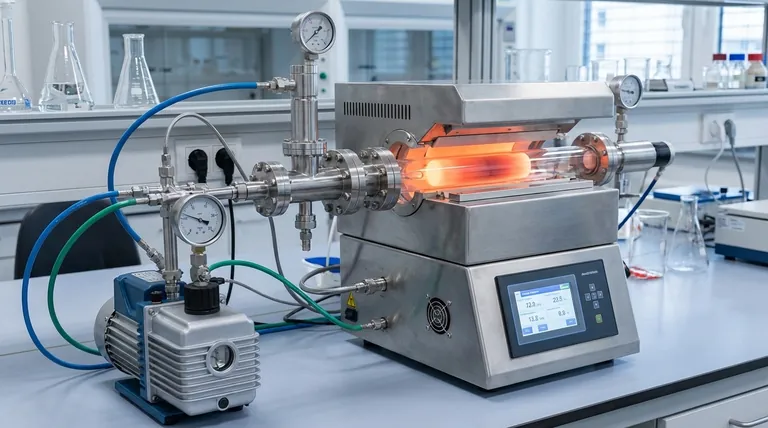
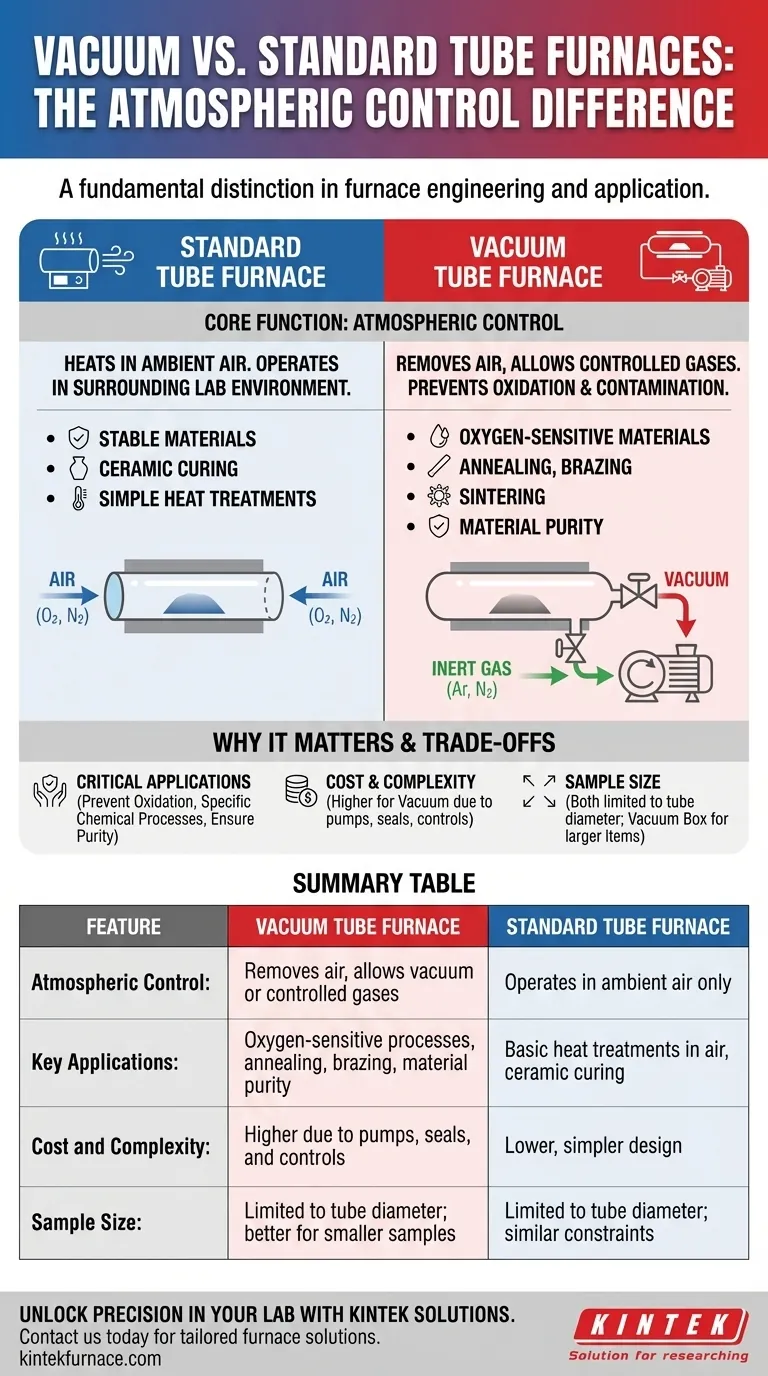
The fundamental difference between a vacuum tube furnace and a standard tube furnace lies in atmospheric control. A vacuum tube furnace is engineered with specialized sealing flanges, ports, and a pump system to remove air and introduce controlled gases. A standard tube furnace lacks this capability and is designed to operate only in the ambient air atmosphere.
The decision is not merely about choosing a furnace with or without a vacuum pump. It is about understanding that atmospheric control is a critical process variable, just like temperature and time. Selecting the right furnace requires matching its atmospheric capabilities to the specific chemical and physical requirements of your material.

The Core Function: Atmospheric Control
A tube furnace is, at its heart, a device for high-temperature thermal processing within a contained cylindrical space. The key distinction emerges from how it manages the atmosphere inside that space.
Standard Tube Furnaces
A standard, or "air," tube furnace simply heats the material within its tube. The atmosphere inside the tube is the same as the surrounding lab environment—ambient air.
These are ideal for processes where the material is stable when heated in the presence of oxygen and nitrogen, such as certain types of ceramic curing or simple heat treatments.
Vacuum Tube Furnaces
A vacuum furnace adds a layer of crucial functionality. It includes high-integrity seals (flanges) on the tube ends and a port connected to a vacuum pump.
This system first removes the atmosphere from the process tube, primarily to eliminate oxygen. Preventing oxidation is the most common reason to use a vacuum furnace.
Once under vacuum, the system can also be used as a controlled atmosphere furnace. A specific gas, like inert argon or nitrogen, can be carefully backfilled into the tube to create a precise, non-reactive environment for the process.
Why Atmospheric Control is Critical
Choosing a vacuum furnace is a decision driven entirely by the needs of your process. This capability is non-negotiable for certain applications.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Many advanced materials, metals, and alloys will rapidly oxidize or become contaminated when heated in air. This can destroy the material's properties. A vacuum environment removes the oxygen, protecting the sample's integrity during heat treatment.
Enabling Specific Chemical Processes
Processes like annealing, brazing, and sintering often require an oxygen-free environment to succeed. Degassing, where trapped gases are removed from a material, can also only be accomplished under vacuum.
Ensuring Material Purity
In fields like semiconductor research or advanced materials science, even trace amounts of atmospheric contaminants can compromise experimental results. A high-vacuum system ensures an ultra-pure processing environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vacuum furnace is not always the best choice. It comes with clear trade-offs in complexity, cost, and physical limitations.
Cost and Complexity
The addition of vacuum pumps, specialized flanges, gauges, and control systems significantly increases the initial cost and ongoing maintenance requirements of the furnace. If your process does not require atmospheric control, this is an unnecessary expense.
Sample Size and Throughput
Tube furnaces, by their design, are best suited for smaller samples that fit within the diameter of the process tube. For processing larger or bulkier items under vacuum, a vacuum muffle or box furnace is a more appropriate choice, as it offers a much larger internal chamber.
Design and Accessibility
Tube furnaces can be solid or "split-tube." A split-tube design hinges open, allowing easier placement of the process tube and its contents. This is often more convenient than sliding a long tube into a solid furnace, especially when complex sample holders are involved.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace requires a clear understanding of your material, your process, and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is basic heat treatment in air: A standard, single-zone tube furnace is the most cost-effective and straightforward solution.
- If your primary focus is processing oxygen-sensitive materials: A vacuum tube furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and ensure material integrity.
- If your primary focus is achieving a highly uniform temperature over a long sample: A three-zone furnace (either standard or vacuum) is required for superior temperature control.
- If your primary focus is processing large or irregularly shaped parts: You should evaluate a vacuum box or muffle furnace, which is designed for greater capacity.
By understanding that atmospheric control is a deliberate engineering choice, you can select a furnace that is precisely tailored to your technical and operational goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Tube Furnace | Standard Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Removes air, allows vacuum or controlled gases | Operates in ambient air only |
| Key Applications | Oxygen-sensitive processes, annealing, brazing, material purity | Basic heat treatments in air, ceramic curing |
| Cost and Complexity | Higher due to pumps, seals, and controls | Lower, simpler design |
| Sample Size | Limited to tube diameter; better for smaller samples | Limited to tube diameter; similar constraints |
Unlock Precision in Your Lab with KINTEK Solutions
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your unique experimental needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your requirements—whether you need atmospheric control for oxygen-sensitive materials or cost-effective standard options.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your processes, improve material integrity, and boost efficiency. Let's find the perfect furnace for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















