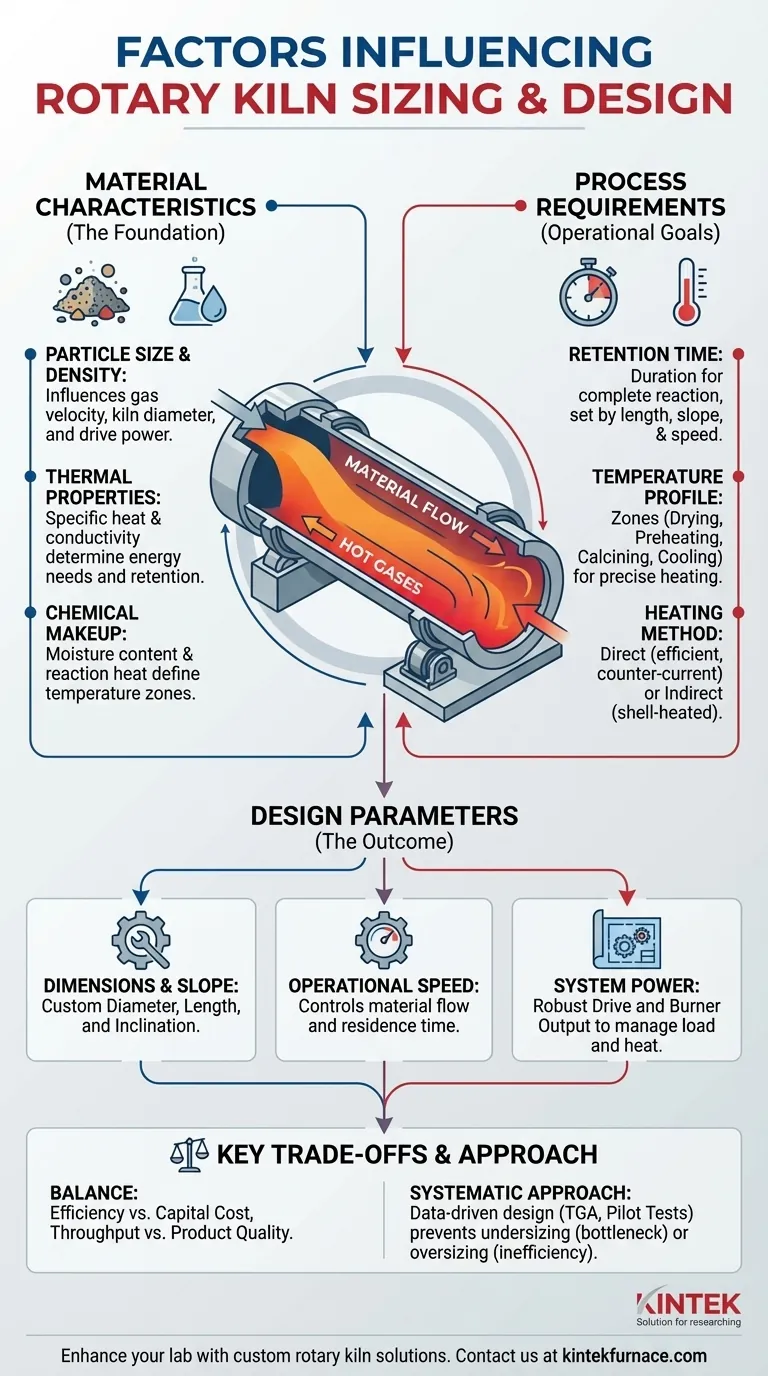
At its core, designing a rotary kiln is a meticulous exercise in balancing three interconnected domains: the inherent characteristics of the material, the specific thermal and chemical transformation required, and the mechanical engineering that makes it possible. The sizing and design are not chosen from a catalog; they are custom-derived from these fundamental inputs to ensure operational efficiency, product quality, and cost-effectiveness.
A rotary kiln is not a generic piece of equipment. It is a purpose-built system where every design parameter—from its diameter and length to its rotational speed—is a direct response to the unique physical, thermal, and chemical properties of the material being processed.

Material Characteristics: The Foundation of Design
The material you intend to process is the single most important factor driving the entire design. Every decision flows from understanding how it behaves before, during, and after heating.
Physical Properties: Size, Density, and Flow
The physical form of the feed material dictates the kiln's basic dimensions and power requirements. Particle size distribution directly influences the maximum allowable gas velocity inside the kiln. Fine powders can be easily carried away by the process gas, necessitating a larger kiln diameter to reduce gas speed, while pelletized or granular feeds can tolerate higher velocities in a smaller-diameter shell.
Bulk density is also critical. High-density materials require more robust support structures and a more powerful drive system to handle the increased load.
Thermal Properties: How the Material Responds to Heat
A material's thermal properties determine the energy input and time required for processing. Specific heat defines how much energy is needed to raise the material's temperature, impacting fuel consumption.
Thermal conductivity measures how efficiently heat moves through the material bed. Poor conductivity may require longer retention times or internal structures like lifters to ensure all material is heated evenly.
Finally, the heat of reaction—whether a process is endothermic (absorbs energy) or exothermic (releases energy)—is a major factor in calculating the overall energy balance and designing the burner system.
Chemical Properties: The Transformation Itself
The chemical makeup defines the core purpose of the kiln. Moisture content, for instance, must be well-understood. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA) can reveal the temperatures at which free water (around 100°C) and chemically bound water (up to 260°C or higher) are released.
This data is essential for designing the kiln's temperature profile and ensuring sufficient energy and time are allocated for each stage of the transformation, from simple drying to complex chemical calcination.
Process Requirements: Defining the Operational Goal
Once the material is understood, you must define the specific operational targets. These requirements translate the material's properties into a set of performance parameters for the kiln.
Retention Time: How Long is Long Enough?
Retention time is the duration a material spends inside the kiln. This is one of the most critical process variables, as it must be long enough for the desired thermal and chemical reactions to complete fully.
It is not a single setting but an outcome determined by three key mechanical factors: the kiln's length, its inclination (slope), and its rotational speed.
Temperature Profile: The Thermal Journey
A kiln is not held at a single temperature. Instead, it operates with a specific temperature profile along its length, creating distinct zones. A typical profile includes a drying zone, a preheating zone, a high-temperature calcining/reaction zone, and a cooling zone.
This profile is meticulously designed based on thermal analysis (like TGA) to ensure the material is heated at the correct rate and reaches the target temperature for the required amount of time. The burner and combustion system, typically at the discharge end, generate this thermal gradient.
Heating Method: Direct vs. Indirect Firing
The majority of rotary kilns use direct, counter-current heating. In this highly efficient setup, the burner fires into the discharge end of the kiln, and hot gases flow up the kiln in the opposite direction of the material flow. This maximizes heat transfer as the hottest gases encounter the most-processed material.
In some cases, indirect heating, where the shell is heated from the outside, is used for materials that cannot come into contact with combustion gases.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Designing a kiln involves navigating a series of critical engineering and economic trade-offs. Being aware of them is essential for making informed decisions.
Efficiency vs. Capital Cost
A longer, larger-diameter kiln generally offers better thermal efficiency and more precise process control. However, this comes at a significantly higher upfront capital cost. A shorter, more compact kiln is cheaper to build but will likely have higher ongoing fuel costs and may offer less operational flexibility.
Throughput vs. Product Quality
There is a constant tension between maximizing production volume (throughput) and ensuring consistent product quality. Increasing the feed rate reduces material retention time. If pushed too far, this can result in an incomplete reaction, leading to off-spec product that requires reprocessing or disposal.
The Risk of Improper Sizing
An undersized kiln will create a permanent production bottleneck, unable to meet capacity demands. An oversized kiln is not only more expensive to purchase but also inefficient to operate, as it consumes excess energy to heat the larger volume and shell, leading to higher operational costs for its entire lifespan.
A Systematic Approach to Kiln Design
To ensure a successful outcome, the design process must be data-driven and methodical. The right approach depends on your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is initial project feasibility: Your first step is comprehensive material testing, starting with lab-scale analysis (TGA) and progressing to batch or pilot-scale kiln tests to validate the process variables.
- If your primary focus is optimizing an existing process: Focus on adjusting the controllable variables—feed rate, rotational speed, and burner output—to fine-tune the retention time and temperature profile for better efficiency or quality.
- If your primary focus is selecting a new kiln: Provide potential vendors with a complete data package on your material properties and explicit process requirements (feed rate, final temperature, retention time) to get an accurately sized and efficient unit.
Ultimately, understanding these interconnected factors empowers you to specify, evaluate, and operate a rotary kiln that serves as a highly effective and reliable processing solution.
Summary Table:
| Factor Category | Key Elements | Impact on Design |
|---|---|---|
| Material Characteristics | Particle size, density, thermal properties, chemical makeup | Determines kiln dimensions, energy needs, and temperature zones |
| Process Requirements | Retention time, temperature profile, heating method | Defines operational parameters like length, slope, and burner type |
| Design Trade-offs | Efficiency vs. cost, throughput vs. quality, sizing risks | Balances capital investment with operational performance |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with a custom rotary kiln solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, tailored to your unique experimental needs. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your material properties and process goals, boosting efficiency and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput



















