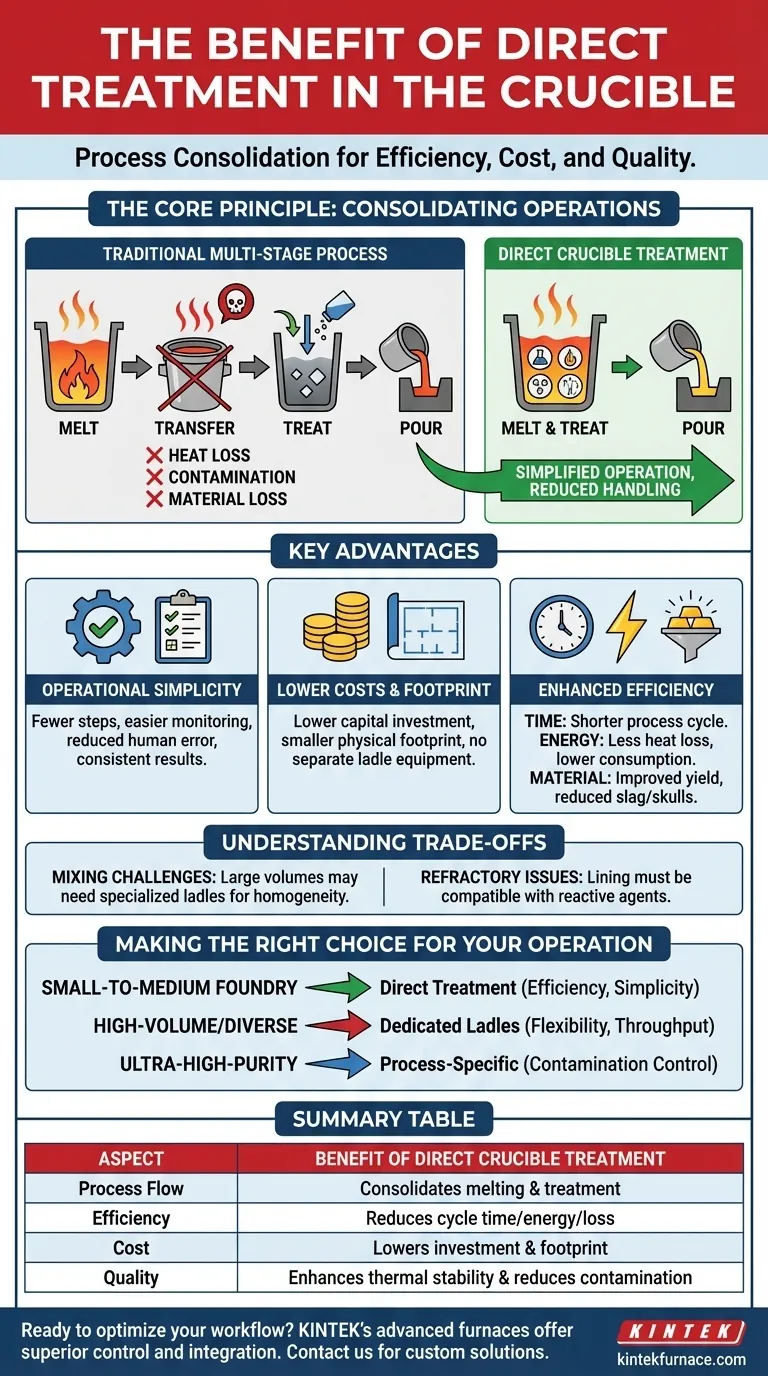
The primary benefit of treating a molten metal directly in its crucible is process consolidation. By performing tasks like alloying, degassing, or inoculation in the same vessel used for melting, you eliminate the need for a separate treatment station, which simplifies the entire operation, reduces handling, and conserves energy.
Treating metal directly in the crucible is a strategic choice to minimize process variables. It moves beyond simple convenience to offer tangible gains in efficiency, cost, and material consistency by reducing the number of steps between melting and casting.

The Core Principle: Consolidating Operations
Direct crucible treatment fundamentally changes the workflow in a foundry or lab. Instead of a multi-stage process (melt -> transfer -> treat -> pour), it becomes a more integrated sequence.
Eliminating the Transfer Step
The most significant change is the removal of the transfer step, where molten metal is poured from the furnace or crucible into a separate treatment ladle. This single change has numerous downstream effects.
By treating the melt in place, you avoid the logistical complexity and time required to move large quantities of high-temperature liquid metal across a facility.
Maintaining Thermal Stability
Transferring molten metal inevitably leads to heat loss. To compensate, the metal must often be superheated (using more energy) or the transfer ladle must be pre-heated (also using energy).
Direct treatment in the crucible minimizes this temperature drop, leading to a more stable and predictable process with lower overall energy consumption.
Reducing Contamination and Material Loss
Every time you pour molten metal, you introduce turbulence. This turbulence can increase gas pickup from the atmosphere and create more dross or slag.
Furthermore, a small amount of metal (known as a "skull") often solidifies and is left behind in the transfer vessel. Direct treatment minimizes these sources of contamination and material loss.
Key Advantages of Direct Crucible Treatment
The principle of consolidation translates into several distinct operational and financial advantages.
Operational Simplicity
Fewer steps mean a simpler process that is easier to manage, monitor, and control. This reduces the potential for human error during transfer and handling.
This streamlined workflow simplifies operator training and can lead to more consistent, repeatable results from batch to batch.
Lower Equipment Costs and Footprint
By eliminating the need for separate treatment ladles and associated handling equipment (like specialized cranes or transport cars), the initial capital investment is lower.
This also reduces the overall physical footprint required for the melting operation, a critical factor in facility design and optimization.
Enhanced Efficiency
Efficiency gains are realized in three key areas:
- Time: The process cycle is shorter without the transfer step.
- Energy: Less heat is lost, so less energy is needed to maintain the target temperature.
- Material: Reduced slag formation and elimination of skulls in transfer ladles improve the overall yield from your raw materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While advantageous, direct crucible treatment is not universally superior. Certain limitations must be considered.
Mixing and Homogeneity
For very large melt volumes or for alloy additions that require vigorous stirring, a specially designed treatment ladle may provide more effective and homogenous mixing. Achieving the same level of mixing in a standard melting crucible can be challenging.
Refractory Compatibility
The refractory lining of the crucible must be compatible with both the melting process and any reactive agents used for treatment. In some cases, a treatment agent may aggressively attack the crucible lining, making a separate, potentially disposable-lined ladle a better choice.
Process Flexibility
If a single large melt needs to be split into several smaller batches with different treatments, a multi-ladle approach is necessary. Direct crucible treatment locks you into a single treatment protocol for the entire batch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
The decision to use direct crucible treatment depends entirely on your production goals, scale, and the specific alloys you work with.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency in a small- to medium-sized foundry: Direct treatment is often the ideal choice for its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and energy savings.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, diverse production: Using dedicated treatment ladles may offer the flexibility and throughput required to manage multiple alloy specifications simultaneously.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high-purity or specialty alloys: The choice depends on which method offers superior control over atmospheric contamination and refractory interactions for your specific process.
Ultimately, choosing to treat your melt directly in the crucible is a powerful way to streamline your workflow and reduce operational complexity.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Benefit of Direct Crucible Treatment |
|---|---|
| Process Flow | Consolidates melting & treatment into one step |
| Efficiency | Reduces cycle time, energy use, and material loss |
| Cost | Lowers equipment investment and operational footprint |
| Quality | Enhances thermal stability and reduces contamination |
Ready to optimize your metal melting and treatment workflow? KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces, including our Muffle and Crucible Furnaces, are engineered for superior thermal control and process integration. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide deep customization to precisely meet your unique operational requirements, whether you're in a foundry or a research lab. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your efficiency and material yield!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















