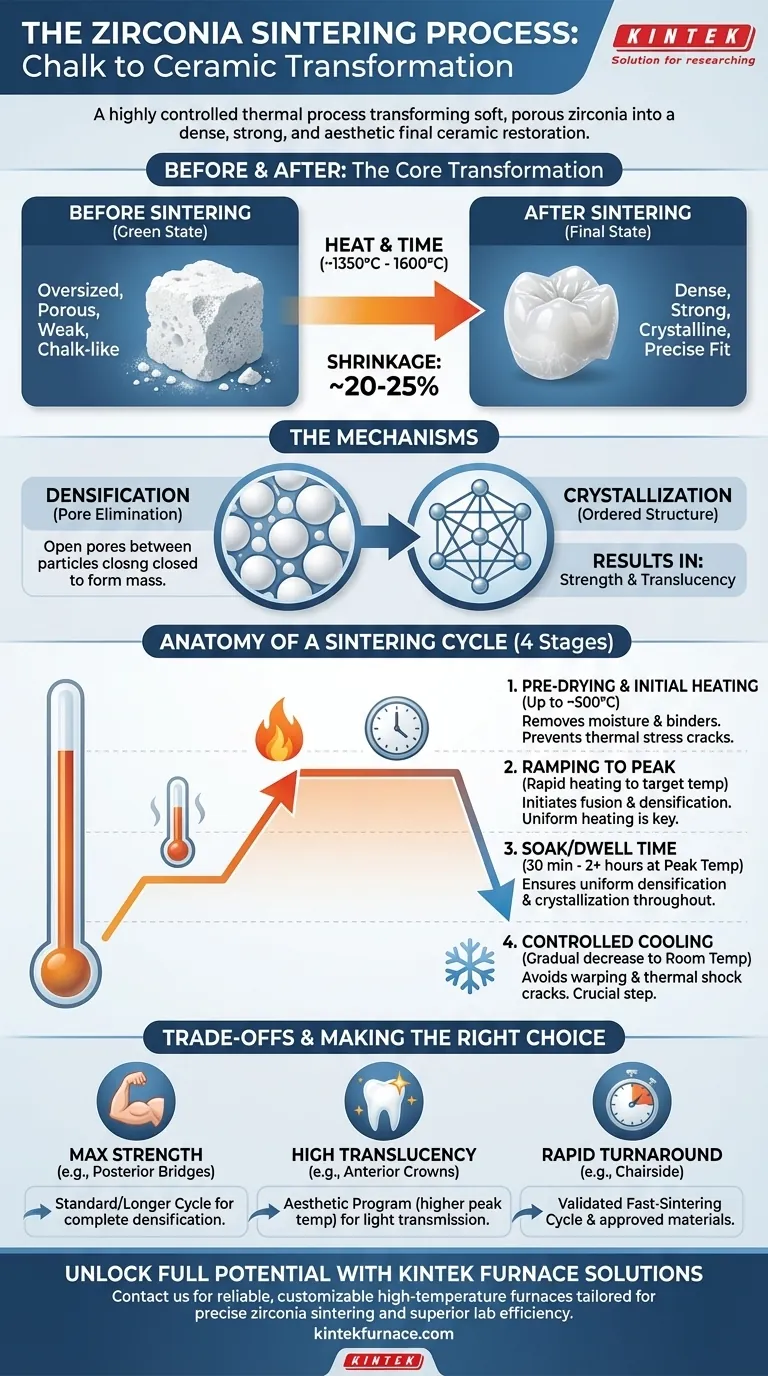
At its core, sintering is a highly controlled thermal process that transforms a soft, porous zirconia pre-form into a dense, strong, and aesthetically pleasing final ceramic restoration. During this process, the material is heated to a temperature just below its melting point, causing its individual particles to fuse together, eliminating porosity and shrinking the object to its final, pre-calculated dimensions.
Sintering is not merely heating; it is a meticulous metallurgical transformation. The process intentionally shrinks the zirconia by roughly 20-25%, turning a chalk-like, oversized milling blank into a strong, dense, and precisely fitting final restoration.
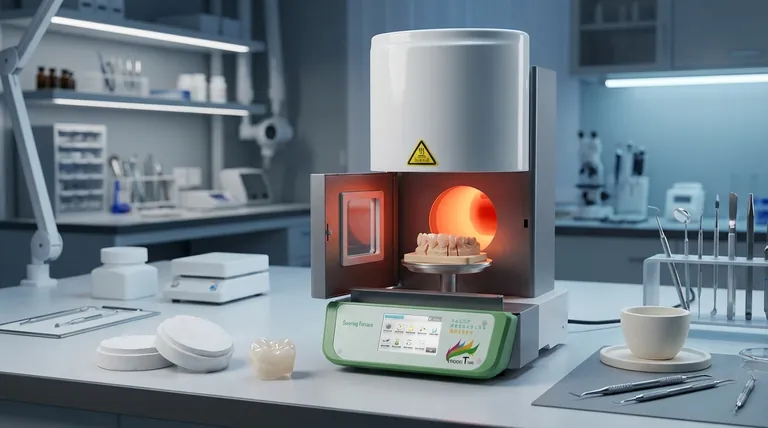

From "Chalk" to Ceramic: The Transformation
Before sintering, a zirconia restoration does not possess the qualities required for clinical use. The sintering cycle is what unlocks the material's potential.
The Starting Point: The "Green" State
The process begins with a zirconia object in its "green" or "white" state. At this stage, it has been milled from a blank but is porous, weak, and feels like a piece of chalk.
To account for the predictable shrinkage that will occur, the restoration is milled significantly larger than its final intended size. This oversize factor is precisely calculated by the CAD/CAM software.
The Core Mechanism: Densification
As the furnace temperature rises, the individual zirconia particles begin to bond at their contact points. The primary goal is densification, where the spaces, or pores, between these particles are systematically eliminated.
Think of it like compacting loose snow into a solid, dense snowball. As the pores disappear, the entire structure shrinks and becomes much denser and more robust.
The Result of Heat: Crystallization
Simultaneously with densification, the heat causes the material's atoms to arrange themselves into a highly ordered and stable crystal structure. It is this final crystalline phase that gives zirconia its exceptional flexural strength and fracture toughness.
The final properties, including strength and translucency, are directly determined by the final density and grain structure achieved during this stage.
Anatomy of a Sintering Cycle
A typical sintering cycle is a carefully programmed sequence of heating and cooling stages, each with a specific purpose. These programs can range from 60 minutes to over 12 hours.
Stage 1: Pre-Drying and Initial Heating
The furnace heats up slowly at first. This gentle ramp-up allows any residual moisture or binders from the milling process to burn off without causing thermal stress, which could lead to cracks.
Stage 2: Ramping to Peak Temperature
The temperature then increases more rapidly toward its target, typically between 1350°C and 1600°C (2462°F and 2912°F), depending on the specific type of zirconia. The rate of this temperature increase is carefully controlled to ensure the restoration heats uniformly.
Stage 3: The "Soak" or Dwell Time
The furnace holds the restoration at the peak temperature for a set period, known as the "soak" or "dwell" time. This can range from 30 minutes to over two hours. This stage is critical for ensuring that densification and crystallization are completed uniformly throughout the entire restoration, even in its thickest parts.
Stage 4: Controlled Cooling
Just as important as heating, the cooling phase must be slow and controlled. Cooling too quickly creates internal stresses (thermal shock) that can cause warping or microscopic cracks, compromising the integrity and fit of the final restoration.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The parameters of the sintering cycle are chosen to balance competing properties. Changing one variable often impacts another, creating a series of critical trade-offs.
The Temperature vs. Translucency Dilemma
Higher sintering temperatures generally result in larger crystal grains, which can increase the material's translucency. However, exceeding the optimal temperature can sometimes lead to a slight reduction in flexural strength. This is a key consideration when choosing between materials for anterior versus posterior restorations.
The Speed vs. Stability Conundrum
Modern furnaces offer "fast sintering" cycles that can be completed in under two hours. While highly efficient for clinic workflow, these cycles demand extremely precise furnace control. The rapid heating and cooling rates increase the risk of thermal stress, potentially leading to lower stability or incomplete sintering if not executed perfectly.
The Shrinkage Factor
The significant shrinkage is a fundamental property, not a flaw. However, it leaves no room for error. Any miscalculation in the initial oversizing, or any deviation in the sintering process that alters the final shrinkage rate, will result in a restoration that does not fit the patient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Mastering the sintering process requires understanding how to tailor the protocol to the desired clinical outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength (e.g., for multi-unit posterior bridges): Adhere to the manufacturer's recommended standard or longer sintering cycle to ensure complete and uniform densification for optimal durability.
- If your primary focus is high translucency (e.g., for aesthetic anterior crowns): Use a zirconia material specifically designed for aesthetics and its corresponding sintering program, which may involve a higher peak temperature to enhance light transmission.
- If your primary focus is rapid turnaround (e.g., for chairside applications): Invest in a furnace capable of executing validated fast-sintering cycles and use only materials specifically approved for such protocols.
Ultimately, precise control over the sintering cycle is what transforms a simple zirconia blank into a high-performance dental restoration.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Temperature Range | Key Process | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Drying & Initial Heating | Up to ~500°C | Removes moisture and binders | Prevents cracks from thermal stress |
| Ramping to Peak | 1350°C - 1600°C | Rapid heating to sintering temperature | Initiates particle fusion and densification |
| Soak/Dwell Time | 30 min - 2+ hours | Holds at peak temperature | Ensures uniform densification and crystallization |
| Controlled Cooling | Gradual decrease | Slow cooling to room temperature | Avoids warping and cracks from thermal shock |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Zirconia Restorations with KINTEK
Are you striving for superior strength, precise fit, and enhanced aesthetics in your dental lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for sintering zirconia and other ceramics. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures that our furnaces precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements, whether you're focusing on maximum durability for multi-unit bridges, high translucency for anterior crowns, or rapid turnaround for chairside applications.
Don't let inconsistent sintering cycles compromise your results—contact us today to discuss how KINTEK's reliable and customizable solutions can elevate your lab's efficiency and output quality. Let's transform your zirconia blanks into high-performance dental restorations together!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the primary functions of ceramic dental furnaces? Achieve Precision and Durability in Dental Restorations
- Why is temperature range important when selecting a dental furnace? Unlock Material Compatibility and Precision
- Why is accurate temperature control important in dental furnaces? Ensure Perfect Restorations Every Time
- What is the importance of dental furnaces in dentistry? Ensure Strong, Precise Dental Restorations
- Why is using a universal setting for all materials in a dental furnace a mistake? Master Precision Sintering for Perfect Restorations



















