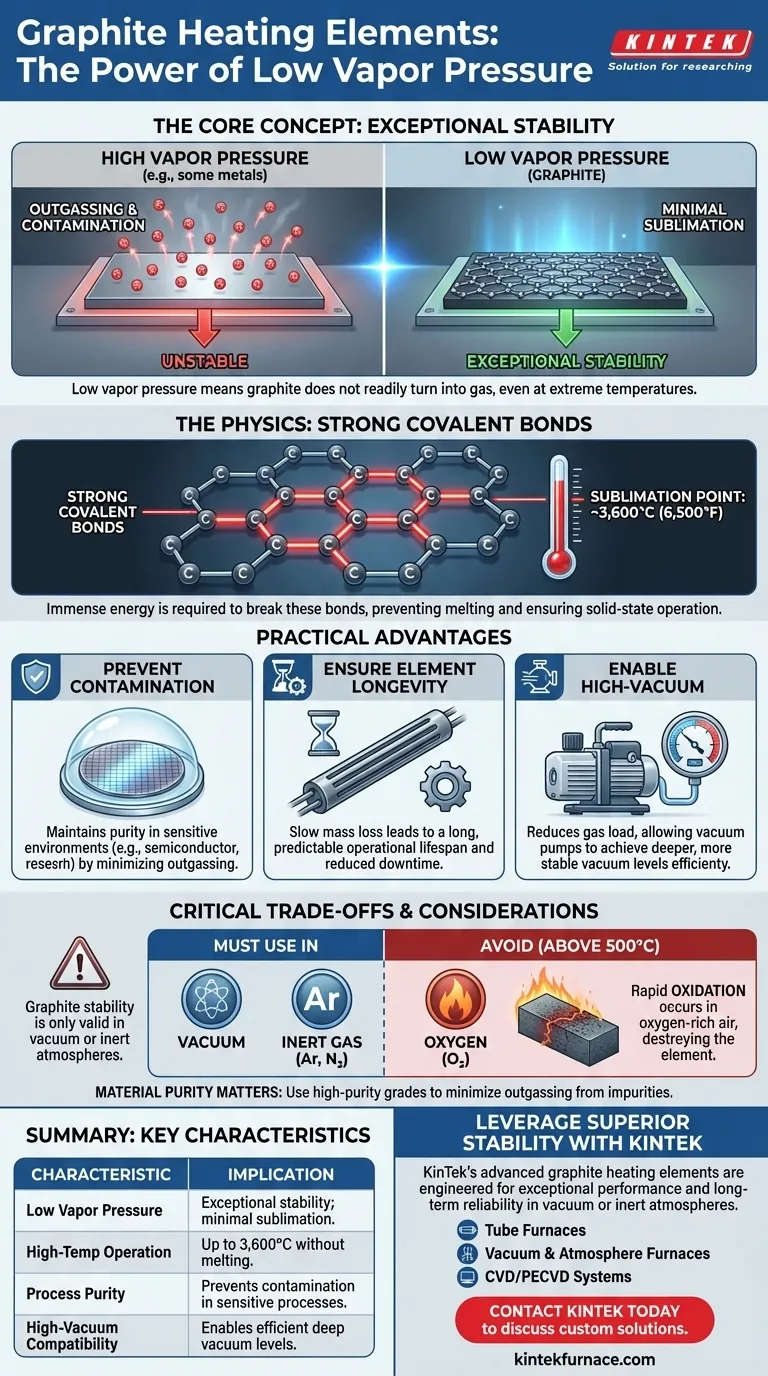
In short, a low vapor pressure indicates exceptional stability at high temperatures. This means that graphite heating elements do not readily turn into a gas (a process called sublimation) even when extremely hot. This characteristic is the primary reason graphite is a dominant material for high-temperature applications in vacuum or inert atmospheres, as it ensures the element remains solid and does not contaminate its surroundings.
The practical significance of graphite's low vapor pressure is its ability to operate at extreme temperatures without degrading itself or contaminating the process. This makes it an ideal choice for high-vacuum and inert atmosphere heating where material purity and element longevity are paramount.
The Physics Behind Graphite's Stability
To fully appreciate why this property is so important, we must first understand the underlying physics and how they translate into tangible engineering advantages.
What is Vapor Pressure?
All materials have a tendency for their atoms or molecules to escape from their surface and become a gas. Vapor pressure is the measure of this tendency.
As temperature increases, atoms gain more energy, and more of them escape into the vapor phase. This increases the pressure that the vapor exerts, making the material less stable at high temperatures.
Why Graphite's Vapor Pressure is So Low
Graphite's stability stems from its atomic structure. It is composed of carbon atoms held together by extremely strong covalent bonds.
It takes an immense amount of thermal energy to break these bonds and allow a carbon atom to escape the solid structure. For this reason, graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure; it sublimes (turns directly from a solid to a gas) at a very high temperature of around 3,600°C (6,500°F).
Practical Implications for High-Temperature Processes
The theoretical stability of graphite has direct, practical consequences for industrial and scientific applications.
Preventing Process Contamination
In sensitive environments like semiconductor manufacturing or materials research, even microscopic amounts of foreign material can ruin a product. A heating element with a higher vapor pressure will continuously "outgas," releasing particles that contaminate the chamber and the workpiece.
Because graphite has a near-zero vapor pressure at most operating temperatures, it introduces virtually no contaminants, preserving the purity of the vacuum or inert atmosphere.
Ensuring Element Longevity
A heating element that is constantly losing mass through sublimation will thin out over time, its electrical resistance will change, and it will eventually fail. This leads to costly downtime and replacement.
Graphite's low sublimation rate means it loses mass incredibly slowly. This gives graphite heating elements a very long and predictable operational lifespan, provided they are used in the correct environment.
Enabling High-Vacuum Operation
Achieving and maintaining a deep vacuum requires removing gas molecules from a chamber. A heating element that is actively outgassing is working directly against the vacuum pump, adding to the gas load and limiting the achievable vacuum level.
Graphite's inertness helps vacuum pumps work more efficiently, allowing them to reach and hold deeper vacuum levels that are critical for many advanced processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its low vapor pressure is a tremendous asset, graphite is not a universally perfect solution. Its primary limitation is its reactivity with oxygen.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
Graphite's high-temperature stability is only valid in a vacuum or an inert gas (like argon or nitrogen).
In the presence of oxygen at temperatures above 450-500°C (842-932°F), graphite will oxidize rapidly. It essentially burns away, completely losing its structural integrity and high-temperature benefits.
Material Purity Matters
Not all graphite is created equal. Lower-purity grades can contain binders, adhesives, or trapped impurities that have a much higher vapor pressure than the graphite itself.
In high-vacuum applications, these impurities can outgas at elevated temperatures, negating the benefit of using graphite in the first place. Using a high-purity, processed grade is essential for sensitive work.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use graphite heating elements must be based on a clear understanding of your operating environment and process requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature operation in a vacuum or inert gas: Graphite is an exceptional choice due to its superior stability and low contamination risk.
- If your process involves an oxygen-rich atmosphere above 500°C: You must use a different material, such as a metallic alloy (e.g., Kanthal) or a ceramic like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂).
- If your application is highly sensitive to trace contamination: Specify a high-purity or purified grade of graphite to minimize outgassing from residual impurities.
Understanding this fundamental property of vapor pressure empowers you to leverage graphite's strengths while avoiding its critical limitations.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Implication for Heating Elements |
|---|---|
| Low Vapor Pressure | Exceptional stability; minimal sublimation at high temperatures. |
| High-Temperature Operation | Can operate up to 3,600°C (sublimation point) without melting. |
| Process Purity | Prevents contamination in sensitive environments like semiconductor manufacturing. |
| Element Longevity | Slow mass loss leads to a long, predictable operational lifespan. |
| High-Vacuum Compatibility | Enables efficient pumping and maintenance of deep vacuum levels. |
| Critical Limitation | Requires a vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation above ~500°C. |
Leverage Graphite's Superior Stability in Your Lab
Do you require high-temperature heating solutions that guarantee process purity and long-term reliability in vacuum or inert atmospheres? KINTEK's advanced graphite heating elements are engineered for exceptional performance, leveraging our deep R&D and in-house manufacturing expertise.
Our product line, including high-temperature Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss how our high-purity graphite solutions can enhance your application's performance and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability
- What is the significance of vacuum in relation to graphite components in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation for Extreme Temperatures



















