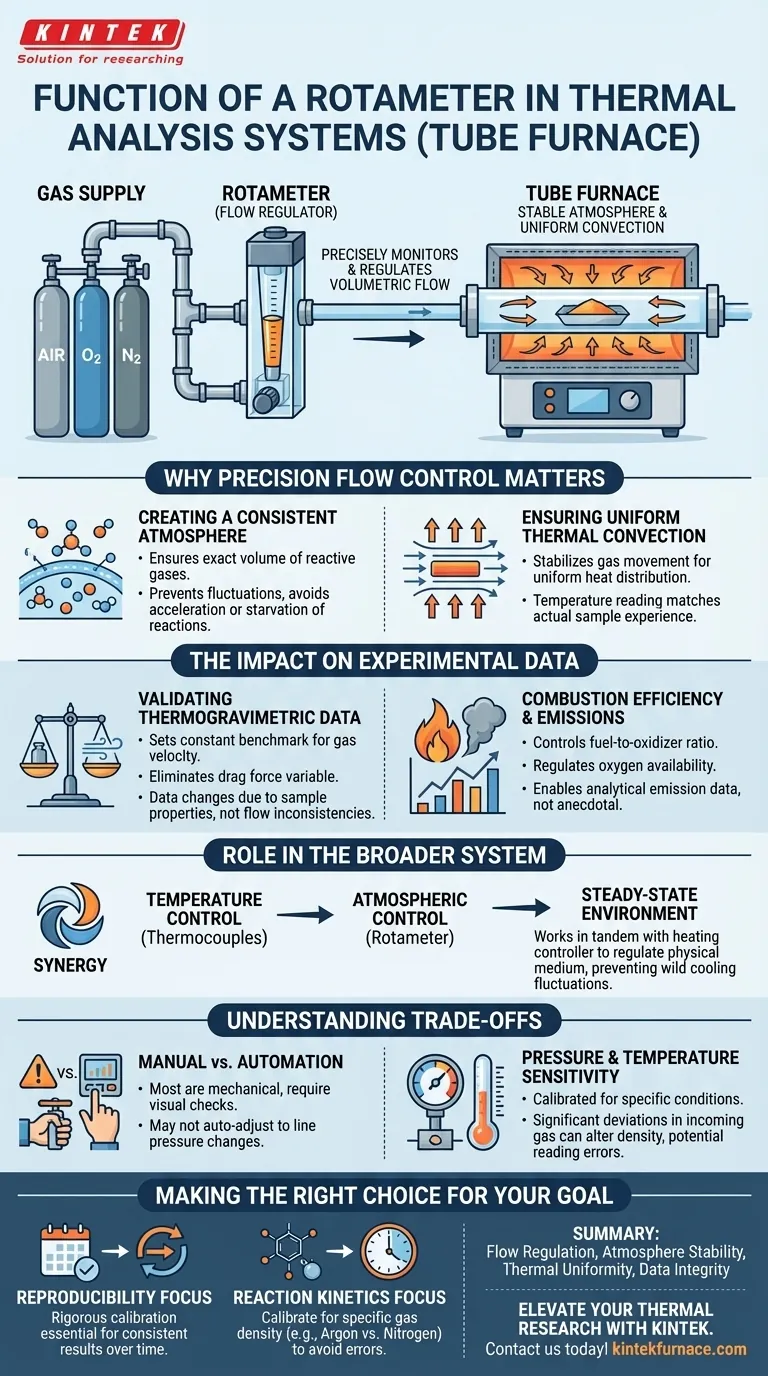
The primary function of a rotameter is to precisely monitor and regulate the volumetric flow rate of gases entering a tube furnace system. Whether you are introducing reactive gases like air, oxygen, or nitrogen, the rotameter serves as the critical "throttle," ensuring the gas supply remains consistent and measurable throughout the entire thermal cycle.
In a thermal analysis system, the rotameter transforms a raw gas supply into a stable experimental atmosphere. By maintaining a constant flow rate, it ensures uniform thermal convection and safeguards the reliability of your combustion and thermogravimetric data.

Why Precision Flow Control Matters
In a tube furnace, temperature is only half the equation. The atmosphere surrounding your sample drives the chemical and physical changes you are trying to measure.
Creating a Consistent Atmosphere
Thermal analysis often requires a specific environment, such as an inert nitrogen blanket or an oxygen-rich combustion zone.
The rotameter ensures that the volume of these reactive gases entering the tube is exact. This prevents atmospheric fluctuations that could inadvertently accelerate or starve the chemical reactions occurring within the sample.
Ensuring Uniform Thermal Convection
Heat transfer within a tube furnace relies heavily on the movement of the gas.
If the gas flow creates turbulence or varies in speed, the heat distribution around the sample becomes uneven. A rotameter stabilizes this flow, promoting uniform thermal convection. This ensures that the temperature reading on your controller matches the actual thermal experience of the sample.
The Impact on Experimental Data
The integrity of your data is directly tied to the stability of your inputs. A rotameter eliminates the variable of "unknown flow," allowing for precise correlation between cause and effect.
Validating Thermogravimetric Data
When measuring weight change over time (thermogravimetry), drag forces from moving gas can affect the balance readings.
To compare data reliably between different experiments, the gas flow must be identical in every run. The rotameter allows you to set a constant benchmark, ensuring that observed changes are due to sample properties, not inconsistencies in gas velocity.
Combustion Efficiency and Emissions
For experiments focusing on combustion or emissions analysis, the ratio of fuel (sample) to oxidizer (gas) is paramount.
The rotameter controls the combustion efficiency by regulating exactly how much oxygen is available to the sample. Without this control, emission data becomes anecdotal rather than analytical.
The Role in the Broader System
A tube furnace is a synergy of thermal and atmospheric controls.
Complementing Temperature Control
While your temperature control system uses thermocouples to adjust the heating elements, the rotameter regulates the physical medium inside the tube.
High-precision temperature control is rendered ineffective if the cooling effect of the gas flow fluctuates wildly. The rotameter works in tandem with the heating controller to maintain a steady-state environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While rotameters are reliable and essential, they are not universally perfect for every application.
Manual Monitoring vs. Automation
Most standard rotameters are mechanical and require visual checks. Unlike digital mass flow controllers, they may not automatically adjust to changes in line pressure without manual intervention.
Pressure and Temperature Sensitivity
Rotameters are calibrated for specific conditions. Significant deviations in the pressure or temperature of the incoming gas line can alter the density of the gas, potentially leading to slight reading errors if not corrected.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of your rotameter, align its usage with your specific experimental objectives:
- If your primary focus is Reproducibility: rigorous calibration of the rotameter is essential to ensure that "5 L/min" today equals "5 L/min" next month.
- If your primary focus is Reaction Kinetics: ensure your rotameter is specifically calibrated for the density of the reactive gas (e.g., Argon vs. Nitrogen) you are using to avoid calculation errors.
Ultimately, a well-managed rotameter converts variable gas pressure into the data reliability required for high-stakes thermal analysis.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Tube Furnace System |
|---|---|
| Flow Regulation | Controls the volumetric flow rate of reactive or inert gases. |
| Atmosphere Stability | Maintains consistent chemical environments (e.g., Nitrogen, Oxygen). |
| Thermal Uniformity | Ensures steady convection for even heat distribution around samples. |
| Data Integrity | Standardizes gas velocity to validate thermogravimetric and combustion data. |
Elevate Your Thermal Research with KINTEK
Precision gas control is the backbone of reproducible thermal analysis. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to your specific laboratory requirements. Whether you need integrated flow control or specialized high-temperature solutions, our experts are ready to assist.
Contact us today to optimize your lab's thermal systems!
Visual Guide
References
- Beata Brzychczyk, L. J. Sikora. Modernization of a Tube Furnace as Part of Zero-Waste Practice. DOI: 10.3390/su17198940
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Ultra High Vacuum Observation Window KF Flange 304 Stainless Steel High Borosilicate Glass Sight Glass
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the technical significance of using a dual-temperature zone tube furnace for CoTe2 tellurization?
- Is it safe to use a quartz tube furnace at high temperatures? Ensure Safety with the Right Tube Material
- What role does a tube furnace play in the preparation of biomass carbon fiber? Enhance Your Bio-Material Carbonization
- What is the basic function of a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Precision Thermal Processing for Material Synthesis
- What are the differences between solid tube and split type tube furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of tube furnaces for certain applications? Unlock Precise Atmosphere and Temperature Control
- Why is a Tube Furnace required for the heat treatment of carbon fiber cloth? Master Surface Activation
- What is the role of horizontal furnaces in battery manufacturing? Achieve Precision Thermal Processing for Superior Battery Performance










