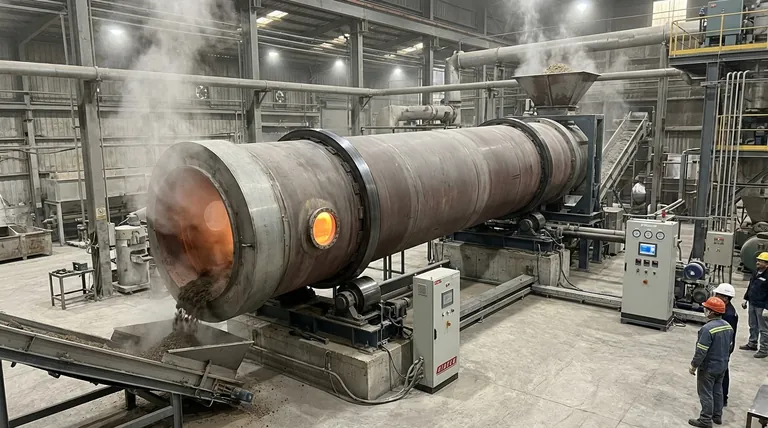
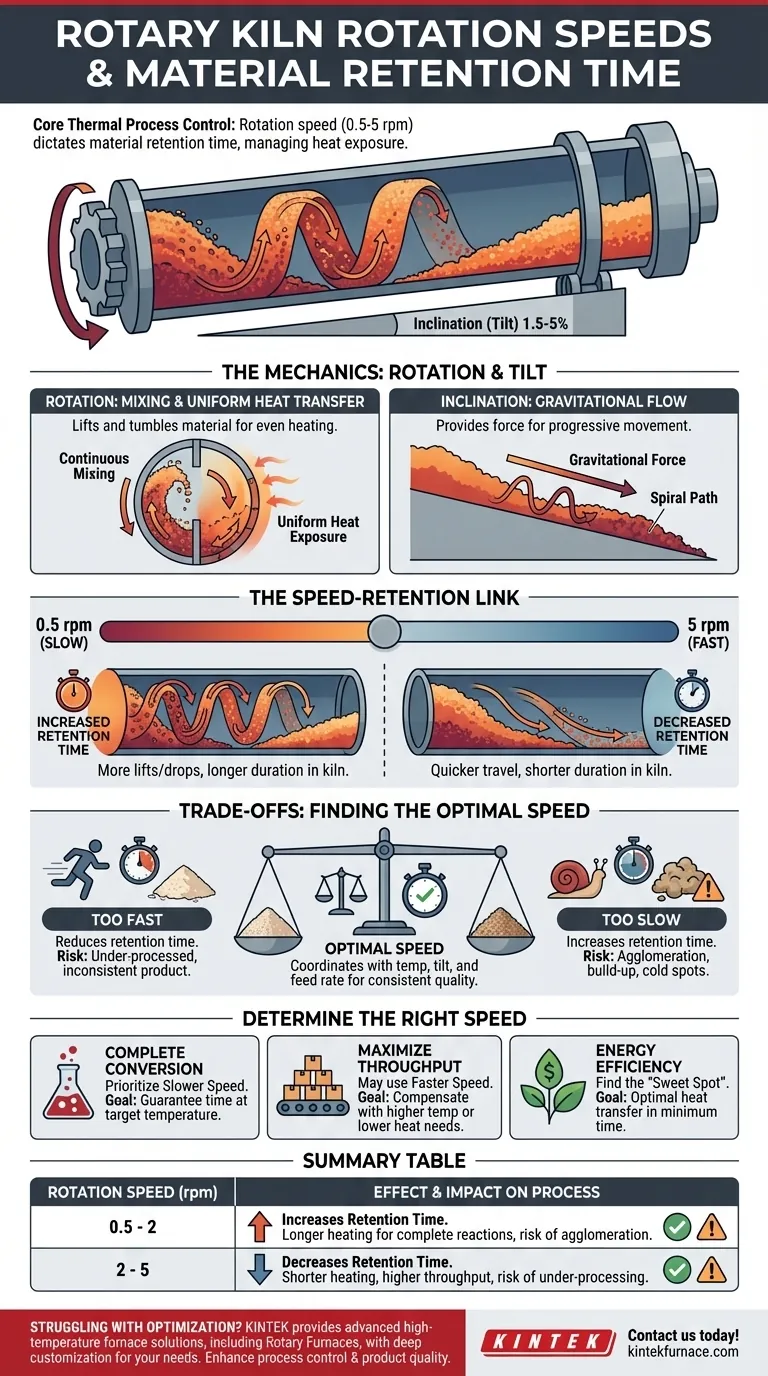
At its core, a rotary kiln's rotation speed is a primary control lever for its entire thermal process. Speeds typically range from 0.5 to 5 revolutions per minute (rpm), and this rate directly dictates the material retention time—the duration a substance spends inside the kiln. Slower rotation increases retention time, while faster rotation decreases it, allowing operators to precisely manage the material's exposure to heat.
The fundamental challenge of kiln operation is not simply moving material, but controlling its thermal journey. Rotation speed, in conjunction with the kiln's slope, is the most direct tool you have to manage how long the material is heated, which is the single most important factor for achieving the desired final product.

The Mechanics of Kiln Operation
A rotary kiln is designed to tumble and transport material through a heated environment. The rotation is the engine of this process, directly influencing both heat transfer and the rate of travel.
The Role of Rotation Speed
The primary function of rotation is to lift the material partway up the interior wall of the kiln, causing it to cascade or tumble back down. This continuous mixing is crucial for exposing all particles to the hot refractory lining and the hot gases flowing through the kiln.
This tumbling action ensures uniform heat transfer throughout the material bed. Without it, only the surface layer would be properly treated.
The Influence of Inclination (Tilt)
Rotary kilns are always installed at a slight downward angle, typically between 1.5% and 5% (a drop of 1.5 to 5 feet for every 100 feet of length).
While rotation tumbles the material, this incline provides the gravitational force needed to move it progressively from the feed end to the discharge end. The combination of rotation and tilt creates a slow, predictable spiral path for the material.
The Link Between Speed and Retention Time
Retention time is a direct consequence of the interplay between rotation speed and kiln geometry. A slower rotation means the material is lifted and dropped more times before it travels a given distance, thus increasing the time it spends inside the kiln.
Conversely, a faster rotation moves material toward the discharge end more quickly, reducing its retention time. This relationship allows operators to fine-tune the process based on the specific thermal requirements of the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Finding the Optimal Speed
Selecting the correct rotation speed is a balancing act. Deviating from the optimal range in either direction introduces significant operational problems and compromises product quality.
The Problem with Rotating Too Fast
A rotation speed that is too high is a common cause of poor product quality. It drastically reduces material retention time.
The material travels through the kiln too quickly to absorb enough heat, leading to incomplete chemical reactions or physical changes. The final product will be under-processed and inconsistent.
The Danger of Rotating Too Slow
While it might seem that a slower speed is always safer, this is not the case. An excessively slow rotation can be just as detrimental.
It can cause material to agglomerate or build up on the kiln walls, creating uneven flow and "cold spots" that are shielded from heat. In severe cases, this build-up can disrupt the process entirely or even damage the kiln's refractory lining.
Balancing Speed with Other Variables
Rotation speed is not an isolated parameter. It must be carefully coordinated with the kiln's temperature profile, its inclination angle, and the material feed rate.
Changing one variable requires adjusting the others to maintain a stable and efficient process. For example, a higher feed rate might necessitate a slightly faster rotation to prevent overloading the kiln.
How to Determine the Right Rotation Speed
The ideal speed is dictated entirely by the process goal and the material being treated. There is no single "best" speed, only the right speed for a specific application.
- If your primary focus is on complete chemical conversion: You will prioritize a slower, more controlled rotation to guarantee the material achieves the necessary retention time at the target temperature.
- If your primary focus is on maximizing throughput: You may use a faster rotation, but only if you can compensate by increasing the temperature profile or if the material requires less heat exposure.
- If your primary focus is on energy efficiency: You must find the "sweet spot" where rotation speed ensures optimal heat transfer and complete processing in the minimum possible time, minimizing fuel consumption per ton of product.
Mastering the relationship between rotation, tilt, and temperature is the key to consistent, efficient, and high-quality kiln operation.
Summary Table:
| Rotation Speed (rpm) | Effect on Retention Time | Impact on Process |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 - 2 | Increases | Longer heating for complete reactions, risk of agglomeration |
| 2 - 5 | Decreases | Shorter heating, higher throughput, risk of under-processing |
Struggling to optimize your rotary kiln's rotation speed for ideal material retention and efficiency? KINTEK can help! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing process control and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can elevate your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems



















