In a vacuum furnace, the heating process is designed to treat materials in a controlled, inert environment, but this very act of heating works against the vacuum itself. As the temperature rises, the vacuum level inevitably degrades, meaning the pressure inside the chamber increases. This phenomenon is a fundamental aspect of vacuum thermal processing and is caused by the release of trapped gases from both the workpiece and the internal furnace components.
The core challenge of vacuum furnace operation is managing a dynamic conflict: the vacuum pump system is constantly working to remove gas, while the heating process is actively releasing new gas into the chamber. The final quality of your product depends entirely on how well you control this balance.
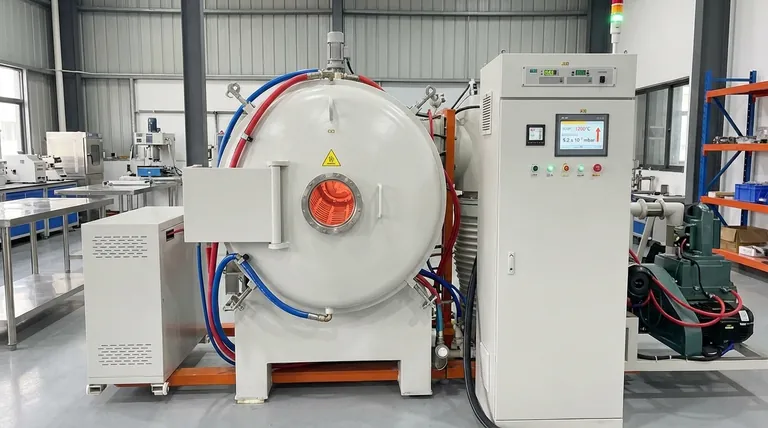

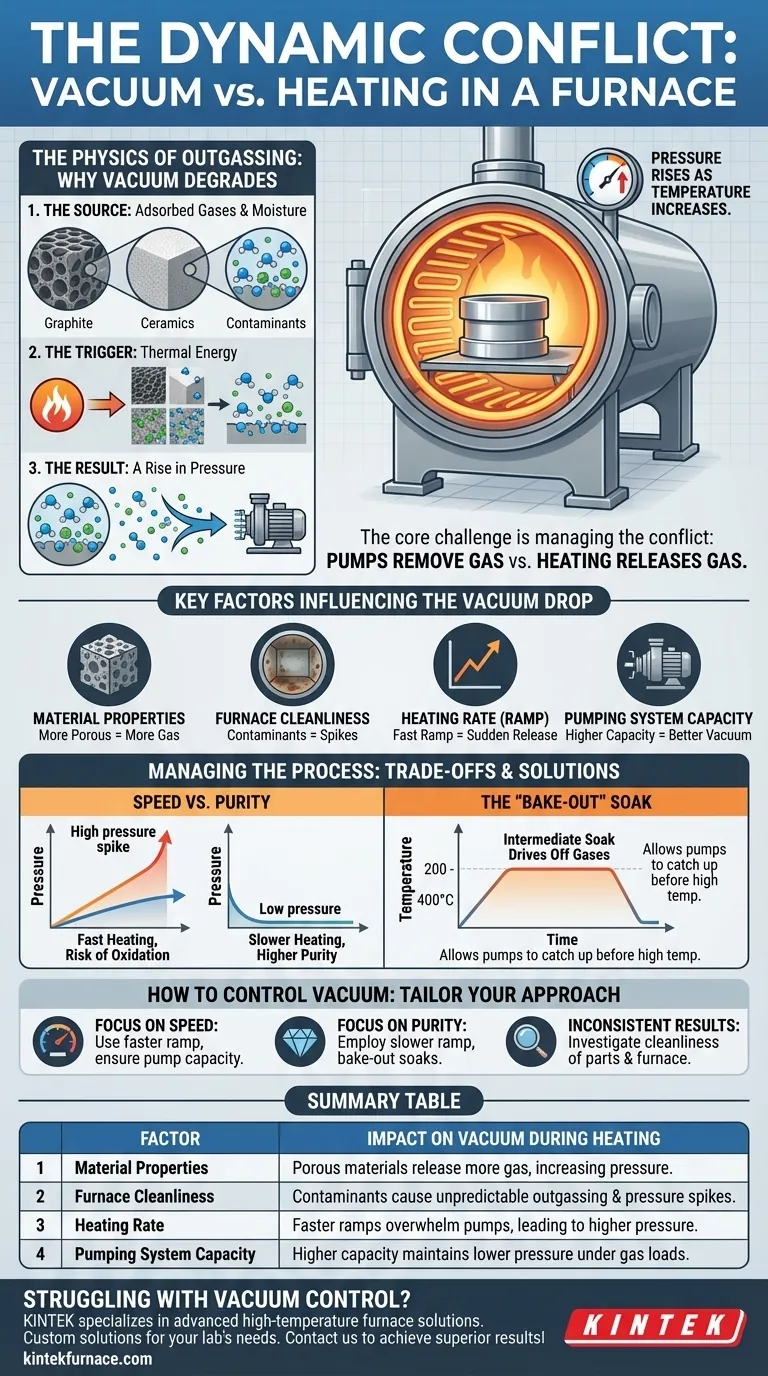
The Physics of Outgassing: Why Vacuum Degrades
The degradation of vacuum during heating is not a system failure; it is a predictable physical process known as outgassing. Understanding its mechanics is crucial for controlling your process.
The Source: Adsorbed Gases and Moisture
Surfaces that appear clean and solid at a microscopic level are covered with molecules from the atmosphere, primarily water vapor, but also oils, cleaning agents, and other volatile compounds. These molecules are physically or chemically bonded (adsorbed) to the material's surface and trapped within its pores.
The Trigger: Thermal Energy
Heating the material provides the necessary thermal energy for these trapped molecules to break their bonds and escape into the chamber. As the temperature climbs, the rate of this gas release increases exponentially.
The Result: A Rise in Pressure
The vacuum pump system is designed to remove a certain volume of gas per unit of time. When the rate of outgassing exceeds the rate at which the pumps can remove the gas, the overall pressure inside the chamber rises, and the vacuum level degrades.
Key Factors Influencing the Vacuum Drop
The severity of the vacuum drop is not constant; it depends on several critical factors that you can often control.
Material Properties and Condition
Porous materials like graphite insulation, ceramics, or unsintered powdered metals have an enormous internal surface area and can hold significantly more trapped gas than dense, non-porous metals. Likewise, a "clean" part that was recently exposed to humid air will outgas more than one stored in a dry environment.
Furnace Cleanliness
The furnace chamber itself is a major source of outgassing. Insulation materials like carbon felt and graphite are highly porous. Over time, they can accumulate contaminants from previous cycles, which will then be released during subsequent heating runs, causing inconsistent results.
Heating Rate (Ramp Rate)
A rapid increase in temperature will cause a sudden, massive release of gas, which can easily overwhelm the pumping system and cause a dramatic pressure spike. A slower, more controlled heating ramp allows the gases to evolve gradually, giving the pumps time to remove them and maintain a better vacuum.
Pumping System Capacity
The size and type of your vacuum pumps determine the maximum gas load they can handle. A system with higher pumping capacity will be able to manage a faster outgassing rate while maintaining a lower chamber pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Managing the Process
Successfully running a vacuum furnace involves balancing competing goals and understanding the consequences of your choices.
Speed vs. Purity
The most common trade-off is between process time and material purity. A fast heating cycle is more economical but risks a significant pressure spike. This temporary loss of vacuum can allow unwanted reactions, like oxidation, to occur on the material's surface, compromising the final product.
The "Bake-Out" Soak
A common strategy to manage this is to use an intermediate temperature "soak." The furnace is heated to a moderate temperature (e.g., 200-400°C) and held there. This is hot enough to drive off most of the water vapor and volatile contaminants but not hot enough to cause metallurgical changes. Once the outgassing subsides and the vacuum level recovers, the cycle continues to the higher target temperature.
The Risk of Overwhelming the Pumps
If the pressure rises too high, it can impact the efficiency and health of certain types of vacuum pumps, like diffusion or turbomolecular pumps. Process control systems often have high-pressure setpoints that will abort a heating cycle to prevent damage to the equipment or the product.
How to Control Vacuum During Heating
Controlling the vacuum level is about managing the rate of outgassing relative to your pumping speed. Your approach should be tailored to your specific process goals.
- If your primary focus is process speed: You can use a faster heating ramp, but you must ensure your pumping system can handle the resulting gas load without letting the pressure exceed the maximum allowed for your process.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity: Employ a slower, more deliberate heating ramp and incorporate bake-out soaks at intermediate temperatures to allow gases to evolve slowly and be removed effectively by the pumps.
- If you are experiencing inconsistent results: The first step is to investigate the cleanliness of both your parts and the furnace interior, as residual contamination is the most common cause of unpredictable outgassing.
Ultimately, mastering the interplay between heat, materials, and vacuum is the defining skill in high-quality thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Vacuum During Heating |
|---|---|
| Material Properties | Porous materials release more gas, increasing pressure |
| Furnace Cleanliness | Contaminants cause unpredictable outgassing and pressure spikes |
| Heating Rate | Faster ramps overwhelm pumps, leading to higher pressure |
| Pumping System Capacity | Higher capacity maintains lower pressure under gas loads |
Struggling with vacuum control in your thermal processes? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, designed to handle outgassing challenges with precision. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity



















