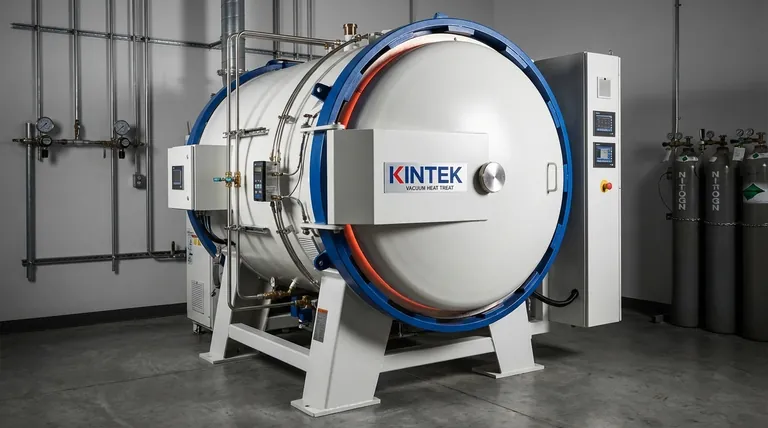
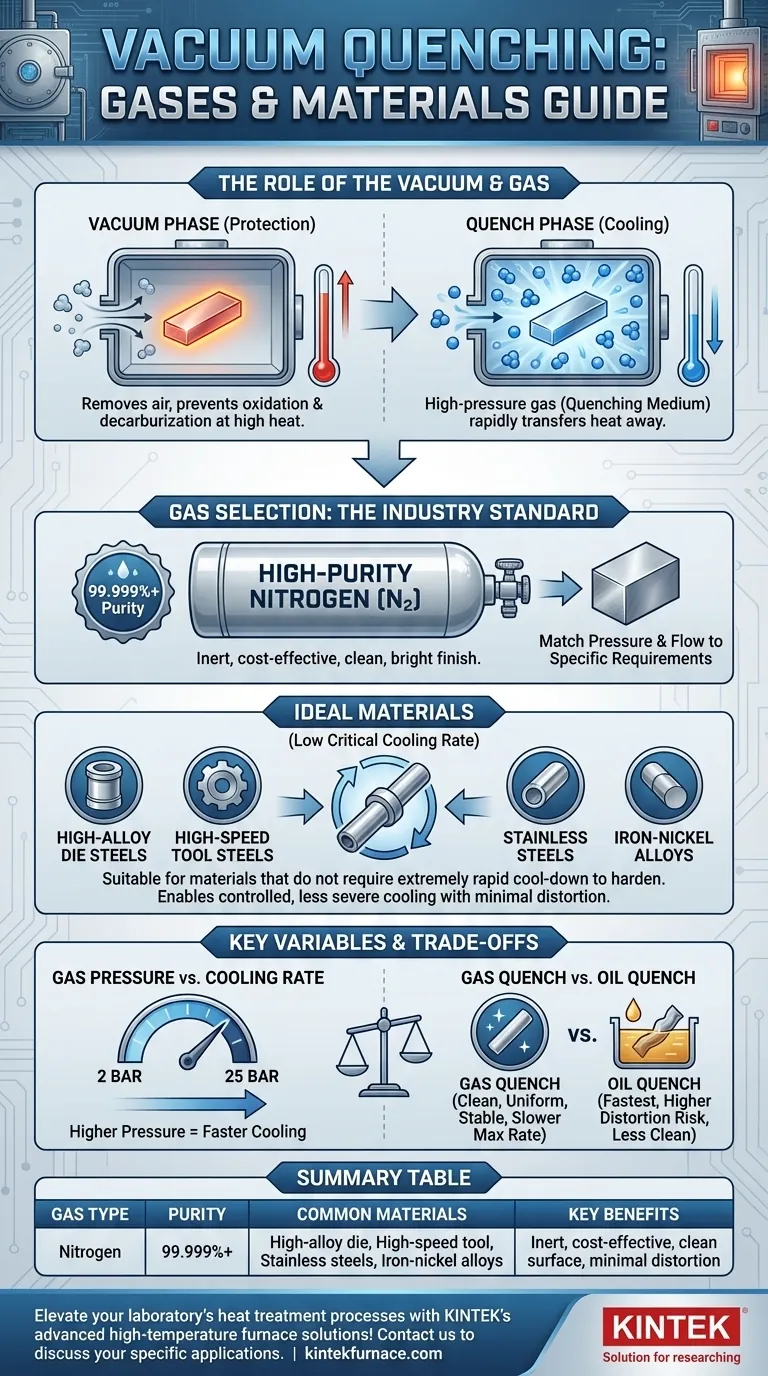
In modern vacuum quenching, the standard gas used is high-purity nitrogen (99.999% or higher). This process is ideal for materials with lower critical cooling rates, such as high-alloy die steels, high-speed tool steels, stainless steels, and certain iron-nickel-based alloys that require hardening with minimal distortion and a clean surface finish.
The core principle is not simply about the gas itself, but about using a controlled, inert atmosphere to achieve precise cooling. Nitrogen is the default choice for its inertness and cost-effectiveness, but the success of the quench depends entirely on matching the gas pressure and flow to the material's specific heat treatment requirements.

The Role of the Vacuum and Gas
To understand the choice of gas, we must first distinguish between the two phases of the process: the vacuum and the quench. They serve separate but related functions.
The Purpose of the Vacuum
A vacuum furnace creates a tightly controlled environment by removing air and other atmospheric contaminants. This is critical for preventing unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation and decarburization on the metal's surface at high temperatures. The vacuum itself provides no cooling; it is purely for preparation and protection.
The Purpose of the Gas
Once the material is heated to its target temperature in the vacuum, the chamber is rapidly backfilled with a high-pressure gas. This gas acts as the quenching medium, rapidly transferring heat away from the part to cool it down and achieve the desired metallurgical properties, such as martensitic hardness.
Gas Selection and Material Suitability
The choice of gas and the materials compatible with gas quenching are fundamentally linked to the required cooling rate.
Nitrogen: The Industry Standard
High-purity nitrogen is the workhorse of vacuum gas quenching. Its primary advantages are that it is relatively inert at most heat-treating temperatures and is cost-effective. It will not readily react with the surface of most steels, ensuring a clean, bright finish.
The 99.999% purity is not arbitrary; it ensures that residual oxygen and moisture levels are low enough to prevent any surface discoloration or oxidation on sensitive alloys.
Why Certain Steels Are Ideal
Gas quenching is a gentler process than traditional oil or water quenching. Therefore, it is only suitable for materials that do not require an extremely rapid cool-down to harden.
These are typically steels with high alloy content, such as high-speed steel or high-carbon, high-chromium tool steels. These alloys have a low critical cooling rate, meaning they can be cooled more slowly and still achieve full hardness. This property makes them perfect candidates for the controlled, less severe cooling provided by a gas quench.
Understanding the Key Variables and Trade-offs
Effective vacuum quenching is a balance between multiple factors. Misunderstanding these can lead to failed parts or undesirable properties.
Gas Pressure vs. Cooling Rate
The cooling power of a gas quench is directly related to its pressure, which typically ranges from 2 to 25 bar. Higher pressure means more gas molecules are available to contact the part's surface, resulting in a faster heat transfer rate. Adjusting the pressure is the primary method for controlling the quench speed to match a specific material's needs.
Gas Quenching vs. Oil Quenching
Gas quenching offers significant advantages in part cleanliness and dimensional stability. Since the cooling is more uniform and less severe than a liquid quench, there is a much lower risk of part distortion or cracking.
However, the trade-off is a slower maximum cooling rate. For low-alloy steels that require a very fast quench, oil quenching may still be necessary to achieve the required hardness.
The Importance of a Contaminant-Free Process
The entire purpose of using a vacuum is to ensure a pristine environment. Any failure to maintain gas purity or vacuum integrity defeats the purpose of the process, potentially compromising the metallurgical and surface properties of the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct quenching parameters is critical for success. Your decision should be guided by the material being processed and the desired final properties.
- If your primary focus is processing standard tool and die steels: High-purity nitrogen is the proven, reliable, and cost-effective gas for the job.
- If your material has a low critical cooling rate (e.g., H13, D2, or M2 steels): Gas quenching is the ideal method to achieve full hardness while minimizing the distortion and cracking risk associated with faster liquid quenches.
- If your goal is maximum cleanliness and dimensional control: The uniform, controlled cooling of a high-pressure gas quench is technically superior to traditional liquid quenching methods.
By understanding these principles, you can confidently specify the correct vacuum quenching parameters to achieve predictable and high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Purity | Common Materials | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | 99.999% | High-alloy die steels, high-speed tool steels, stainless steels, iron-nickel alloys | Inert, cost-effective, clean surface, minimal distortion |
Elevate your laboratory's heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering superior performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications and achieve optimal results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability



















