At its core, an IGBT induction melting furnace is a modern industrial furnace that uses a specific type of high-power, high-frequency switch—the Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)—to control its power supply. This technology allows for the rapid, efficient, and precise melting of metals like steel, iron, copper, and aluminum by leveraging electromagnetic induction. Unlike older systems, IGBT-based furnaces provide a constant power output and create significantly less electrical interference on the power grid.
The central advantage of an IGBT furnace is not just that it melts metal, but how it controls the energy to do so. By using modern solid-state electronics, it achieves faster melting speeds, higher energy efficiency, and greater operational stability compared to previous generations of induction technology.
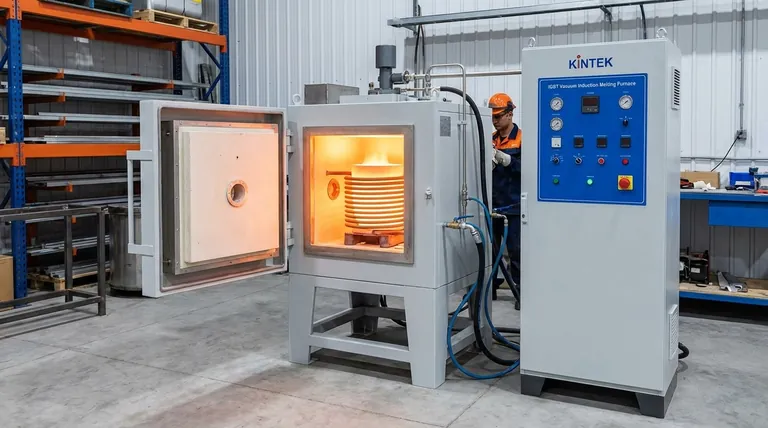

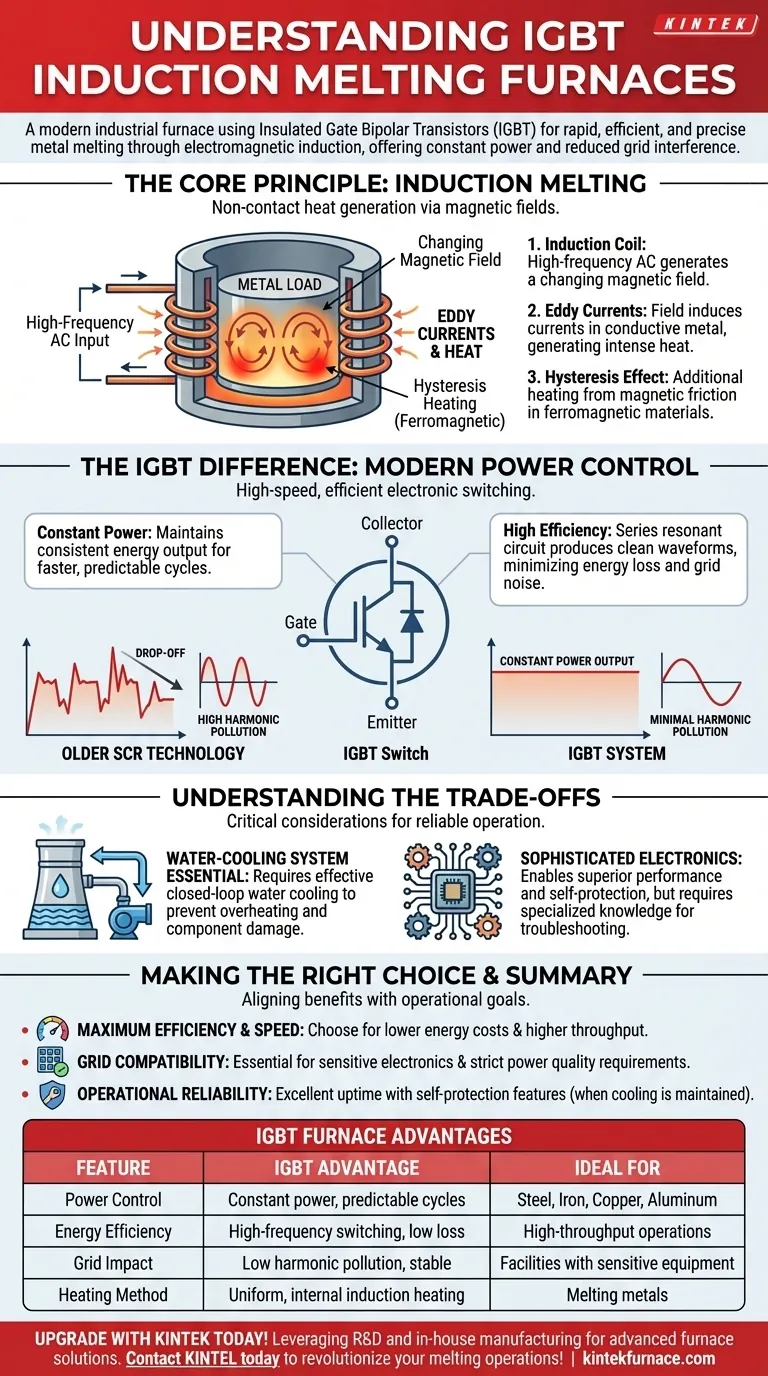
The Core Principle: How Induction Melting Works
To understand the IGBT's role, we must first understand the fundamental process of induction heating. This is a non-contact method that uses powerful magnetic fields to generate heat directly within the target material.
The Role of the Induction Coil
The process begins with a high-frequency alternating current (AC) passing through a copper coil. This coil surrounds a crucible containing the metal charge to be melted.
Generating Heat Through Eddy Currents
The powerful AC flowing through the coil generates a rapidly changing magnetic field. When the conductive metal is placed inside this field, the magnetic fluctuations induce powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, to flow within the metal itself. The metal's natural electrical resistance causes these eddy currents to dissipate energy in the form of intense heat, causing the material to melt from the inside out.
The Added Effect in Ferromagnetic Materials
For ferromagnetic materials like iron, there is an additional heating effect. The rapidly alternating magnetic field forces the magnetic domains within the iron to constantly realign. This internal friction generates even more heat, a process known as hysteresis heating, which contributes to a faster melting cycle.
The IGBT Difference: Modernizing Power Control
The "IGBT" in the name refers to the critical component that manages the furnace's power supply. This is the key technological differentiator that provides its main advantages.
What is an IGBT?
An Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) is a high-power semiconductor device used as an electronic switch. In a furnace, it precisely chops and shapes electricity from the grid into the high-frequency AC needed by the induction coil. Its ability to switch on and off thousands of times per second with very little energy loss is what makes it so efficient.
The Advantage of Constant Power Output
A defining feature of IGBT systems is their ability to maintain constant power output throughout the entire melting process. The power delivered to the melt does not decrease as the furnace lining wears or as the properties of the load change. This ensures consistent, predictable, and faster melting cycles compared to older SCR (Silicon-Controlled Rectifier) technology, which often sees power drop-off under varying conditions.
Why IGBTs are More Efficient
IGBT technology operates as a series resonant circuit, which is inherently more efficient at starting and running. It produces very clean electrical waveforms, resulting in minimal harmonic pollution. This means it does not inject disruptive "noise" back into the facility's power grid, preventing interference with other sensitive electronic equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, IGBT technology comes with its own set of operational considerations. Understanding these is key to reliable performance.
The Criticality of the Cooling System
The high power being switched by the IGBT modules generates significant heat. An effective water-cooling system is not just a feature but an absolute necessity. These systems often use distilled water in a closed loop to prevent mineral buildup (scaling), as any interruption or failure in cooling will immediately shut down the furnace and can damage the power components.
Complexity of Modern Electronics
The electronics that drive an IGBT furnace are sophisticated. While this enables superior performance and self-protection features, it also means that troubleshooting and repair require specialized knowledge and components. This stands in contrast to older, mechanically simpler systems that may be easier to diagnose with basic electrical skills.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
An IGBT induction furnace is a powerful tool, but its benefits are most pronounced when aligned with specific operational goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum efficiency and speed: The constant power output and high electrical efficiency of an IGBT furnace make it the superior choice for minimizing energy costs and maximizing production throughput.
- If your primary focus is grid compatibility and low interference: The minimal harmonic pollution of an IGBT system makes it essential for facilities with sensitive electronics or strict power quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is operational reliability: A modern IGBT furnace offers excellent uptime due to its comprehensive self-protection functions, provided its critical cooling system is meticulously maintained.
Ultimately, choosing an IGBT furnace is an investment in a more controlled, efficient, and stable melting process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | IGBT Furnace Advantage |
|---|---|
| Power Control | Constant power output for faster, predictable melting cycles |
| Energy Efficiency | High-frequency switching minimizes energy loss |
| Grid Impact | Low harmonic pollution, stable for sensitive equipment |
| Heating Method | Non-contact induction heating for uniform, internal melting |
| Ideal For | Steel, iron, copper, aluminum, and high-throughput operations |
Ready to upgrade your melting process with superior control and efficiency?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse foundries and metalworking facilities with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including IGBT Induction Melting Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique production requirements and maximize your operational uptime.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss how our IGBT furnace technology can revolutionize your metal melting operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















