In essence, gas quenching is a heat treatment process that rapidly cools heated steel parts using a high-pressure stream of gas to achieve specific hardness and strength properties. Unlike traditional methods that submerge parts in oil or water, gas quenching offers a highly controlled, cleaner alternative, fundamentally changing the risk profile for distortion and part quality.
Gas quenching trades the raw cooling power of liquids for unparalleled process control. This makes it the superior choice for high-value, dimensionally sensitive components, but limits its use to steels with sufficient hardenability.
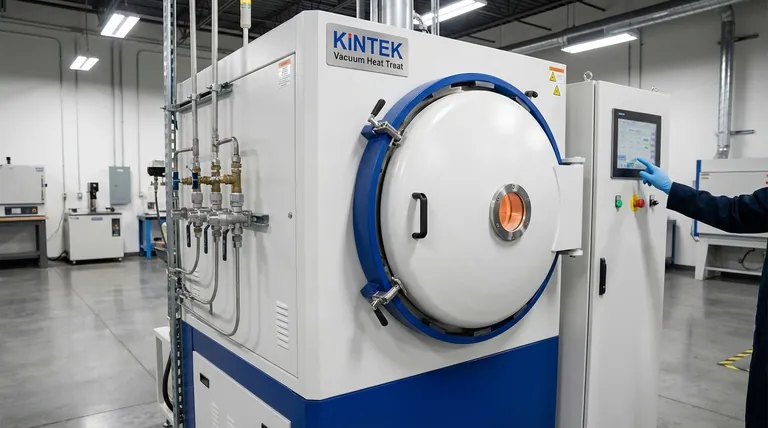

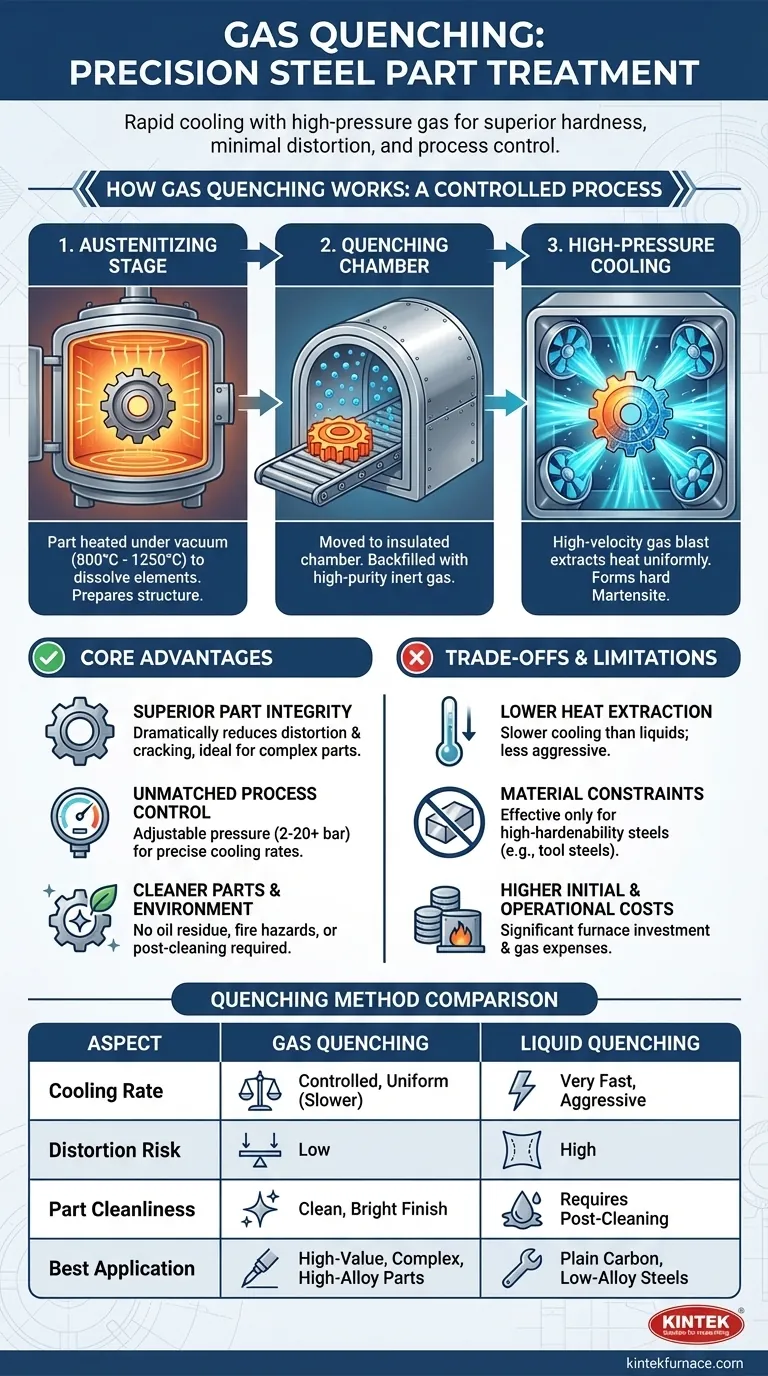
How Gas Quenching Works: A Controlled Process
Gas quenching is almost always performed inside a vacuum furnace, which provides a pristine, controlled environment from start to finish. The process follows a precise sequence.
The Austenitizing Stage
First, the steel part is heated under a vacuum to a specific critical temperature, typically between 800°C and 1250°C. This stage, known as austenitizing, dissolves carbon and alloying elements into a uniform solid solution, transforming the steel's crystal structure and preparing it for hardening.
The Quenching Chamber
Once the part is thoroughly soaked at its austenitizing temperature, it is moved into an insulated cooling chamber. The chamber is then backfilled with a high-purity inert gas at a controlled pressure.
High-Pressure Cooling
High-velocity turbines or fans blast the quenching gas onto the part from all directions. This convective cooling rapidly and uniformly extracts heat, forcing the steel's internal structure to transform into martensite, a very hard and strong crystal phase. The cooling rate is precisely managed by adjusting the gas type, pressure, and flow velocity.
The Core Advantages of Using Gas
Choosing gas over a liquid like oil or water is a deliberate engineering decision driven by the need for precision and part quality.
Superior Part Integrity
Because gas cooling is more uniform and less violent than liquid immersion, it dramatically reduces thermal shock. This results in significantly less distortion, warping, and cracking, which is critical for complex geometries, thin-walled parts, or components with tight dimensional tolerances.
Unmatched Process Control
Gas pressure, which can range from 2 to 20 bar or more, is easily and precisely adjustable. This allows heat treaters to fine-tune the cooling rate to match the specific steel alloy and part thickness, achieving the desired metallurgical properties without over-stressing the component.
Cleaner Parts and Environment
Gas-quenched parts emerge from the furnace clean, bright, and free of residue. This eliminates the need for costly and labor-intensive post-quench cleaning operations required to remove oil. It also removes fire hazards, oil fumes, and the need to dispose of used quenching liquids.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, gas quenching is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is governed by a clear set of physical and economic trade-offs.
Lower Heat Extraction Rate
The primary limitation of gas is its lower thermal conductivity compared to liquids. Even at high pressures, gas simply cannot pull heat out of a part as aggressively as oil or water.
Material and Hardenability Constraints
This lower cooling power means gas quenching is only effective for steels with high hardenability. These are typically air-hardening tool steels or highly alloyed steels designed to harden with slower cooling rates. It is generally unsuitable for plain carbon or low-alloy steels, which require a very fast quench to form martensite.
Part Size and Thickness Limits
The lower heat extraction rate also limits the maximum cross-sectional thickness that can be effectively hardened. The core of a very thick part may cool too slowly, failing to achieve the required hardness, even if the surface hardens properly.
Higher Initial and Operational Costs
Vacuum furnaces capable of high-pressure gas quenching are a significant capital investment. Furthermore, the cost of high-purity gases like nitrogen, helium, or argon adds to the operational expense compared to less expensive quench oils.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between gas and liquid quenching hinges entirely on the part's material, complexity, and final requirements.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion on high-value, complex parts: Gas quenching is the definitive choice for preserving dimensional accuracy.
- If your primary focus is hardening air-hardening tool steels or high-alloy materials: Gas quenching provides the ideal combination of cooling speed and control for these materials.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for low-alloy or plain carbon steels: Traditional liquid quenching remains the more practical and effective method.
Ultimately, understanding these trade-offs empowers you to select the process that delivers the required performance without compromising the integrity of your component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Gas Quenching | Traditional Liquid Quenching |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Medium | High-pressure inert gas (e.g., nitrogen, helium) | Oil or water |
| Cooling Rate | Controlled and uniform, slower than liquids | Very fast and aggressive |
| Distortion Risk | Low due to reduced thermal shock | High, can cause warping and cracking |
| Part Cleanliness | Clean, bright finish, no residue | Requires post-cleaning for oil removal |
| Suitable Materials | High-hardenability steels (e.g., tool steels) | Plain carbon and low-alloy steels |
| Cost | Higher initial and operational costs | More cost-effective for certain applications |
Optimize your steel part treatment with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored systems like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise matching to your unique experimental needs, whether for gas quenching or other processes. Contact us today to enhance part integrity, achieve superior hardness, and streamline your heat treatment workflows!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion



















