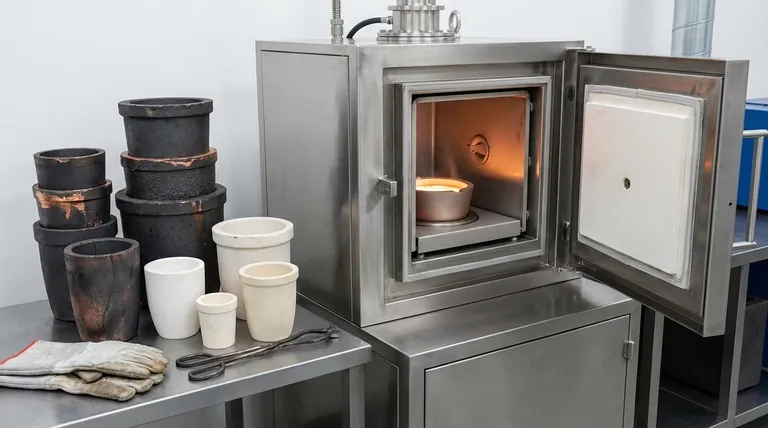
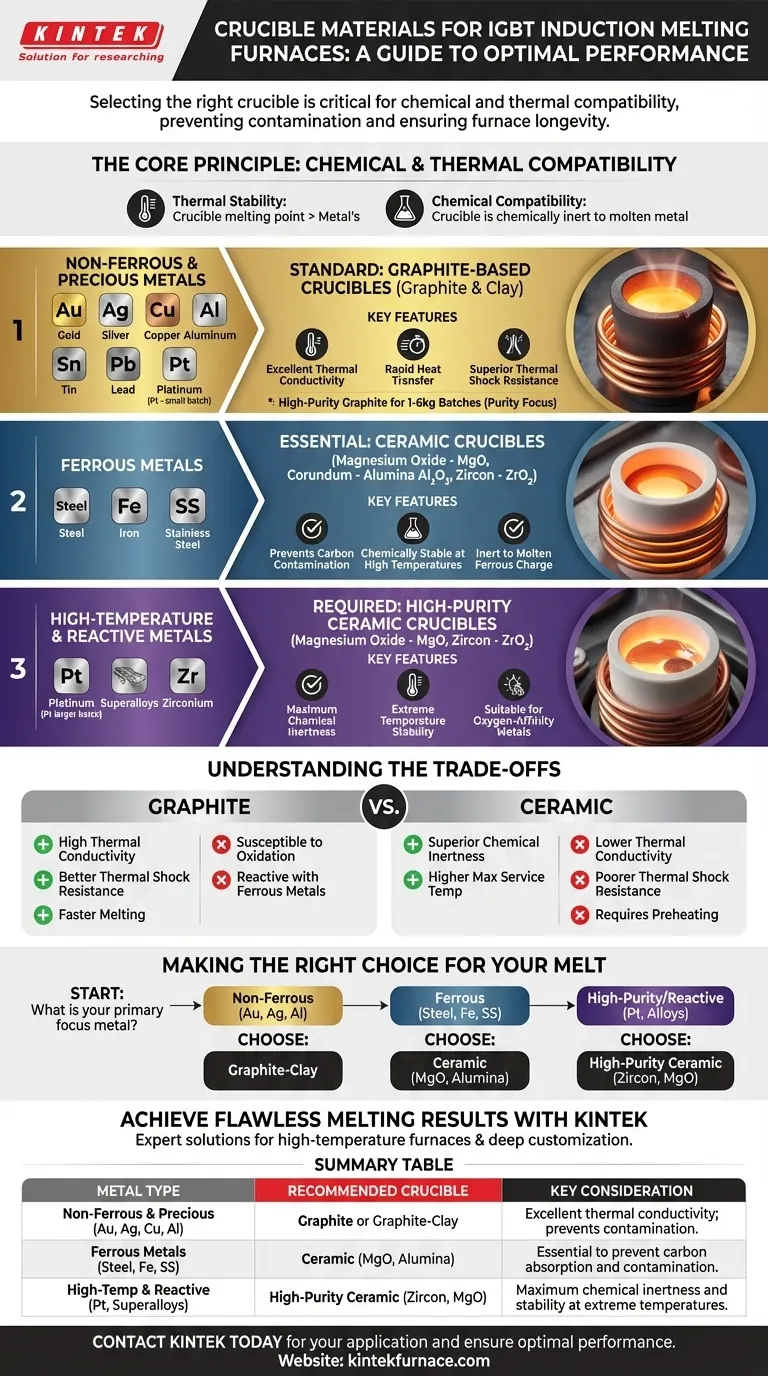
In an IGBT induction furnace, the choice of crucible material is dictated by the metal's melting temperature and its chemical reactivity. For non-ferrous and precious metals like gold, silver, and copper, graphite-based crucibles are standard. For ferrous metals like steel and iron, which are highly reactive with carbon, ceramic crucibles such as magnesium oxide or corundum are required.
Selecting the right crucible is not merely about containing molten metal; it's a critical decision to prevent chemical reactions that contaminate your final product and cause premature crucible failure. The fundamental principle is to match the crucible's chemical inertness to the metal being melted.

The Core Principle: Chemical and Thermal Compatibility
The effectiveness of an induction melting process hinges on the crucible. It must withstand the target temperature without melting, cracking, or, most importantly, reacting with the molten charge.
This interaction is governed by two factors: thermal stability (the crucible's melting point must be significantly higher than the metal's) and chemical compatibility (the crucible must be chemically inert to the molten metal).
For Non-Ferrous & Precious Metals
For metals like gold, silver, copper, aluminum, tin, and lead, graphite-based crucibles are the industry standard.
These materials, often a mix of graphite and clay, offer excellent thermal conductivity, which allows for rapid and efficient heat transfer from the induction coil to the metal. They also possess superior resistance to thermal shock.
High-purity graphite crucibles are specifically used for smaller batches (1-6 kg) of precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum, where maintaining purity is paramount.
For Ferrous Metals
Melting steel, stainless steel, and iron introduces a significant chemical challenge: carbon contamination. Molten steel is highly reactive and will readily absorb carbon from a graphite crucible, altering the final alloy's properties.
To prevent this, you must use ceramic crucibles. The most common materials are magnesium oxide (MgO), corundum (Alumina, Al₂O₃), and zircon (Zirconia, ZrO₂). These materials are chemically stable at high temperatures and do not react with the molten ferrous charge.
For High-Temperature & Reactive Metals
Specialty applications involving platinum, superalloys, and reactive metals like zirconium require the most stable crucibles available.
While platinum can sometimes be melted in high-purity graphite, magnesium oxide and zircon crucibles are often preferred to guarantee purity and withstand extreme temperatures. Their exceptional chemical inertness makes them suitable for metals with a high affinity for oxygen.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single crucible material is perfect for all applications. The choice always involves balancing performance, lifespan, and cost.
Graphite Crucibles: Pros & Cons
The primary advantage of graphite is its excellent thermal conductivity and thermal shock resistance. This translates to faster melting times and a lower risk of cracking during rapid heating and cooling cycles.
However, graphite crucibles are susceptible to oxidation. They will slowly burn away in the presence of air at high temperatures, which limits their lifespan. Their reactivity with ferrous metals is their most significant limitation.
Ceramic Crucibles: Pros & Cons
Ceramic crucibles offer superior chemical inertness and a higher maximum service temperature, making them essential for reactive metals like steel.
Their main drawbacks are lower thermal conductivity (leading to slightly slower melting) and poorer thermal shock resistance. Ceramic crucibles often require a careful preheating protocol to prevent cracking. They are also typically more expensive than their graphite counterparts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Melt
Your specific goal determines the correct crucible. Base your decision on the type of metal you are melting to ensure both a successful process and a high-quality final product.
- If your primary focus is non-ferrous metals like gold, silver, or aluminum: A graphite-clay crucible is the most efficient and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is steel, iron, or stainless steel: You must use a ceramic crucible like magnesium oxide or corundum to prevent carbon contamination of your melt.
- If your primary focus is high-purity platinum or reactive alloys: A high-purity ceramic crucible, such as zircon or magnesium oxide, is necessary for its chemical stability at extreme temperatures.
Matching the crucible to the metal is the foundational step toward achieving a clean, successful, and high-quality melt.
Summary Table:
| Metal Type | Recommended Crucible Material | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Ferrous & Precious (Gold, Silver, Copper, Aluminum) | Graphite or Graphite-Clay | Excellent thermal conductivity; prevents contamination of precious metals. |
| Ferrous Metals (Steel, Iron, Stainless Steel) | Ceramic (Magnesium Oxide, Corundum/Alumina) | Essential to prevent carbon absorption and alloy contamination. |
| High-Temperature & Reactive Metals (Platinum, Superalloys) | High-Purity Ceramic (Zircon/Zirconia, Magnesium Oxide) | Maximum chemical inertness and stability at extreme temperatures. |
Achieve Flawless Melting Results with KINTEK
Selecting the correct crucible is the first critical step to a successful melt. The wrong choice can lead to contaminated products, failed experiments, and costly downtime.
Why choose KINTEK for your high-temperature furnace needs?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
We understand the nuances of high-temperature processing. Let our experts help you select the perfect furnace and crucible system for your specific metals and goals.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and ensure optimal performance and purity in every melt.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries



















