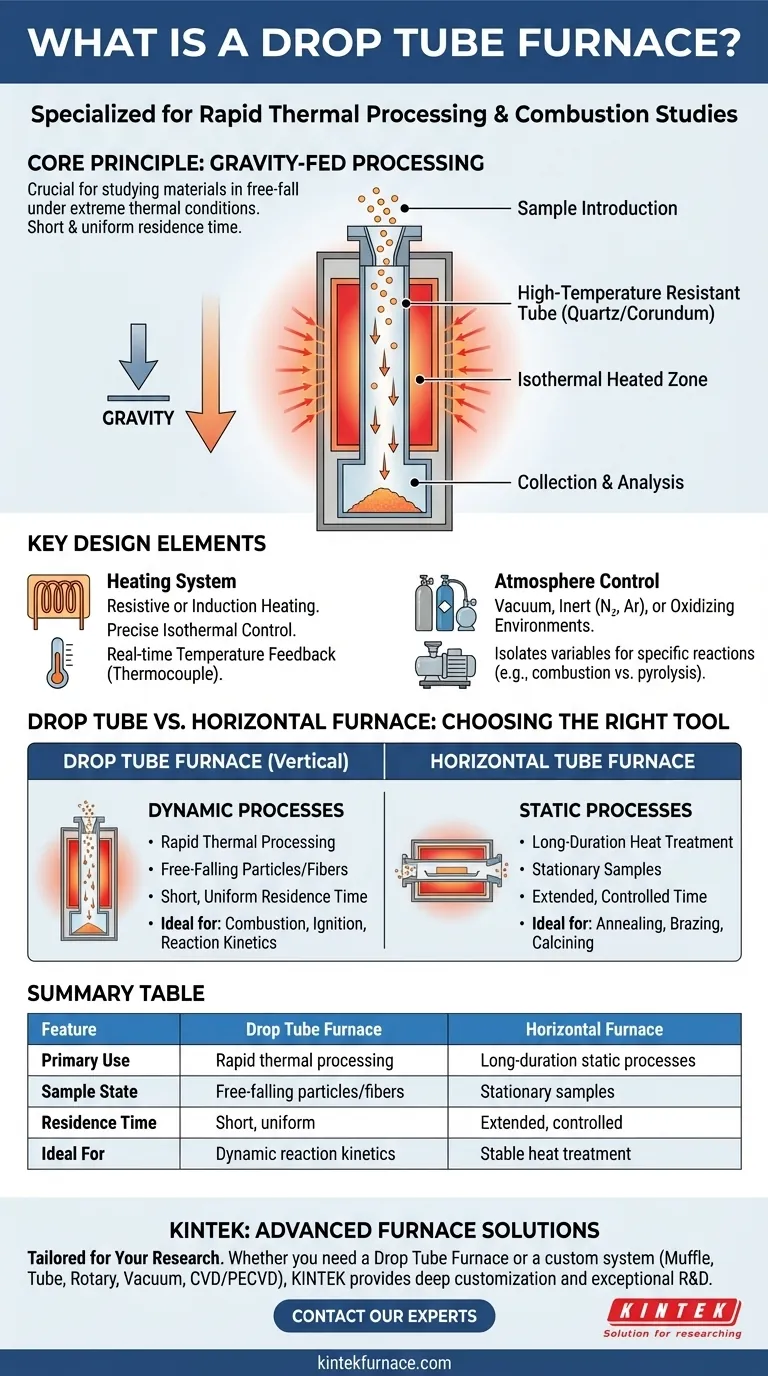
In essence, a drop tube furnace is a specialized piece of laboratory equipment designed for a very specific purpose: to study how materials behave when dropped through an intensely hot, precisely controlled environment. It is a vertically oriented furnace that uses gravity to pass a sample through a thermal processing zone, making it ideal for researching rapid processes like combustion and ignition.
The critical distinction of a drop tube furnace is its vertical design. This isn't an arbitrary choice; it is fundamental to its function, enabling the study of materials in free-fall under extreme thermal conditions, a scenario impossible to replicate in a standard horizontal furnace.
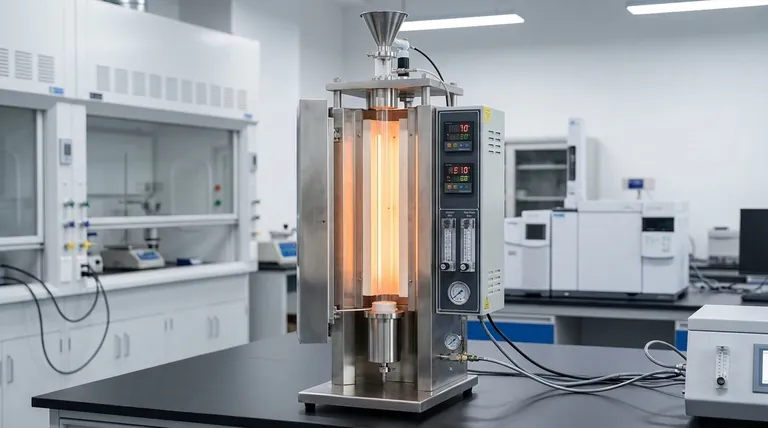

The Purpose of Vertical Design
A drop tube furnace’s entire construction is dictated by its primary research application: understanding dynamic thermal reactions.
The Principle of Gravity-Fed Processing
The furnace consists of a long, vertical tube, typically made of high-temperature resistant materials like quartz or corundum to prevent contamination.
Material samples, often fine particles, are introduced at the top and fall through the central heated zone. This free-fall provides a very short and uniform residence time at high temperatures, which is crucial for studying rapid reaction kinetics.
Simulating Industrial Conditions
This setup is ideal for simulating processes like oxy-steam combustion or gasification, where fuel particles are injected into a hot chamber.
By controlling the furnace's atmosphere and temperature, researchers can precisely analyze ignition characteristics, reaction rates, and the byproducts formed during these brief, intense events.
Key Design and Operational Elements
The effectiveness of a drop tube furnace hinges on its ability to create a stable, reproducible, and precisely controlled environment.
The Heating System
Heating is achieved either through resistive heating elements (like silicon carbide rods) surrounding the tube or via medium-frequency induction heating.
The goal is to create an isothermal (uniform temperature) zone through which the sample falls, ensuring every particle experiences the same thermal history. A thermocouple provides real-time temperature feedback for precise control.
Atmosphere Control
These furnaces can operate under a variety of atmospheric conditions, including vacuum, inert gas (like nitrogen or argon), or an oxidizing environment.
This capability is essential for isolating variables. For example, studying combustion requires an oxidizing atmosphere, while studying thermal decomposition without burning (pyrolysis) requires an inert one.
The Insulation and Casing
A robust insulation layer surrounds the heating chamber to minimize heat loss and ensure energy efficiency. The entire assembly is housed in a durable outer casing, typically made of stainless steel, for structural integrity and operator safety.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Drop Tube vs. Horizontal Furnace
Choosing the correct furnace type is critical, as they are designed for fundamentally different tasks. The orientation—vertical versus horizontal—is the most important factor.
When to Use a Drop Tube Furnace
A drop tube furnace is the superior choice for experiments involving rapid thermal processing of particles or fibers. Its design is optimized for studying dynamic events where the sample is in motion.
If your research involves ignition delay, combustion efficiency, or the rapid thermal decomposition of free-falling materials, this is the correct instrument.
When a Horizontal Furnace is Better
A horizontal tube furnace is built for static, long-duration processes. It is used for tasks like annealing, brazing, and calcining, where a sample is placed in the furnace and held at a specific temperature for an extended period.
Attempting to study falling particles in a horizontal furnace would be impractical, just as using a drop tube furnace for a multi-hour annealing process would be inefficient and difficult to manage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct equipment, you must first define your experimental objective.
- If your primary focus is studying combustion or rapid particle reactions: The drop tube furnace is specifically engineered for gravity-fed, short-duration thermal analysis.
- If your primary focus is long-duration heat treatment of a static sample: A horizontal tube furnace provides the stability and sample-handling required for annealing or calcining.
- If your primary focus is precise atmospheric control during a reaction: Both furnace types offer this, but the drop tube is designed to study how a material reacts as it passes through that atmosphere, not just while it sits in it.
Ultimately, understanding the core design principle—gravity-driven processing—is the key to deploying this powerful research tool effectively.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Drop Tube Furnace | Horizontal Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Rapid thermal processing (combustion, ignition) | Long-duration static processes (annealing, calcining) |
| Sample State | Free-falling particles/fibers | Stationary samples |
| Residence Time | Short, uniform | Extended, controlled |
| Ideal For | Dynamic reaction kinetics | Stable heat treatment |
Need a furnace tailored for your specific research? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Whether you require a Drop Tube Furnace for combustion studies or a custom Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, or CVD/PECVD system, our deep customization capabilities ensure your unique experimental requirements are met precisely. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















