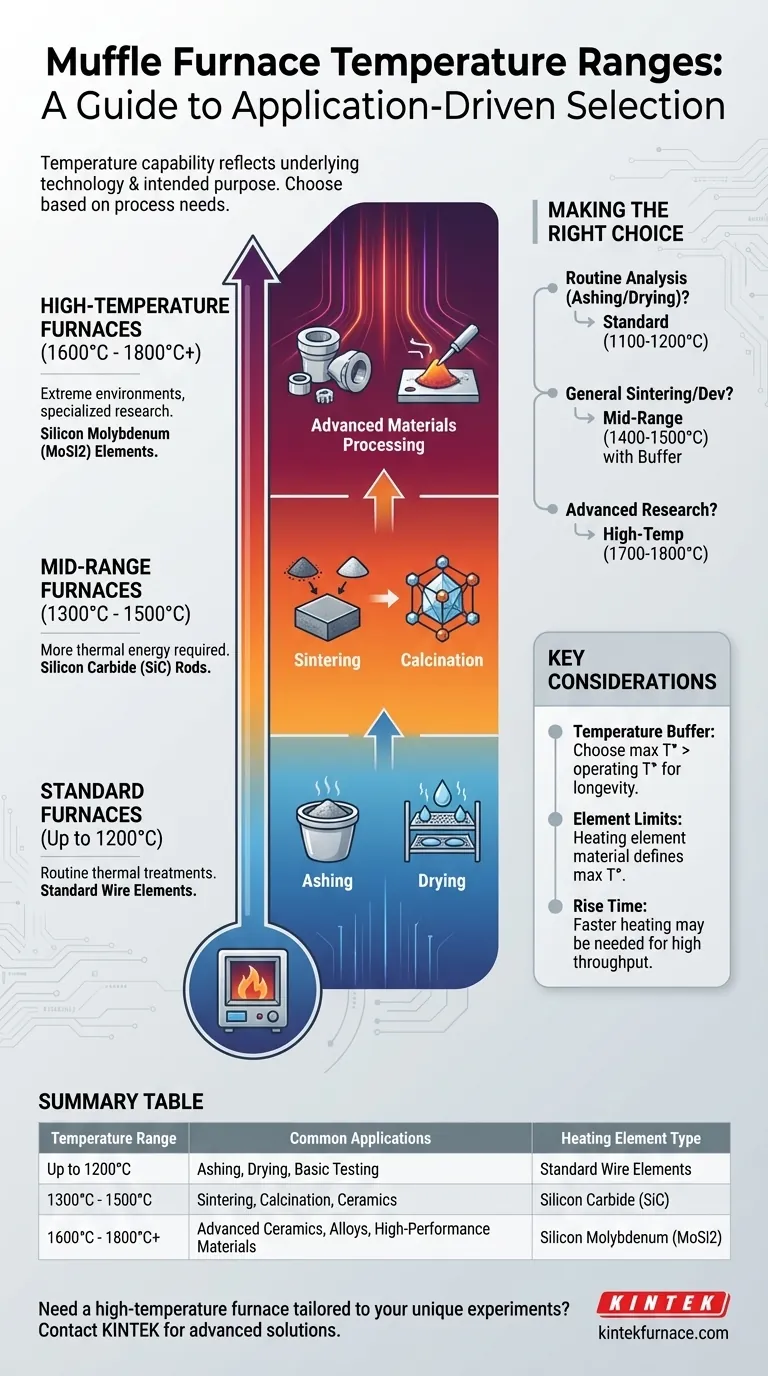
In practice, muffle furnace temperature ranges are segmented by their intended application and internal technology. Standard laboratory models typically operate up to 1200°C (2192°F), which is sufficient for common processes like ashing. High-temperature models, designed for advanced materials processing, can reliably reach 1600°C to 1800°C (2912°F to 3272°F).
The specific temperature range of a muffle furnace is not just a feature but a direct reflection of its underlying heating technology and intended purpose. Understanding your process—whether it's low-temperature drying or high-temperature sintering—is the first step to selecting the correct equipment.

Understanding the Temperature Tiers
Muffle furnaces are not one-size-fits-all. They are engineered in distinct tiers, with each tier's temperature capability determined by its construction and, most critically, the material used for its heating elements.
Standard Furnaces (Up to 1200°C)
These are the most common box-type furnaces found in general-purpose labs. Their range is ideal for routine thermal treatments that don't require extreme heat.
Common applications include ashing, drying, heat-treating certain metals, and basic materials testing. These furnaces provide excellent temperature control and uniformity in a widely applicable range.
Mid-Range Furnaces (1300°C - 1500°C)
This category represents a step up in performance, often utilizing more robust heating elements like silicon carbide (SiC) rods.
These furnaces are workhorses for processes like calcination and the sintering of many types of ceramics and powdered metals, which require more thermal energy than standard models can provide. Tube-type furnaces often operate in this range.
High-Temperature Furnaces (1600°C - 1800°C+)
Operating at these extreme temperatures requires specialized technology, most commonly silicon molybdenum (MoSi2) heating elements.
These furnaces are reserved for advanced research, the development of high-performance ceramics, and testing materials with exceptionally high melting points. Vacuum and other specialized models are often required to achieve these temperatures and process conditions.
How Application Dictates Temperature
The process you need to perform is the single most important factor in determining the required temperature. Each thermal process has a specific energy requirement to achieve the desired physical or chemical change.
Ashing and Drying
These are lower-temperature processes, often performed well below 1000°C. The goal is to remove moisture or organic material without altering the inorganic base material, making a standard 1200°C furnace more than sufficient.
Sintering and Calcination
These processes transform a material's structure by heating it below its melting point. Sintering fuses powders together, and calcination induces phase transitions. Both require significant energy, typically placing them in the 1100°C to 1500°C range.
Advanced Materials Processing
Creating or testing advanced ceramics, alloys, or composites demands the highest temperatures. These materials are designed for extreme environments, and processing them requires a furnace that can operate reliably from 1600°C to 1800°C or higher.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves more than just matching its maximum temperature to your process. Understanding the operational constraints is key to ensuring accuracy and long equipment life.
The Importance of a Temperature Buffer
A critical best practice is to choose a furnace with a maximum temperature slightly higher than your highest intended operating temperature.
Consistently running a furnace at its absolute maximum limit will significantly shorten the life of its heating elements and refractory insulation. A buffer of 100°C to 200°C provides operational flexibility and promotes longevity.
Heating Element Technology is the Limiter
The maximum temperature is fundamentally limited by the material of the heating elements. Standard wire elements are suitable for up to 1200°C, while silicon carbide and silicon molybdenum are required for progressively higher temperatures. This is the primary driver of cost and performance differences.
Beyond Temperature: Rise Time
Rise time—the time it takes for the furnace to reach its target temperature—is another important consideration. Furnaces with more powerful, high-temperature elements often heat up faster, which can be critical for high-throughput environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Use your primary application as your guide to select the appropriate furnace tier.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis like ashing or drying: A standard box furnace with a maximum temperature of 1100°C to 1200°C is the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose sintering or materials development: A mid-range furnace capable of reaching 1400°C to 1500°C provides the necessary capability with a safe operational buffer.
- If your primary focus is advanced research on high-performance ceramics or alloys: You must invest in a high-temperature furnace rated for 1700°C to 1800°C to meet your process demands.
By matching the furnace's capabilities to your specific thermal process, you ensure accurate results and a long-term return on your investment.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Common Applications | Heating Element Type |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 1200°C | Ashing, Drying, Basic Materials Testing | Standard Wire Elements |
| 1300°C - 1500°C | Sintering, Calcination, Ceramics Processing | Silicon Carbide (SiC) |
| 1600°C - 1800°C+ | Advanced Ceramics, Alloys, High-Performance Materials | Silicon Molybdenum (MoSi2) |
Need a high-temperature furnace tailored to your unique experiments? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise performance for your specific thermal processes. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















