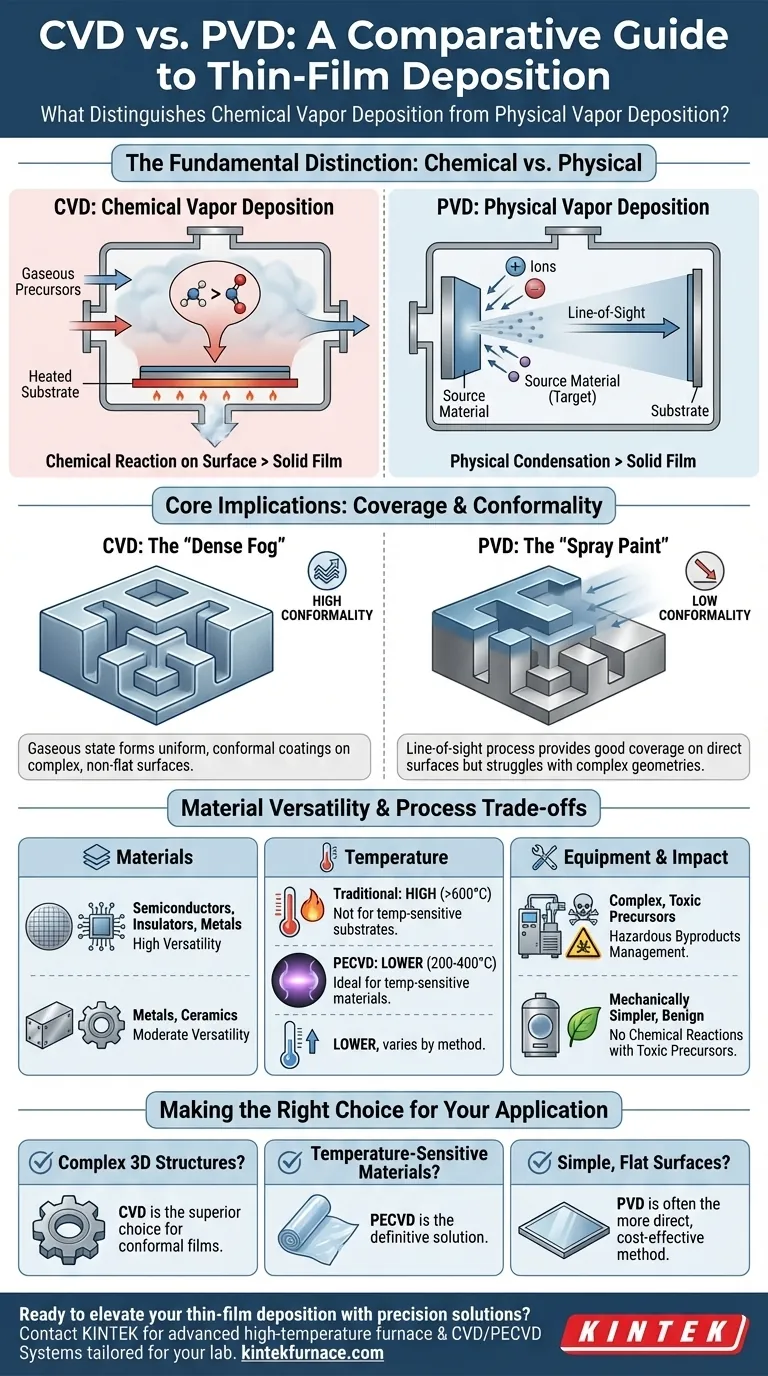
At its core, the distinction between Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) lies in the state of the starting material and the nature of the deposition process. CVD uses gaseous precursors that undergo a chemical reaction on a substrate to form a solid film, whereas PVD transforms a solid source material into a vapor through physical means, which then condenses onto the substrate.
The fundamental choice between CVD and PVD is a trade-off between process and outcome. CVD excels at creating highly uniform, conformal coatings on complex shapes through a chemical reaction, while PVD offers a more direct, line-of-sight physical process often used for simpler geometries.
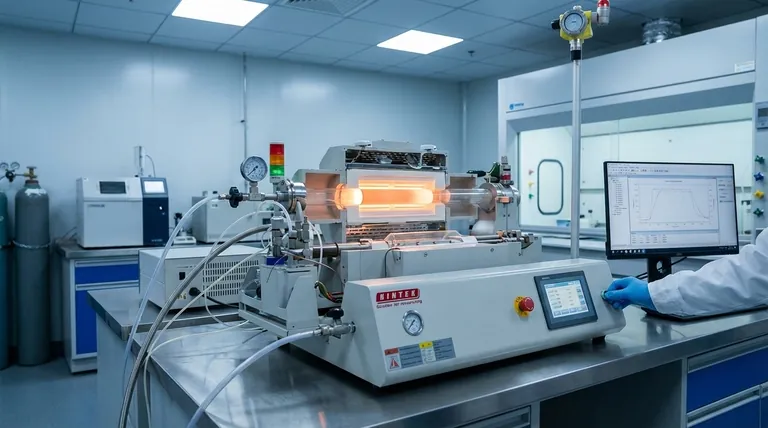

The Fundamental Distinction: Chemical vs. Physical
The names "Chemical Vapor Deposition" and "Physical Vapor Deposition" directly describe their core mechanisms. Understanding this difference is the key to selecting the right technology for your goal.
How CVD Works: A Chemical Reaction on the Surface
In CVD, one or more volatile gaseous precursors are introduced into a reaction chamber.
These gases are not the final film material itself. Instead, they decompose or react with each other on the heated substrate surface, forming a new solid material as a thin film.
Because the deposition relies on a flowing gaseous state, the process is diffuse and multidirectional, allowing the film to form uniformly over complex, non-flat surfaces.
How PVD Works: A Physical Condensation
PVD begins with a solid source material, often called a "target."
This solid target is transformed into a vapor using a physical process, such as sputtering (bombarding the target with energetic ions) or thermal evaporation (heating the target until it vaporizes).
This vapor then travels in a straight line—a line-of-sight trajectory—and condenses on the substrate, forming the film. No significant chemical reaction occurs.
Core Implications for Film Properties
The difference between a chemical reaction and a physical condensation has profound effects on the final film's characteristics and the types of materials you can deposit.
Coverage and Conformality: A "Fog" vs. a "Spray Paint"
Imagine trying to coat a complex, three-dimensional object.
CVD acts like a dense fog that settles evenly on every exposed surface, wrapping around corners and filling trenches. This ability to create a film of uniform thickness on a non-flat surface is called conformality.
PVD, with its line-of-sight nature, behaves more like spray paint. It provides excellent coverage on surfaces directly facing the source but struggles to coat the sides of deep features or the backside of an object.
Material Versatility: Beyond Just Metals
PVD is a highly effective and common method for depositing thin films of metals and certain ceramic compounds.
CVD, however, offers significantly greater versatility. Through the chemistry of its precursor gases, it can deposit a wider range of materials, including semiconductors (like silicon) and insulators (like silicon dioxide and silicon nitride), which are foundational to the electronics industry.
Understanding the Process Trade-offs
Choosing a deposition method isn't just about the final film; it's also about the process requirements and their limitations.
The Critical Role of Temperature
Traditional thermal CVD processes often require very high substrate temperatures (often >600°C) to provide the necessary energy to drive the chemical reactions.
This high heat requirement makes it unsuitable for depositing films on temperature-sensitive substrates, such as plastics or certain pre-processed electronic components.
A Key Variation: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
To overcome the temperature limitations of traditional CVD, Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) was developed.
PECVD uses an electric field to generate a plasma, an energized state of gas. This plasma provides the energy needed for the chemical reaction to occur, allowing deposition at much lower temperatures (typically 200-400°C).
This crucial difference makes PECVD ideal for coating temperature-sensitive materials while often producing higher-quality films with less stress.
Equipment and Environmental Impact
CVD processes can be more complex, often requiring sophisticated equipment to handle precursor gases, many of which can be toxic or corrosive. This also necessitates systems for managing hazardous byproducts.
PVD systems are often mechanically simpler and are generally considered to have a more benign environmental footprint, as they are not based on chemical reactions with toxic precursors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal determines which technology is the superior choice. Base your decision on the required film properties and substrate limitations.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D structures uniformly: CVD is the superior choice due to its inherent ability to deposit conformal films.
- If your primary focus is depositing films on temperature-sensitive materials like polymers: PECVD is the definitive solution, combining the benefits of CVD with a low-temperature process.
- If your primary focus is applying a simple metallic or ceramic coating to a relatively flat surface: PVD is often the more direct, cost-effective, and efficient method.
Ultimately, mastering thin-film deposition comes from aligning the unique strengths of each process with the specific demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | CVD | PVD |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Chemical reaction with gaseous precursors | Physical vaporization of solid target |
| Deposition Mechanism | Diffuse, multidirectional (like fog) | Line-of-sight (like spray paint) |
| Conformality | High, uniform on complex shapes | Low, struggles with non-flat surfaces |
| Material Versatility | High (e.g., semiconductors, insulators) | Moderate (e.g., metals, ceramics) |
| Typical Temperature | High (>600°C for thermal CVD) | Lower, varies by method |
| Ideal Applications | Complex 3D structures, electronics | Flat surfaces, simple geometries |
Ready to elevate your thin-film deposition with precision solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace systems tailored for your lab. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is designed with strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're working with complex 3D coatings or temperature-sensitive materials, our expertise ensures optimal performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your research and production processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- Why is the tube design important in CVD furnaces? Ensure Uniform Deposition for High-Quality Films



















