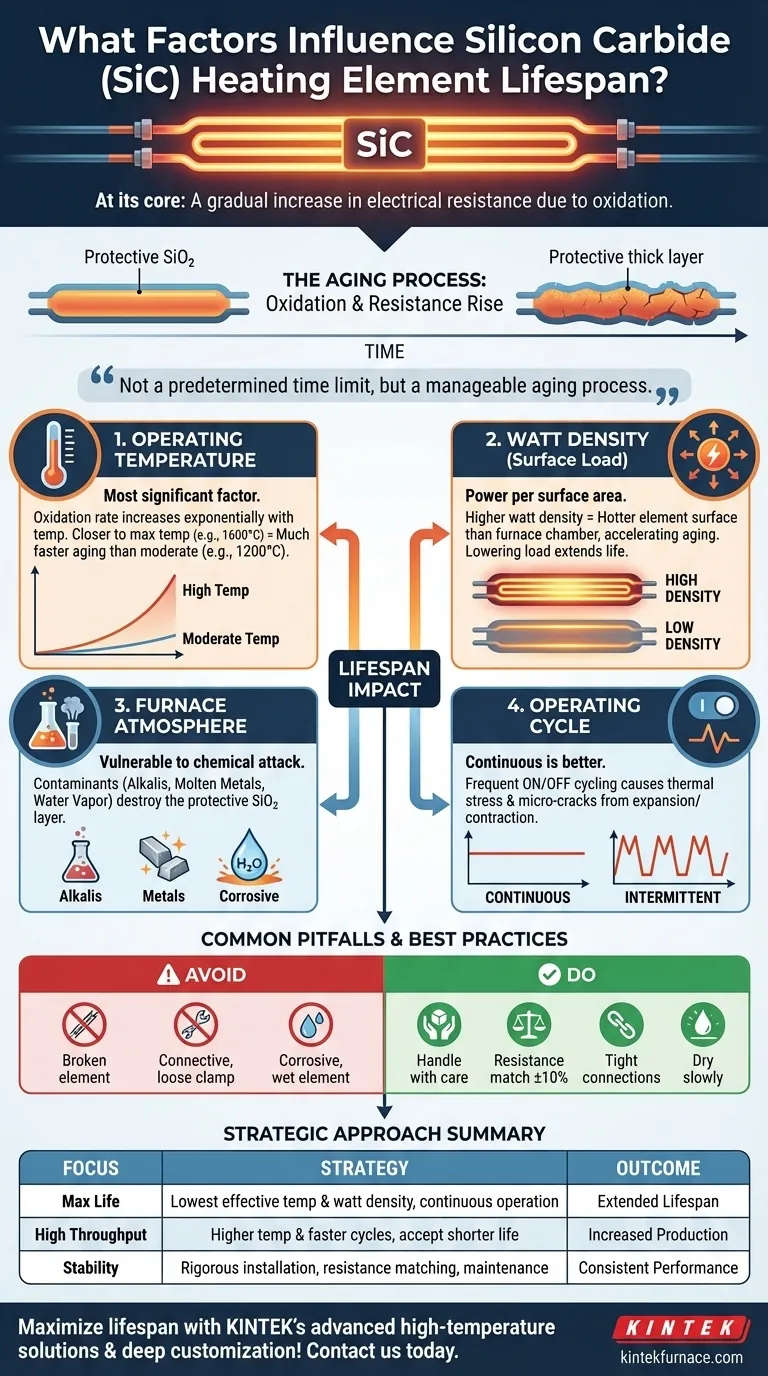
At its core, the lifespan of a silicon carbide (SiC) heating element is determined by the rate at which its electrical resistance increases through oxidation. This aging process is not fixed; it is directly accelerated or slowed by a handful of critical operational and environmental factors. The primary influences are operating temperature, watt density (surface load), the chemical composition of the furnace atmosphere, and the nature of the operating cycle.
The central challenge in managing SiC element lifespan is controlling the slow, inevitable process of oxidation. While these elements are designed for extreme heat, their longevity is a direct result of how well you manage their operating environment and electrical load, not a predetermined time limit.

The Fundamental Aging Process: Oxidation
Silicon carbide does not simply "burn out" like a light bulb. Instead, it ages through a predictable chemical process.
The Protective, and Limiting, Oxide Layer
When heated in the presence of oxygen, the surface of the SiC element forms a thin, protective layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂). This layer is crucial, as it shields the underlying SiC from rapid, destructive oxidation.
However, this SiO₂ layer is less electrically conductive than the SiC material. As the element is used over time, this layer slowly thickens, causing the element's total electrical resistance to increase.
Reaching the End of Life
An element is typically considered at the end of its useful life when its resistance has increased to a point where the available power supply can no longer provide enough voltage to reach the desired operating temperature. This is a gradual decline, not a sudden failure.
Key Factors Controlling Element Lifespan
You can directly influence the rate of this aging process by controlling several key variables.
Operating Temperature
This is the most significant factor. The rate of oxidation increases exponentially with temperature. Operating an element closer to its maximum rated temperature (e.g., 1600°C) will cause it to age much faster than operating it at a more moderate temperature (e.g., 1200°C).
Watt Density (Surface Load)
Watt density is the amount of power loaded onto the element's surface area (watts per square inch or cm²). A higher watt density means the element must run hotter to dissipate that energy into the furnace.
Even in the same furnace, an element with a high watt density will have a surface temperature significantly hotter than the furnace's chamber temperature, accelerating its aging. Lowering the watt density is a key strategy for extending life.
Furnace Atmosphere and Contamination
The chemical environment inside the furnace has a profound impact. While SiC elements are robust, they are vulnerable to specific chemical attacks that can destroy the protective SiO₂ layer or corrode the element itself.
Common contaminants include:
- Alkali and Alkaline Oxides: These react with SiC at temperatures above 1300°C, forming silicates that degrade the element.
- Molten Metals: Direct contact with certain melting metals like cobalt, nickel, and iron can lead to rapid corrosion.
- Water Vapor: Excessive water vapor can accelerate the oxidation process, increasing the rate of resistance gain.
Operating Cycle (Continuous vs. Intermittent)
Continuous operation at a stable temperature is far less damaging than intermittent (on/off) cycling. Each time the element cools and heats up, thermal expansion and contraction create mechanical stress on the element and its protective oxide layer, potentially causing micro-cracks that expose fresh SiC to oxidation.
Common Pitfalls and Installation Best Practices
Premature failure is often caused by avoidable mistakes during installation and handling rather than the aging process itself.
The Brittleness Factor
SiC elements are ceramic and therefore hard but very brittle. They must be handled with extreme care during installation and cannot be subjected to mechanical shock or stress. Dropping an element or forcing it into misaligned furnace openings will cause it to fail.
The Importance of Resistance Matching
For uniform heating and balanced loading, all elements in a single control zone should have similar resistance values, typically within a +/- 10% tolerance. If a new, low-resistance element is mixed with old, high-resistance elements, the new element will draw a disproportionate share of the power, overheat, and fail quickly.
Electrical Connection Integrity
Ensure clamps and connection straps make firm, clean contact with the element's aluminized ends. A loose connection can cause arcing, which will overheat and destroy the connection point, leading to element failure.
Moisture Contamination
Elements should be stored in a dry location. If they absorb moisture, they should be dried out slowly by heating them at a low temperature (around 100-200°C) for several hours before ramping up to full power. Rapidly heating a damp element can cause it to crack.
Maximizing Lifespan: A Strategic Approach
Your operational goals will determine your strategy for managing element life.
- If your primary focus is maximum element life: Operate at the lowest effective temperature and watt density for your process, and favor continuous operation over frequent cycling.
- If your primary focus is high throughput: Accept that running at higher temperatures and with faster cycles will shorten element lifespan and budget for more frequent replacements accordingly.
- If your primary focus is processing in aggressive atmospheres: Be vigilant about identifying and mitigating sources of chemical contaminants and ensure your furnace is well-ventilated.
- If your primary focus is operational stability: Implement a rigorous installation and maintenance protocol, focusing on careful handling, resistance matching, and secure electrical connections.
Ultimately, viewing your heating elements as manageable assets rather than simple consumables is the key to maximizing their value and performance.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | Higher temperatures exponentially accelerate oxidation, reducing lifespan |
| Watt Density | Increased surface load raises temperature, speeding up aging |
| Furnace Atmosphere | Contaminants like alkalis and moisture can degrade the protective oxide layer |
| Operating Cycle | Frequent on/off cycling causes thermal stress, shortening life |
Maximize the lifespan of your silicon carbide heating elements with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, helping you control factors like temperature and atmosphere for longer element life and improved efficiency. Don't let premature failures slow you down—contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















