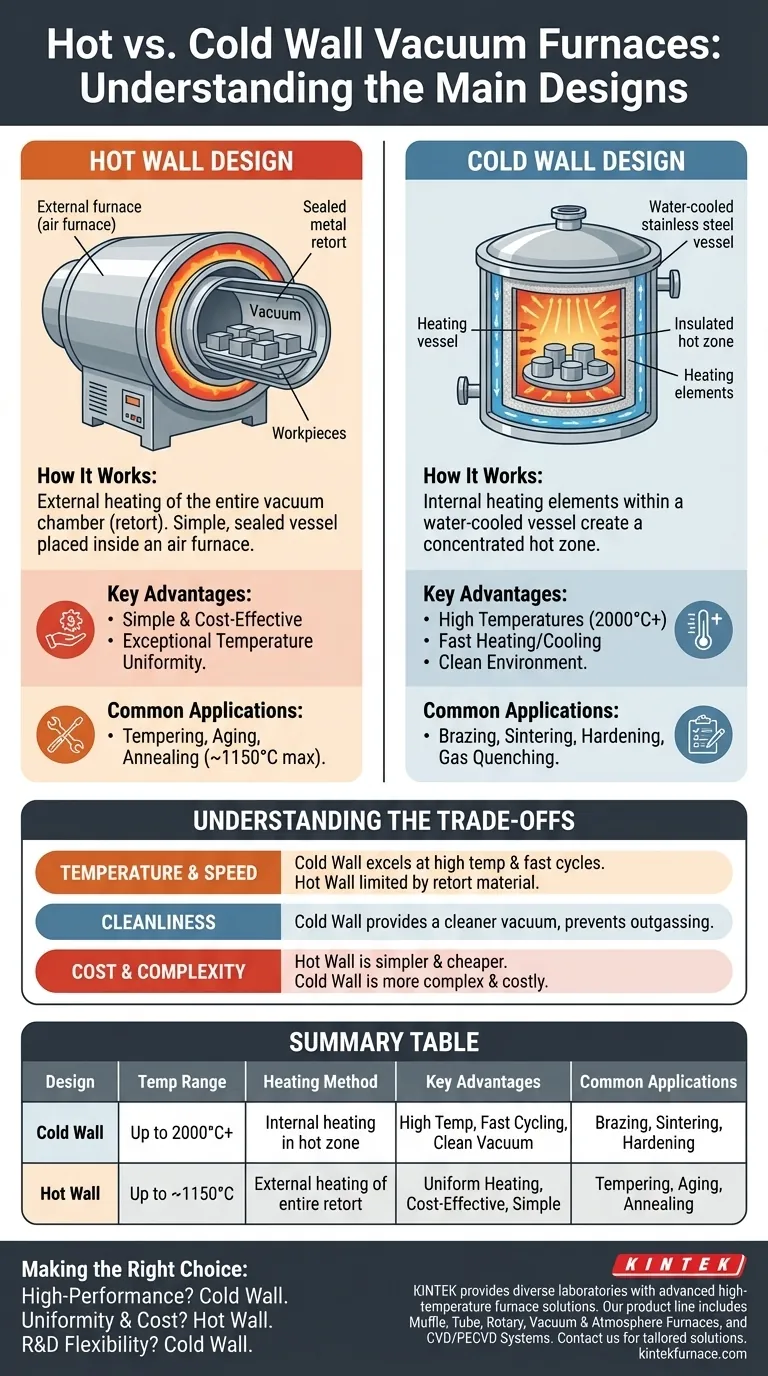
At a fundamental level, the two main designs of vacuum furnaces are the hot wall and cold wall configurations. A hot wall furnace heats the entire vacuum chamber from the outside, while a cold wall furnace uses internal heating elements to create a concentrated hot zone inside a water-cooled vessel. This core architectural difference dictates the furnace's performance, capabilities, and ideal applications.
The choice between a hot wall and cold wall furnace is a foundational decision. It determines the achievable temperature, processing speed, and cleanliness of the vacuum environment, directly impacting which material processes—from simple annealing to high-performance brazing—are possible.

The Cold Wall Design: The Industry Standard
The vast majority of modern, high-performance vacuum furnaces utilize a cold wall design. This architecture separates the heating function from the vacuum containment function.
How It Works
A cold wall furnace consists of an outer vessel, typically made of stainless steel, that is jacketed with channels for water cooling. Inside this cool vessel, a "hot zone" is constructed using layers of graphite or metallic radiation shields. Heating elements, also located inside the hot zone, radiate heat to the workpiece.
Key Advantages
The primary advantage is the ability to reach very high temperatures (often exceeding 2000°C) while the main vessel remains at a safe, near-ambient temperature. This design also allows for much faster heating and cooling cycles, as only the lightweight internal hot zone needs to change temperature.
Common Applications
The high-temperature capability and clean environment of cold wall furnaces make them ideal for demanding processes. This includes vacuum brazing, sintering of ceramics and powdered metals, and critical heat treatments like hardening, gas quenching, and annealing of sensitive alloys.
The Hot Wall Design: Simplicity and Uniformity
Hot wall furnaces, also known as retort furnaces, represent a simpler design philosophy where the vacuum chamber itself is heated.
How It Works
In this configuration, a sealed vessel (the retort), often made from a high-temperature nickel alloy or ceramic, contains the workpiece under vacuum. This entire retort is then placed inside a separate, larger air furnace which heats it from the outside.
Key Advantages
Hot wall furnaces are mechanically simpler and can provide exceptional temperature uniformity, as the entire part is soaked in a uniformly heated environment. They are often more cost-effective for applications within their temperature limits.
Primary Applications
Because the structural integrity of the retort material degrades at very high temperatures, hot wall furnaces are limited to lower-temperature processes. They are commonly used for vacuum tempering, aging, and annealing where precise, uniform heating below approximately 1150°C is required.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these designs involves balancing performance requirements against cost and complexity.
Temperature and Speed
Cold wall furnaces are the clear winners for high-temperature work and speed. They can safely reach temperatures that would destroy a hot wall retort and can be rapidly cooled for quenching processes. Hot wall designs are fundamentally limited by the material strength of the heated retort.
Cleanliness and Contamination
Cold wall designs provide a cleaner vacuum environment. Because the outer vessel stays cool, it does not outgas impurities into the vacuum. In a hot wall furnace, the entire heated retort can become a source of contamination, which is a critical issue for processing reactive or high-purity materials.
Cost and Complexity
Hot wall furnaces are generally simpler and less expensive to build and maintain. The cold wall design is inherently more complex, requiring water-cooling systems, intricate internal hot zone construction, and more sophisticated power feedthroughs.
A Note on Orientation
Both hot and cold wall furnaces can be built in either horizontal or vertical configurations. This is a secondary choice driven by the logistics of loading and unloading specific parts, not a fundamental design principle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The optimal furnace design is dictated entirely by your material, process requirements, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-performance heat treating, brazing, or sintering: You almost certainly need a cold wall furnace for its high-temperature capability, fast cycling, and process cleanliness.
- If your primary focus is lower-temperature annealing or tempering with an emphasis on uniformity: A hot wall furnace offers a simpler, cost-effective, and highly uniform solution for these applications.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A laboratory-scale cold wall furnace provides the most versatility for experimenting with a wide range of materials and processes.
Understanding the distinction between hot and cold wall architecture empowers you to select the precise tool needed to achieve your desired material properties.
Summary Table:
| Design | Temperature Range | Heating Method | Key Advantages | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold Wall | Up to 2000°C+ | Internal heating elements in hot zone | High temperature, fast cycling, clean vacuum | Brazing, sintering, hardening, gas quenching |
| Hot Wall | Up to ~1150°C | External heating of entire retort | Uniform heating, cost-effective, simple | Tempering, aging, annealing |
Ready to optimize your lab's performance with the right vacuum furnace? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your material processing efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















