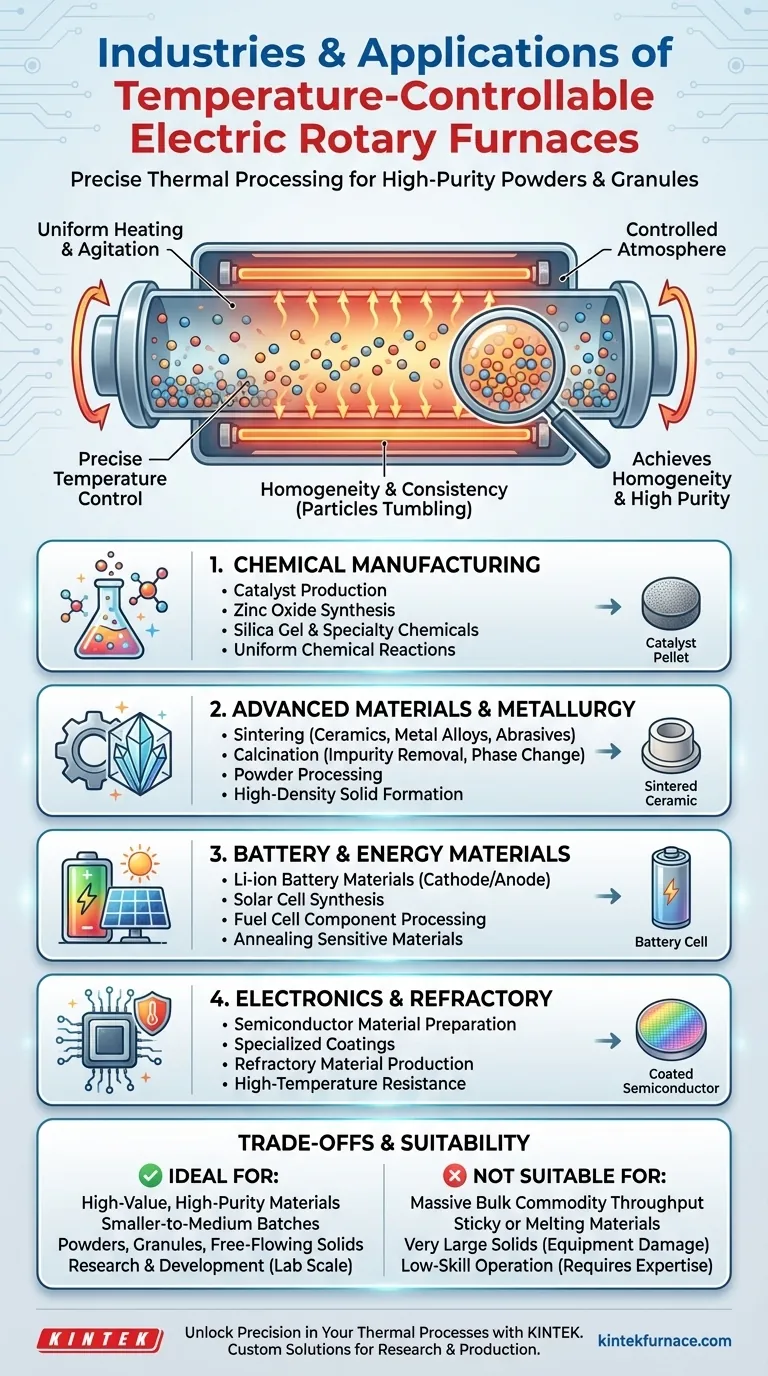
In short, temperature-controllable electric rotary furnaces are cornerstone tools in industries requiring precise thermal processing of powdered or granular materials. Key sectors include chemical manufacturing, advanced materials science, metallurgy, and the electronics industry, where they are essential for creating high-purity and highly consistent products.
The true value of a rotary furnace lies not in the specific industries it serves, but in the process capability it offers: uniformly heating and agitating materials under tightly controlled atmospheric and thermal conditions. This is why it is indispensable for developing and producing advanced materials where consistency is paramount.
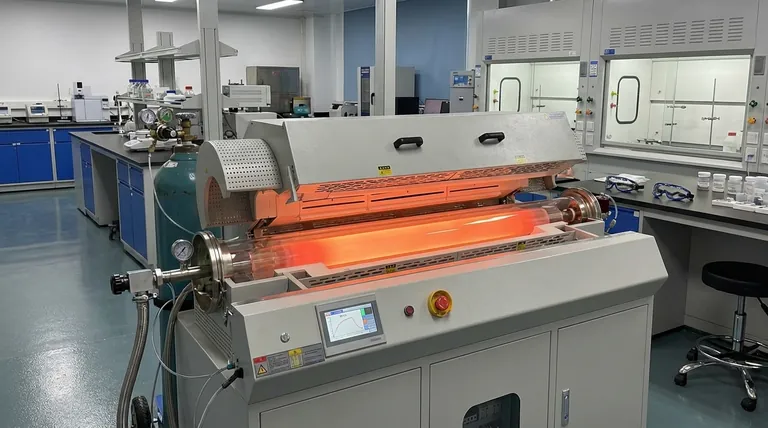

The Core Function: Processing Materials with Unmatched Uniformity
An electric rotary furnace is not simply a hot tube; it is a highly engineered system designed for a specific purpose. Understanding its core function reveals why it is so critical in certain fields.
What Makes a Rotary Furnace Unique?
The defining feature is the slow, continuous rotation of the furnace tube. This tumbling action constantly exposes new surfaces of the material to the heat source and the internal atmosphere.
This agitation is crucial for achieving homogeneity. It prevents hot spots, ensures all particles undergo the same thermal cycle, and facilitates uniform chemical reactions throughout the batch.
The Role of Electric Heating and Precision Control
Unlike fuel-fired kilns, electric heating elements allow for exceptionally precise temperature control. This is often coupled with sophisticated control systems that can execute complex temperature profiles with high repeatability.
For advanced materials like semiconductors or catalysts, this level of control is not a luxury—it is a requirement for achieving the desired material properties and ensuring reproducible results.
Key Industrial Applications and Processes
The furnace's capabilities directly map to specific, high-value industrial processes. Its use in an industry is a signal that material consistency and purity are top priorities.
Chemical Synthesis and Catalyst Production
Industries use these furnaces for producing materials like zinc oxide, silica gel, and various catalysts. The dynamic roasting environment ensures that chemical reactions proceed evenly, yielding a product with consistent activity and structure.
Advanced Materials and Metallurgy
In metallurgy and materials science, rotary furnaces are used for sintering, a process that fuses powders together to form a solid, dense object. This is common for creating advanced ceramics, metal alloys, and abrasive powders.
They are also used for calcination, a thermal decomposition process to remove impurities or create a new phase of a material.
Battery and Energy Materials
The production of materials for lithium-ion batteries, solar cells, and fuel cells relies heavily on precise thermal processing. A rotary furnace provides the controlled environment needed to synthesize and anneal these sensitive materials, directly impacting the final performance of the energy device.
Electronics and Refractory Materials
For the electronics industry, these furnaces help prepare semiconductor materials and specialized coatings. Their use also extends to producing refractory materials, which are designed to withstand extremely high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, an electric rotary furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Throughput vs. Precision
These furnaces are masters of precision but are generally not designed for the massive throughput seen in bulk commodity processing. They are better suited for high-value, smaller-to-medium batch sizes where quality is more important than sheer volume.
Material Suitability
The ideal materials are powders, granules, or small, free-flowing solids. Materials that can melt and become sticky, or those that are very large, are not suitable for a rotary furnace as they will not tumble correctly and can damage the equipment.
Operational Complexity
The rotating seals required to maintain a controlled atmosphere can add complexity and maintenance requirements compared to a static furnace. The system's sophistication requires a higher degree of operator skill to run effectively.
Is a Rotary Furnace Right for Your Application?
The decision to use a temperature-controllable electric rotary furnace comes down to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material synthesis: A rotary furnace is ideal for ensuring uniform reactions, preventing contamination, and achieving consistent batch-to-batch quality.
- If your primary focus is large-scale bulk drying of a simple material: A less complex and potentially more cost-effective direct-fired rotary kiln might be a better fit.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A laboratory-scale rotary tube furnace offers the process control, flexibility, and data accuracy needed for repeatable experiments.
Ultimately, choosing this technology is a decision to prioritize material consistency and process control above all else.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Chemical Manufacturing | Catalyst production, zinc oxide synthesis |
| Advanced Materials Science | Sintering, calcination of ceramics and alloys |
| Metallurgy | Metal powder processing, refractory material production |
| Electronics | Semiconductor material preparation, specialized coatings |
| Battery and Energy | Lithium-ion battery materials, solar cell synthesis |
Unlock Precision in Your Thermal Processes with KINTEK
Are you working with powders or granular materials that demand uniform heating and exact temperature control? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for industries like chemical synthesis, materials science, and electronics. Our product line—including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure our equipment precisely meets your unique experimental and production needs for superior consistency and purity.
Don't let process variability hold you back—contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your material quality and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















