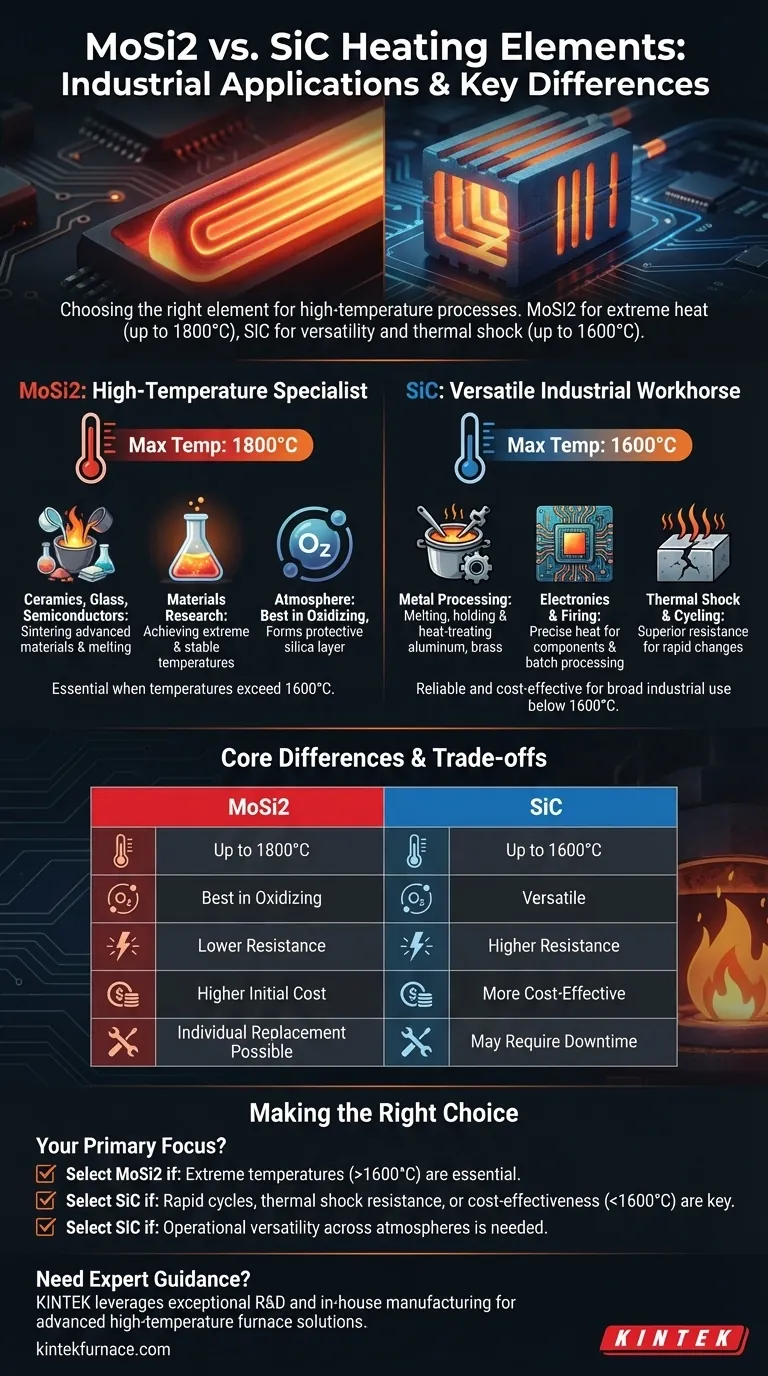
In industrial settings, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are chosen for distinct high-temperature applications. MoSi2 is primarily used for the most extreme temperature processes, such as ceramics sintering and glass melting. SiC serves as a versatile workhorse in a broader range of applications like metal treatment and electronics manufacturing, especially where temperatures remain below 1600°C.
The choice between MoSi2 and SiC is fundamentally a decision driven by maximum operating temperature and atmospheric conditions. MoSi2 is the specialist for the highest temperatures (up to 1800°C) in oxidizing environments, while SiC offers greater versatility and thermal shock resistance at slightly lower temperatures.
MoSi2: The High-Temperature Specialist
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements are defined by their ability to perform reliably at extreme temperatures. Their effectiveness is rooted in the formation of a protective silica glass layer in oxidizing atmospheres.
Key Application: Ceramics, Glass, and Semiconductors
MoSi2 is the element of choice when process temperatures approach or exceed 1600°C. This makes it essential for sintering advanced ceramics, melting specialty glass, and certain stages of semiconductor production.
Its ability to maintain stability at these high temperatures ensures product quality and process consistency where other materials would fail.
Key Application: Materials Research
In laboratory and R&D furnaces, achieving very high and stable temperatures is critical for developing and testing new materials. MoSi2 elements provide the necessary heat for this demanding environment.
SiC: The Versatile Industrial Workhorse
Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements are prized for their excellent mechanical strength, high thermal conductivity, and resistance to thermal shock. They are a reliable and often more cost-effective choice for a wide array of industrial processes.
Key Application: Metal Processing and Treatment
SiC is widely used in furnaces for melting, holding, and heat-treating metals like aluminum and brass. Its robustness and consistent heat distribution are ideal for these demanding, heavy-industrial environments.
Key Application: Electronics and Firing Processes
In the manufacturing of electronic components and the firing of general ceramics and glass, SiC provides precise and reliable heat. Its ability to handle rapid heating and cooling cycles makes it particularly effective for batch processing.
Understanding the Core Differences
Choosing the correct element requires moving beyond the application name and analyzing the underlying process requirements. The material properties of MoSi2 and SiC dictate their ideal use cases.
Operating Temperature: The Primary Deciding Factor
The most significant difference is the maximum temperature. MoSi2 elements can operate in air at temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F).
SiC elements have a lower maximum operating temperature, typically around 1600°C (2912°F). For any process running below this threshold, SiC is a viable candidate.
Atmospheric Conditions
MoSi2 performs best in oxidizing atmospheres, where it forms its protective quartz-glass layer. Using it in reducing atmospheres can lead to degradation.
SiC, by contrast, is more versatile and can be used across different atmospheres, offering greater flexibility in process design.
Thermal Shock and Cycling
SiC exhibits superior resistance to thermal shock due to its high thermal conductivity and mechanical strength. This makes it ideal for applications that require fast startups, shutdowns, or frequent temperature changes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
An objective decision must also weigh cost, maintenance, and operational constraints.
Initial Cost vs. Required Temperature
For applications operating well below 1600°C, SiC is often the more cost-effective solution. The premium cost of MoSi2 is only justified when its higher temperature capabilities are essential.
Element Maintenance and Lifespan
A practical advantage of MoSi2 is that individual, damaged elements can often be replaced without shutting down the furnace for a full rebuild. SiC elements, being more structurally rigid, may require more significant downtime for replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Base your decision on the specific, non-negotiable requirements of your industrial heating application.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures (above 1600°C): Choose MoSi2 for its unmatched performance in extreme heat.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating cycles or thermal shock resistance: Choose SiC for its superior mechanical and thermal properties in dynamic environments.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for applications below 1600°C: SiC typically provides the best balance of performance and value.
- If your primary focus is operational versatility across different atmospheres: SiC offers greater flexibility compared to the oxygen-dependent MoSi2.
By aligning your specific operational demands with the fundamental properties of each material, you can select the most reliable and efficient heating element for your industrial process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | MoSi2 Heating Elements | SiC Heating Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Max Operating Temperature | Up to 1800°C | Up to 1600°C |
| Key Applications | Ceramics sintering, glass melting, semiconductors, materials research | Metal processing, electronics, firing processes |
| Atmosphere Suitability | Best in oxidizing atmospheres | Versatile across various atmospheres |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Lower | Higher |
| Cost Consideration | Higher cost, justified for extreme temperatures | More cost-effective below 1600°C |
Need expert guidance on selecting the perfect heating element for your industrial process? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in ceramics, glass, metals, or electronics, we can help optimize your heating applications for efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your high-temperature challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















