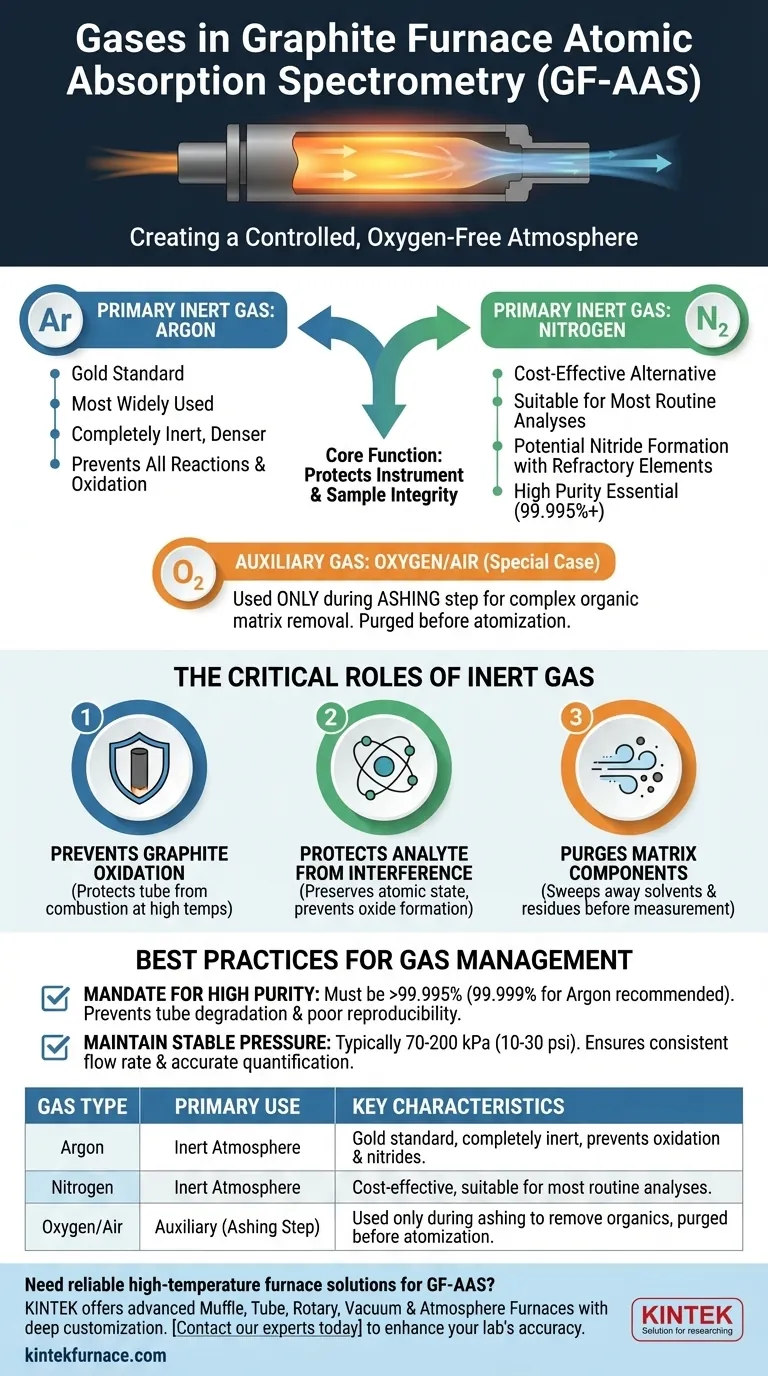
In a graphite furnace, two main gases are used: a primary inert gas and, in some applications, an auxiliary gas. The inert gas is almost always high-purity argon or, less commonly, high-purity nitrogen. This gas is essential for protecting the instrument and ensuring the chemical integrity of the sample during analysis.
The core function of the gas in Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (GF-AAS) is to create a controlled, oxygen-free atmosphere. This prevents the high-temperature graphite tube from incinerating and protects the sample atoms from forming unwanted chemical compounds that would invalidate the measurement.
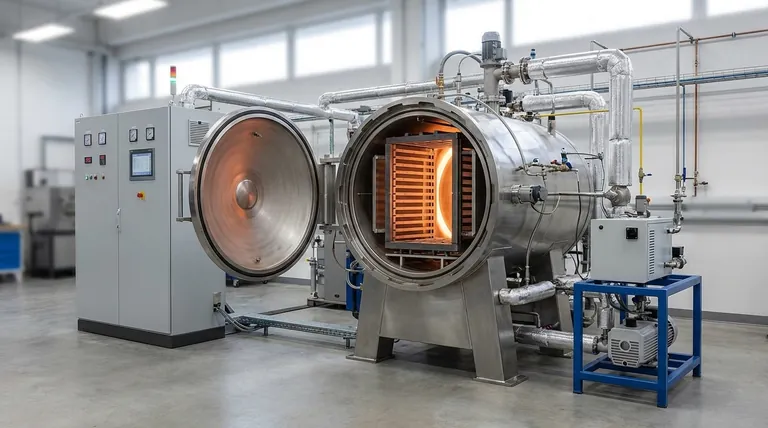

The Critical Role of the Inert Gas
A graphite furnace operates by heating a sample to extreme temperatures (often over 2000°C) inside a small graphite tube. The inert gas flowing through and around this tube is not optional; it is fundamental to the entire process.
Preventing Graphite Oxidation
At the temperatures required for atomization, the carbon graphite tube would instantly combust and be destroyed if it came into contact with oxygen.
The constant flow of an inert gas like argon purges the system of ambient air, creating a protective blanket that allows the tube to reach and sustain high temperatures without being consumed.
Protecting the Analyte from Interference
The goal of GF-AAS is to measure the light absorbed by free, neutral atoms of a specific element.
If oxygen were present, the hot analyte atoms would readily form stable oxides (e.g., Al₂O₃). These molecules do not absorb light at the same wavelength as free atoms, leading to a drastically low or non-existent analytical signal. The inert atmosphere preserves the atomic state of the element being measured.
Purging Matrix Components
The GF-AAS temperature program consists of multiple steps, including drying and ashing, which occur before the final, high-temperature atomization.
During these preliminary steps, the inert gas flow acts as a physical transport mechanism, sweeping away vaporized solvent and pyrolyzed matrix components. This "cleans up" the sample before the measurement step, reducing background noise and potential interferences.
Understanding the Gas Choices
While both argon and nitrogen are inert, the choice between them can have subtle implications for performance and cost.
Argon: The Gold Standard
Argon is the most widely used and recommended inert gas for GF-AAS.
Being denser than air and nitrogen, it provides a slightly more effective protective environment within the furnace. It is completely inert and will not react with any analyte, even at the highest atomization temperatures.
Nitrogen: The Cost-Effective Alternative
High-purity nitrogen is a viable and often cheaper alternative to argon.
For a majority of analyses, it performs perfectly well. However, at very high temperatures, nitrogen can potentially react with a small number of refractory elements (like titanium or vanadium) to form stable nitrides, which can cause a suppression of the analytical signal.
The "Auxiliary" Gas: A Special Case
Some GF-AAS methods, particularly for samples with a heavy organic matrix, may introduce an auxiliary gas like oxygen or air during the ashing step only.
This is a controlled way to help burn off, or "ash," the complex matrix at a moderate temperature. This gas is then fully purged and replaced by the inert gas long before the high-temperature atomization step begins. It is never present during the actual measurement.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
The quality and delivery of the gas are just as important as the choice of gas itself.
The Mandate for High Purity
Using a low-purity gas is a primary source of problems. The specifications of "high-purity" and "oxygen-free" are critical.
Even trace amounts of oxygen (a few parts per million) will significantly shorten the life of the graphite tube and can cause poor analytical reproducibility. Always use a grade of 99.995% purity or higher.
Maintaining Correct and Stable Pressure
The gas pressure, typically set between 70-200 kPa (10-30 psi), dictates the flow rate through the furnace.
Inconsistent pressure leads to variable flow rates, which affects how efficiently the matrix is removed and how long the atom cloud resides in the light path. Stable pressure is key to achieving the repeatable results required for accurate quantification.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting and managing your gas supply is foundational to successful graphite furnace analysis.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and analyzing a wide range of elements: Use high-purity (99.999%) argon as it is the universally accepted standard and eliminates any risk of nitride formation.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis on a budget: High-purity (99.995%+) nitrogen is a suitable and cost-effective choice for most common elemental analyses.
- If you are analyzing samples with a very complex organic matrix: Consider if an oxygen ashing step in your program could improve results, but ensure your system is properly configured for this and that it is fully purged before atomization.
Ultimately, the proper management of the gas environment is a non-negotiable prerequisite for generating reliable and accurate data with a graphite furnace.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Primary Use | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Argon | Inert Atmosphere | Gold standard, completely inert, prevents oxidation and nitride formation. |
| Nitrogen | Inert Atmosphere | Cost-effective alternative, suitable for most routine analyses. |
| Oxygen/Air | Auxiliary (Ashing Step) | Used only during ashing to remove organic matrix, purged before atomization. |
Need a reliable high-temperature furnace solution for your GF-AAS or other analytical processes?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements like those in GF-AAS.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our robust and precise furnace technology can enhance the accuracy and reliability of your lab's analyses.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability
- Why is graphite a preferred material for heating elements in high-temperature vacuum furnaces?
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency



















