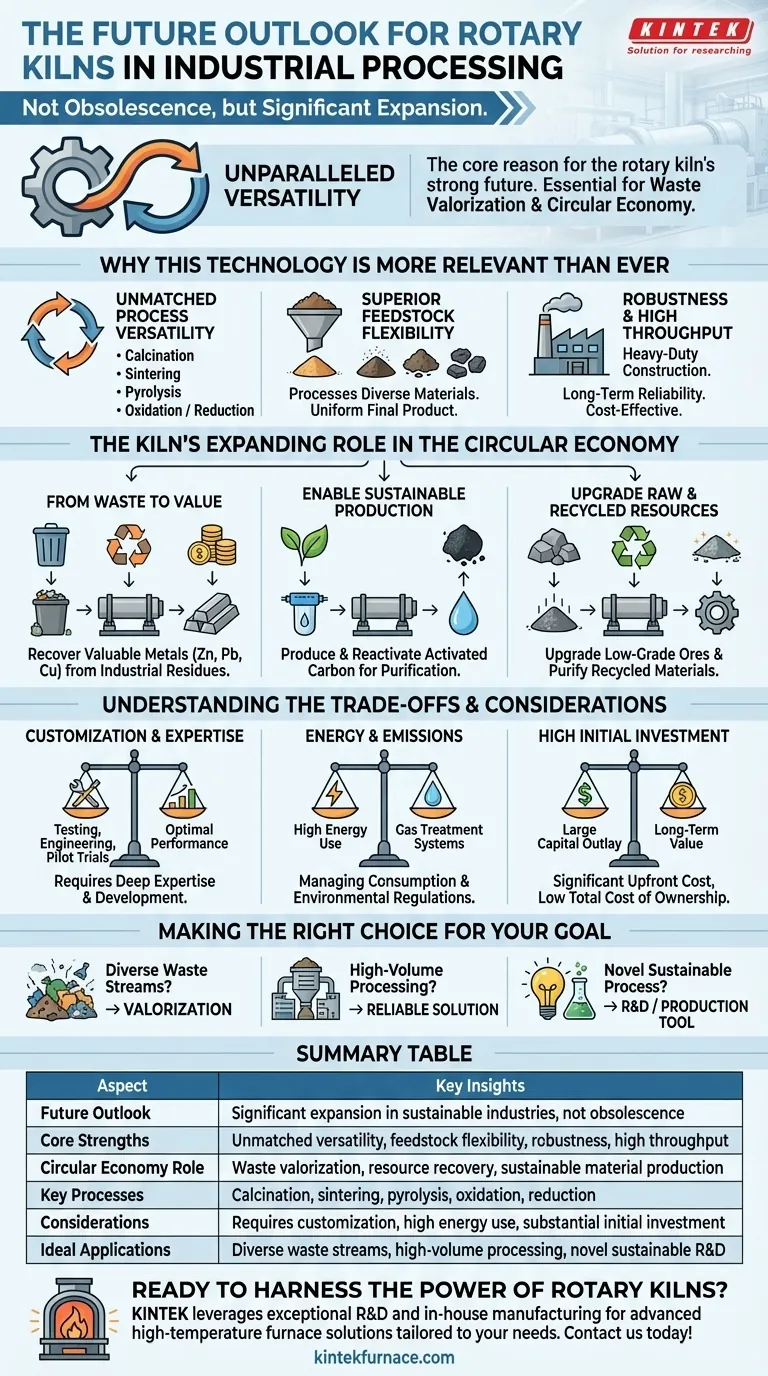
The future outlook for rotary kilns is not one of obsolescence, but of significant expansion. Far from being a legacy technology, the rotary kiln is evolving into a cornerstone of modern, sustainable industry. Its fundamental design, which allows for precise thermal processing of a wide variety of materials, makes it uniquely suited to solve the challenges of waste valorization and the circular economy.
The core reason for the rotary kiln's strong future is its unparalleled versatility. Its ability to perform a vast range of thermal processes on diverse and inconsistent feedstocks makes it an essential tool for turning industrial waste and byproducts into valuable resources.

Why This 150-Year-Old Technology is More Relevant Than Ever
The rotary kiln's enduring relevance stems from a combination of fundamental strengths that are difficult to replicate. These attributes are not just useful for traditional manufacturing but are critical for the emerging industrial landscape.
Unmatched Process Versatility
A single rotary kiln can be configured to perform a multitude of thermal processes. This is its primary advantage over more specialized equipment.
Key processes include calcination to remove water or volatiles, sintering to create a solid mass, pyrolysis for thermal decomposition in an oxygen-free environment, and targeted oxidation or reduction reactions. This adaptability allows one machine to serve many purposes across different industries.
Superior Feedstock Flexibility
Rotary kilns excel at processing a wide array of materials that other systems cannot handle effectively. They can process everything from fine powders and filter cakes to sludges and lumpy, non-uniform solids.
The tumbling action ensures that every particle is exposed to the controlled temperature and atmosphere, resulting in a highly uniform final product regardless of the initial feedstock's inconsistency.
Robustness and High Throughput by Design
Designed for demanding environments like mines and chemical plants, rotary kilns are known for their heavy-duty construction and long-term reliability.
Their relatively simple operational principles and capacity for continuous, high-volume processing make them a cost-effective and dependable workhorse for large-scale industrial applications.
The Kiln's Expanding Role in the Circular Economy
While essential in traditional industries, the most significant growth area for rotary kilns is in creating value from materials once considered waste. This positions the technology at the heart of the circular economy.
From Waste Stream to Value Stream
Kilns are highly effective at recovering valuable elements from industrial byproducts and waste.
For example, they can be used to volatilize and capture valuable metals like zinc, lead, and copper from furnace dusts or other industrial residues, transforming a disposal liability into a revenue source.
Enabling Sustainable Material Production
The technology is crucial for producing and regenerating sustainable materials. A key example is the production of activated carbon for air and water purification.
Furthermore, kilns are used to reactivate spent activated carbon, restoring its absorptive properties and allowing it to be reused multiple times. This dramatically reduces waste and the need for virgin materials.
Upgrading Raw and Recycled Resources
Rotary kilns improve the efficiency of resource extraction and use. They are used to upgrade low-grade ores, such as bauxite or phosphate rock, making previously uneconomical deposits viable.
This same capability allows for the processing and purification of recycled materials, preparing them for re-entry into the manufacturing lifecycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, the rotary kiln is not a universal solution. A clear understanding of its operational demands is essential for successful implementation.
Customization Requires Deep Expertise
The kiln's greatest strength—its adaptability—is also a source of complexity. It is not an off-the-shelf product.
Achieving optimal performance for a specific material requires thorough testing and process development. This involves significant upfront engineering, material analysis, and pilot-scale trials to define the precise temperature profiles, rotation speeds, and atmospheric conditions.
Energy Consumption and Emissions
As a high-temperature thermal process, a rotary kiln is inherently energy-intensive. Managing energy consumption is a primary operational cost and a key focus for modern design.
Furthermore, processing certain feedstocks can generate emissions that require robust gas handling and treatment systems to meet environmental regulations.
High Initial Capital Investment
The heavy-duty construction, large scale, and need for custom engineering mean that a rotary kiln system represents a significant capital investment. While its long-term reliability often yields a low total cost of ownership, the initial outlay is substantial.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a rotary kiln should be driven by your specific processing objective.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse or inconsistent waste streams: The kiln's unmatched feedstock flexibility makes it the superior choice for valorizing complex materials.
- If your primary focus is high-volume mineral or chemical processing: The kiln's proven reliability, high throughput, and uniform processing deliver a robust, long-term manufacturing solution.
- If your primary focus is developing a novel, sustainable process: The kiln's process versatility makes it a powerful R&D and production tool, provided you commit the resources for proper testing and development.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln is a foundational technology, providing a bridge from the linear industrial models of the past to the circular, more efficient economies of the future.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Insights |
|---|---|
| Future Outlook | Significant expansion in sustainable industries, not obsolescence |
| Core Strengths | Unmatched versatility, feedstock flexibility, robustness, high throughput |
| Circular Economy Role | Waste valorization, resource recovery, sustainable material production |
| Key Processes | Calcination, sintering, pyrolysis, oxidation, reduction |
| Considerations | Requires customization, high energy use, substantial initial investment |
| Ideal Applications | Diverse waste streams, high-volume processing, novel sustainable R&D |
Ready to harness the power of rotary kilns for your industrial processing needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique requirements. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're focused on waste valorization, circular economy initiatives, or high-throughput production, we can help you achieve precise thermal processing with reliability and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing



















