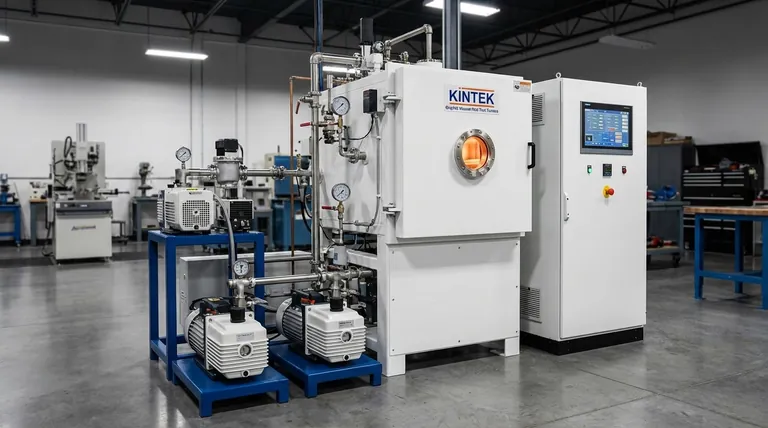
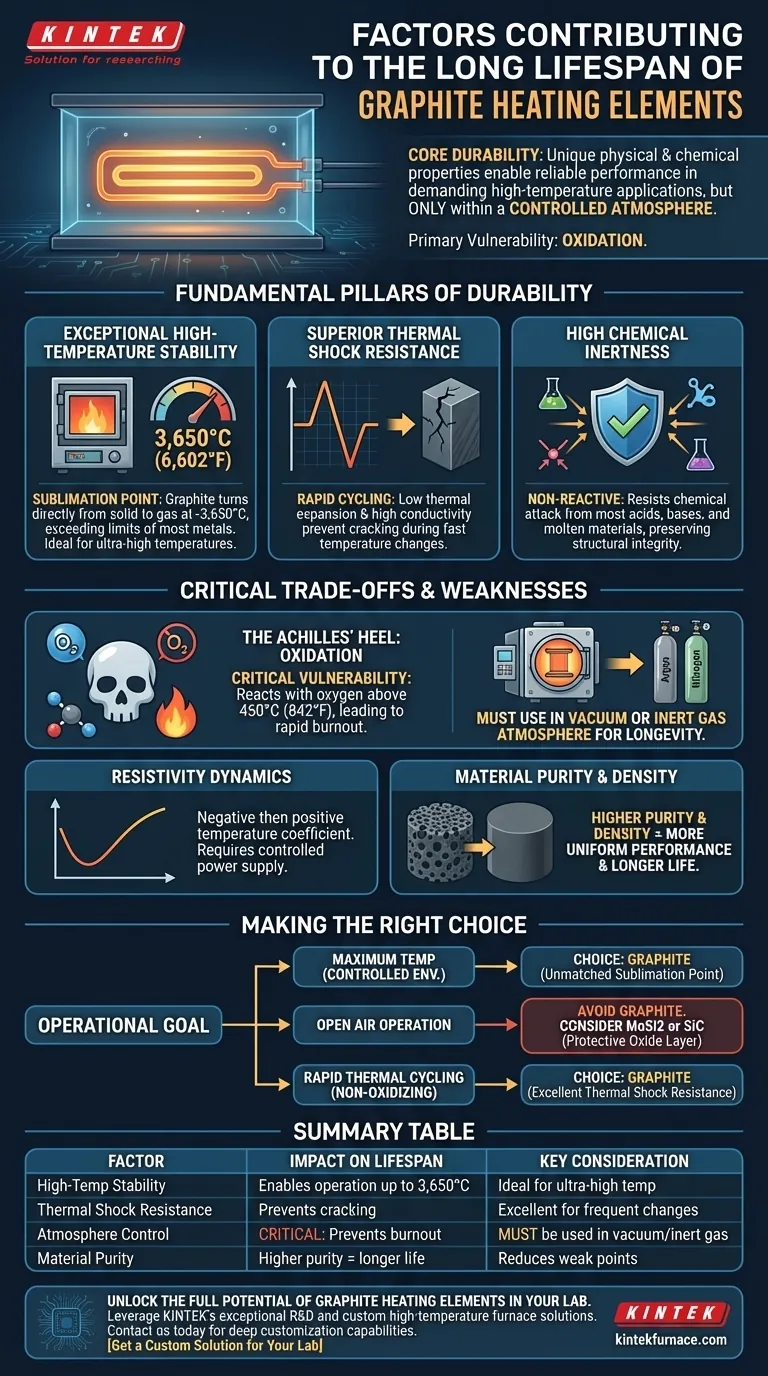
At its core, the durability of a graphite heating element stems from a unique combination of inherent physical and chemical properties. Its ability to withstand extreme heat without melting, resist damage from rapid temperature changes, and remain stable in specific chemical environments allows it to perform reliably for extended periods in demanding high-temperature applications.
Graphite's impressive lifespan is not universal; it is a direct result of its exceptional thermal stability within a controlled atmosphere. Its primary vulnerability is oxidation, making the operating environment the single most critical factor determining its longevity.

The Fundamental Pillars of Graphite's Durability
To understand why graphite lasts, we must look at its performance under thermal and chemical stress. Its molecular structure gives it advantages that many metals and ceramics lack.
Exceptional High-Temperature Stability
Graphite does not have a melting point at atmospheric pressure. Instead, it sublimes—turning directly from a solid to a gas—at an incredibly high temperature, around 3,650°C (6,602°F).
This property makes it one of the most refractory materials available, capable of operating at temperatures far beyond the limits of most metallic heating elements.
Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
Furnaces often undergo rapid heating and cooling cycles. Graphite handles this stress exceptionally well.
Its low coefficient of thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity prevent it from cracking or degrading when subjected to rapid temperature changes. Materials that expand and contract significantly are prone to mechanical failure over time; graphite is not.
High Chemical Inertness
In the correct environment, graphite is highly non-reactive. It resists chemical attack from most acids, bases, and molten materials.
This chemical inertness ensures that the element's structural integrity is not compromised by reactive substances within the furnace, preserving its form and function.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
The longevity of a graphite element is conditional. While its strengths are significant, its operational weaknesses are just as critical to understand. Ignoring them will lead to premature failure.
The Achilles' Heel: Oxidation
Graphite's most significant limitation is its reaction with oxygen. In an oxidizing atmosphere like open air, graphite will begin to burn away at temperatures as low as 450°C (842°F). This process accelerates dramatically as temperatures rise.
For this reason, graphite heating elements are used exclusively in vacuum furnaces or furnaces filled with an inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen. This controlled atmosphere protects the element from oxygen, allowing it to reach ultra-high temperatures without degrading.
Resistivity and Power Dynamics
Graphite has a negative temperature coefficient of resistance up to around 500°C, meaning its resistance decreases as it heats up. Above this point, the coefficient turns positive.
This behavior must be managed by the power supply controller. The system must be designed to handle these changes in electrical load to maintain stable and efficient temperature control, preventing overcurrent situations during startup.
The Impact of Material Purity
Not all graphite is created equal. The lifespan of a heating element is directly influenced by the purity and density of the graphite used.
Lower-purity grades contain contaminants that can act as catalysts for oxidation or create structural weak points. High-density, high-purity graphite provides a more uniform structure, leading to more predictable performance and a longer operational life.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the service life of a graphite heating element, your operational strategy must be tailored to its fundamental properties.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature in a controlled environment: Graphite is an exceptional choice for vacuum or inert gas furnaces due to its unmatched sublimation point.
- If your application involves operating in open air: You must avoid graphite and instead consider elements like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) or Silicon Carbide (SiC) that form a protective oxide layer.
- If you require frequent and rapid thermal cycling: Graphite's excellent thermal shock resistance makes it highly reliable, provided those cycles occur within a non-oxidizing atmosphere.
Ultimately, protecting a graphite element from oxygen is the single most important factor in unlocking its remarkable longevity.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Lifespan | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature Stability | Enables operation up to 3,650°C (sublimation point) | Ideal for ultra-high-temperature applications |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Prevents cracking from rapid heating/cooling cycles | Excellent for processes requiring frequent temperature changes |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists attack from acids, bases, and molten materials | Protects structural integrity in specific environments |
| Atmosphere Control | CRITICAL: Prevents oxidation and burnout above 450°C | Must be used in vacuum or inert gas (e.g., Argon, Nitrogen) |
| Material Purity & Density | Higher purity/density leads to more uniform performance and longevity | Reduces weak points and contamination risks |
Unlock the full potential of graphite heating elements in your lab.
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique experimental requirements. Our expertise in Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems ensures you get the precise performance and longevity your research demands.
Contact us today to discuss how our deep customization capabilities can optimize your high-temperature processes and extend the life of your critical components.
Get a Custom Solution for Your Lab
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness
- What is the primary function of a vacuum graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme-Temperature Material Purity
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- Why is graphite a preferred material for heating elements in high-temperature vacuum furnaces?
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision



















