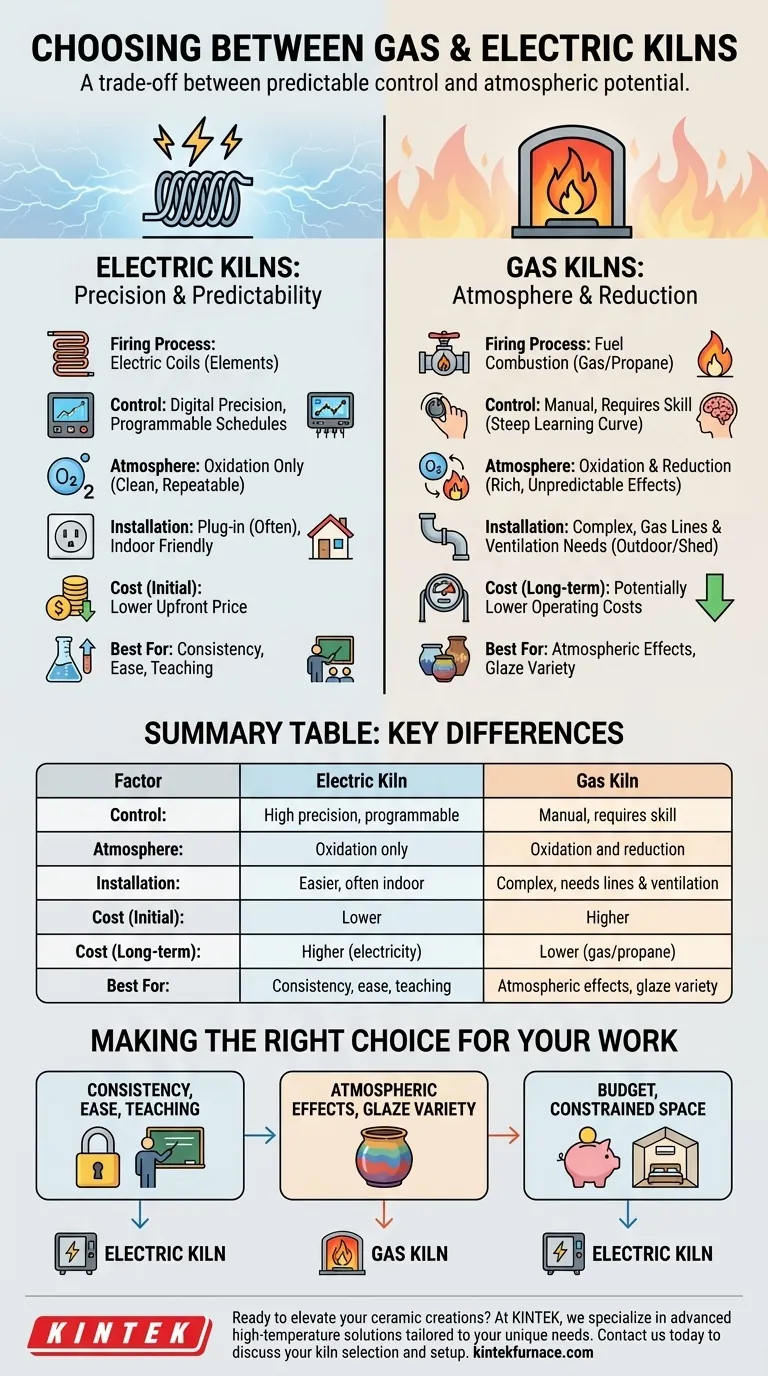
Choosing between a gas and electric kiln is a foundational decision that shapes your ceramic work, your studio process, and your budget. The right choice depends less on which type is universally "better" and more on which is the ideal tool for your specific artistic goals. While electric kilns offer unparalleled precision and ease of use, gas kilns provide the unique ability to manipulate the kiln's atmosphere, which can dramatically alter glaze results.
The core decision is a trade-off between the predictable control of an electric kiln and the atmospheric potential of a gas kiln. Understanding this difference is the key to aligning your equipment investment with your creative vision.

The Firing Process: Control vs. Atmosphere
The fundamental difference between gas and electric kilns lies in how they generate heat. This distinction directly impacts the firing process and the final appearance of your work.
Electric Kilns: Precision and Predictability
Electric kilns use resistant metal coils, called elements, to generate heat. This process is exceptionally clean and easy to control with modern digital controllers.
You can program precise firing schedules with specific temperatures and hold times. This ensures your results are highly repeatable from one firing to the next.
This level of control, combined with slower, even heating and cooling cycles, makes electric kilns ideal for achieving consistent outcomes, especially for production work, sculpture, or when working with commercial glazes.
Gas Kilns: Atmosphere and Reduction
Gas kilns burn a fuel source (natural gas or propane) to generate heat. This combustion process creates an active atmosphere inside the kiln that you can manipulate.
By controlling the ratio of fuel to air, you can create an oxidation (oxygen-rich) or reduction (oxygen-starved) atmosphere. A reduction atmosphere forces the fire to seek oxygen from the clay bodies and glazes themselves, producing rich, often unpredictable colors and effects that are impossible to achieve in a standard electric kiln.
Gas kilns also tend to heat and cool faster, allowing for quicker firing cycles once you have mastered the process.
Installation and Operational Realities
Beyond the firing process, the practical requirements for installing and running each kiln type are vastly different and significantly impact your budget and studio setup.
Space and Infrastructure
Electric kilns are generally simpler to install. Smaller models can often plug into existing high-voltage outlets (like a clothes dryer outlet), making them a common choice for home studios or smaller spaces. They require proper ventilation but can typically be used indoors.
Gas kilns have extensive infrastructure needs. They require professionally installed gas lines and a robust ventilation system to safely exhaust combustion byproducts like carbon monoxide. Due to these requirements, gas kilns are often installed outdoors or in a dedicated, well-ventilated kiln shed.
Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Costs
For a given size, electric kilns often have a lower upfront purchase price, making them more accessible.
While gas kilns can have a higher initial cost due to the kiln itself and the necessary installation, their long-term operating costs can be lower. This depends heavily on the local price of electricity versus natural gas or propane.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither kiln type is perfect for every situation. Being aware of their limitations is critical for making an informed decision.
The Limitations of Electric Kilns
The primary drawback of an electric kiln is the inability to create a true reduction atmosphere. While some effects can be simulated with special additives, they cannot replicate the depth and richness of a fuel-fired reduction firing. Their firing cycles are also typically slower.
The Demands of Gas Kilns
Gas kilns require a steeper learning curve. Successfully managing the atmosphere and temperature is a hands-on skill that takes practice to master. They also demand more maintenance, including regular inspection and cleaning of burners and dampers, and have much stricter safety and code compliance requirements.
Environmental and Safety Factors
Gas kilns directly produce emissions, making proper ventilation a non-negotiable safety requirement. The environmental impact of electric kilns is indirect, tied to how the electricity that powers them is generated. Both types are powerful tools that must be operated with strict adherence to safety regulations to prevent fire or injury.
Making the Right Choice for Your Work
To make your decision, consider your primary objective as an artist or maker.
- If your primary focus is consistency, ease of use, or teaching: An electric kiln is the superior choice for its programmable precision and reliability.
- If your primary focus is achieving rich, varied glaze surfaces and atmospheric effects: A gas kiln is the necessary tool for true reduction firing.
- If your primary focus is budget and you work in a constrained space: An electric kiln offers a more accessible and flexible entry point.
Ultimately, the best kiln is the one that empowers you to create the work you envision.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Electric Kiln | Gas Kiln |
|---|---|---|
| Control | High precision, programmable | Manual, requires skill |
| Atmosphere | Oxidation only | Oxidation and reduction |
| Installation | Easier, often indoor | Complex, needs gas lines and ventilation |
| Cost (Initial) | Lower | Higher |
| Cost (Long-term) | Higher (electricity) | Lower (gas/propane) |
| Best For | Consistency, ease, teaching | Atmospheric effects, glaze variety |
Ready to elevate your ceramic creations with the right kiln? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your unique needs. Whether you're a studio artist, educator, or production potter, our expertise in customizing Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems ensures you get precise, reliable equipment that enhances your workflow and artistic outcomes. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your kiln selection and setup—let's bring your vision to life!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems



















