At its core, the strong process performance of a vacuum tube furnace stems from its ability to create a highly controlled environment. This is achieved through precise thermal management, advanced automation that minimizes human error, and a design that fundamentally prevents material contamination by removing atmospheric gases like oxygen.
The defining advantage of a vacuum furnace is not just its ability to get hot, but its power to meticulously control the entire process environment. This control prevents unwanted chemical reactions, ensuring the final material's integrity, purity, and performance.

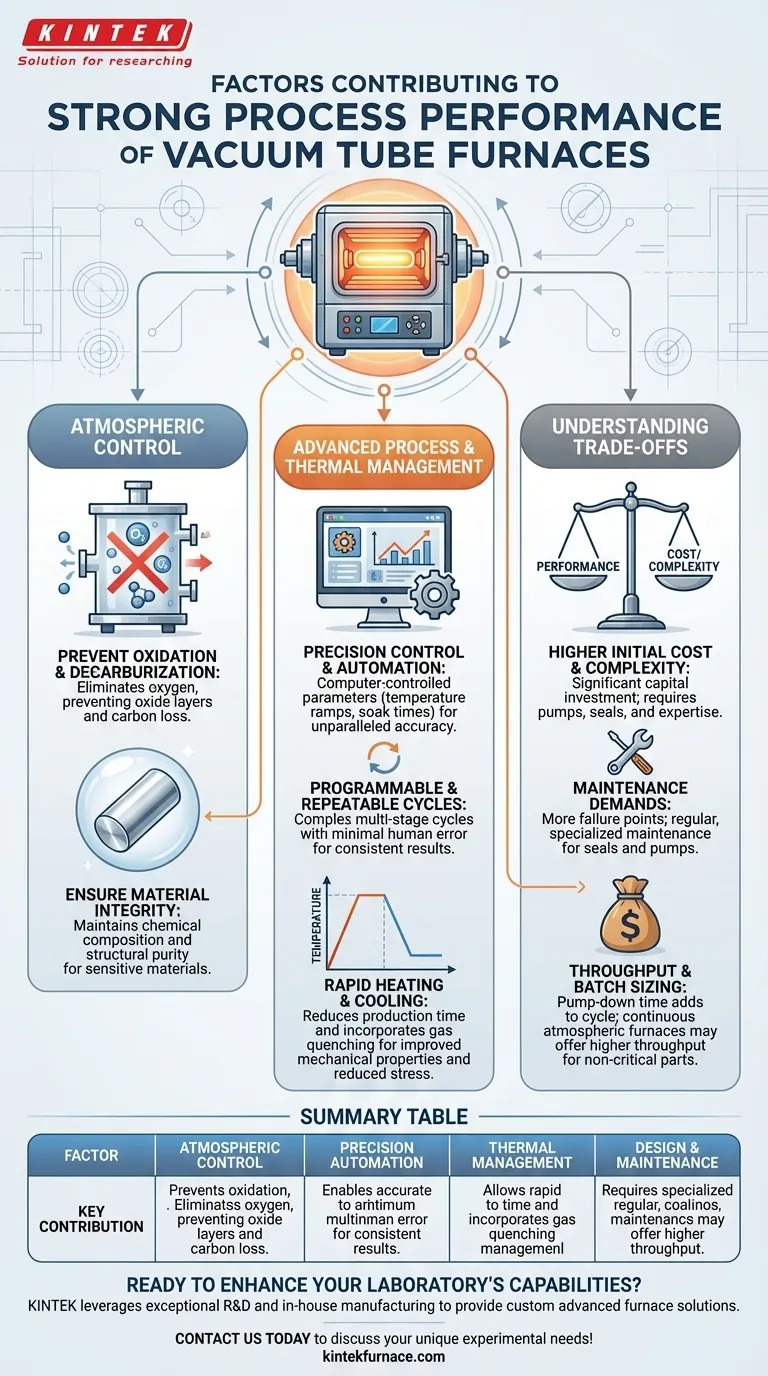
The Foundation of Performance: Atmospheric Control
The primary function that sets a vacuum furnace apart is its ability to operate at pressures below the standard atmosphere. This single capability is the source of its most significant performance benefits.
Preventing Oxidation and Decarburization
By removing air from the heating chamber, the furnace eliminates the oxygen that would otherwise react with the material at high temperatures. This prevents the formation of oxide layers (scaling) and the loss of carbon from the surface of steel alloys (decarburization), which are common issues in conventional furnaces.
Ensuring Material Integrity
This controlled, inert environment ensures that the material being processed maintains its intended chemical composition and structural purity. For sensitive alloys, electronics, or medical-grade materials, this lack of contamination is not just a benefit—it is an absolute requirement for achieving desired performance characteristics.
Advanced Process and Thermal Management
Modern vacuum furnaces are not simple ovens. They are sophisticated, integrated systems designed for precision and efficiency from start to finish.
Precision Control and Automation
These furnaces feature electromechanical and computer-controlled systems. Process parameters like temperature ramps, soak times, and cooling rates are programmed and executed automatically, ensuring unparalleled accuracy and consistency from one batch to the next.
Programmable and Repeatable Cycles
Automation allows for complex, multi-stage heat treatment cycles to be performed with perfect repeatability. This drastically reduces the potential for human error and guarantees that every part receives the exact same treatment, which is critical for quality control in industrial production.
Rapid Heating and Cooling
Many models are engineered for rapid heating rates to minimize production time. More importantly, they often incorporate controlled, fast cooling capabilities (gas quenching) which can reduce thermal stress, prevent unwanted phase changes, and improve the final mechanical properties of the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vacuum furnaces offer superior performance, they introduce unique considerations that are important to understand.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
The technology required to create and maintain a vacuum—including pumps, seals, and advanced control systems—makes these furnaces a significantly larger capital investment than their atmospheric counterparts. Operation also requires a higher level of technical expertise.
Maintenance Demands
Vacuum systems have more failure points than simpler furnaces. Seals can degrade, and vacuum pumps require regular, specialized maintenance to ensure they operate at peak efficiency. Neglecting this can compromise the entire process.
Throughput and Batch Sizing
The need to pump down the chamber to a vacuum adds time to the beginning of every cycle. For high-volume, low-margin parts where surface finish is not critical, a continuous atmospheric furnace may offer higher throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your process requirements and end-product goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum material purity and preventing oxidation: A vacuum furnace is the only choice to guarantee a controlled, non-reactive environment.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and consistency: The advanced automation and computer-controlled cycles of a vacuum furnace will deliver the most reliable results.
- If your primary focus is improving mechanical properties through controlled cooling: The fast quenching capabilities of a modern vacuum furnace provide a level of control that is difficult to achieve otherwise.
By understanding these core principles and trade-offs, you can confidently determine if a vacuum furnace is the right strategic investment for your operational goals.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Contribution |
|---|---|
| Atmospheric Control | Prevents oxidation and decarburization by removing oxygen, ensuring material purity |
| Precision Automation | Enables accurate, repeatable cycles with minimal human error for consistent results |
| Thermal Management | Allows rapid heating and controlled cooling to improve material properties and reduce stress |
| Design and Maintenance | Requires specialized upkeep but prevents contamination, supporting long-term reliability |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with a custom vacuum tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs precisely. Contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace solutions can boost your process performance and material purity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















