At its core, a vacuum brazing furnace is a specialized piece of industrial equipment designed to join two or more metal components into a single, robust assembly. It achieves this by melting a filler metal with a lower melting point than the base materials, which then flows into the joint via capillary action. The key distinction is that this entire process occurs within a high-vacuum environment, which is fundamental to its function and the quality of the result.
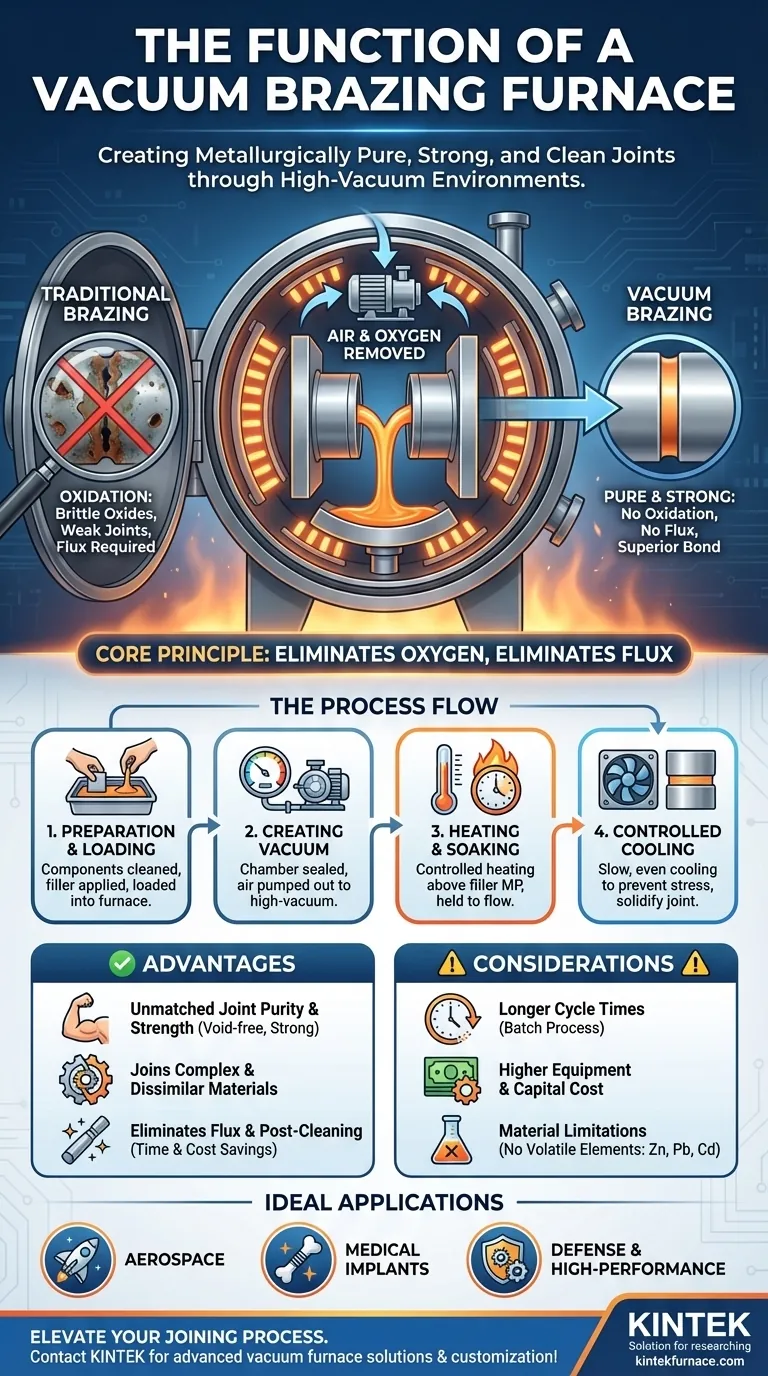
The true purpose of a vacuum brazing furnace isn't just to join metals; it's to create metallurgically pure, strong, and clean joints by removing atmospheric contaminants, primarily oxygen, that would otherwise compromise the integrity of the bond at high temperatures.

The Core Principle: Brazing in a Contaminant-Free Zone
To understand the furnace's function, you must first understand the problem it solves. When metals are heated to high temperatures, they readily react with oxygen in the air, forming brittle oxides on the surface.
Why Oxidation is the Enemy
These oxide layers prevent the filler metal from properly wetting and adhering to the base materials. This results in weak, unreliable joints filled with voids and inclusions. Traditional brazing methods must use a chemical agent called flux to dissolve these oxides.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
A vacuum brazing furnace solves this problem at its source. By pumping the air out of its sealed chamber, it removes the oxygen. This creates an ultra-clean environment where no oxides can form on the metal parts during the heating cycle.
This degassing effect also pulls trapped gases out of the base materials themselves, which further improves the structural integrity and hardness of the final brazed joint.
Eliminating the Need for Flux
Because the vacuum prevents oxidation, flux is no longer necessary. This is a significant advantage, as it completely eliminates the need for post-braze cleaning to remove corrosive flux residue, saving both time and cost while preventing a common source of future part failure.
How the Vacuum Brazing Process Works
The process is a precisely controlled sequence of steps designed to ensure maximum joint quality and repeatability.
Preparation and Loading
Components are first cleaned and assembled, with the filler metal placed at the joints. The filler is often a thin foil, paste, or wire. The completed assembly is then loaded into the furnace.
Creating the Vacuum Environment
The furnace chamber is sealed, and a system of powerful pumps removes the air until a specific, low-pressure vacuum level is reached. For certain applications, the chamber might then be backfilled with an inert gas like argon to create a protective atmosphere at a specific pressure.
The Heating and Soaking Cycle
Heating elements inside the furnace then raise the temperature of the assembly in a highly controlled manner. The temperature is brought above the melting point of the filler metal but safely below that of the base components. The assembly is held at this "soaking" temperature for a short period (e.g., 5-10 minutes) to allow the molten filler to flow and fill the joints completely.
Controlled Cooling
Finally, the assembly is cooled slowly and evenly. This controlled cooling is critical to prevent thermal stress and distortion, ensuring the final part is dimensionally stable and the joint solidifies properly.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
While powerful, vacuum brazing is a specific tool for specific challenges. Understanding its pros and cons is key to deploying it correctly.
Advantage: Unmatched Joint Purity and Strength
By eliminating oxides and fluxes, vacuum brazing produces exceptionally clean, strong, and void-free joints. The final bond is often as strong as the parent materials themselves, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
Advantage: Joining Complex and Dissimilar Materials
The precise temperature control and uniform heating allow for the joining of intricate geometries, thin-walled sections, and dissimilar metals that would be difficult or impossible to join with other methods.
Consideration: Cycle Time and Equipment Cost
Vacuum brazing is typically a batch process. The time required to pump down the vacuum, heat, soak, and cool can be significant compared to manual methods. Furthermore, the furnace and its supporting vacuum systems represent a substantial capital investment.
Consideration: Material Limitations
The process is not suitable for base materials or filler metals that contain volatile elements with high vapor pressures, such as zinc, lead, or cadmium. Under vacuum, these elements can outgas and contaminate the furnace and the assembly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Deciding whether to use vacuum brazing depends entirely on the technical requirements and value of the final product.
- If your primary focus is mission-critical performance: Choose vacuum brazing for applications in aerospace, medical implants, or defense where joint failure is not an option.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing complex assemblies: Use vacuum brazing when joining dissimilar materials or intricate designs that demand precise, uniform heat without distortion.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, clean production: Consider vacuum brazing when the cost and time savings from eliminating post-braze chemical cleaning justify the initial investment.
Ultimately, a vacuum brazing furnace provides a superior solution for creating high-purity metal joints when quality and reliability cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Joins metal components using a filler metal in a high-vacuum environment to prevent oxidation and ensure clean, strong bonds. |
| Key Advantages | Produces metallurgically pure joints, eliminates flux and post-cleaning, joins complex geometries and dissimilar materials, and enhances joint strength. |
| Process Steps | 1. Preparation and loading of components with filler metal. |
- Creating a high-vacuum environment.
- Controlled heating and soaking above filler metal melting point.
- Slow, controlled cooling to prevent stress and distortion. | | Ideal Applications | Aerospace, medical implants, defense, and other high-performance industries where joint reliability is critical. | | Considerations | Longer cycle times, higher equipment costs, and not suitable for materials with volatile elements like zinc or cadmium. |
Ready to elevate your metal joining processes with precision and reliability? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, or other high-performance fields, our vacuum brazing furnaces deliver unmatched purity and strength for critical applications. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your laboratory's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness



















